Question 1
Which of the following properties would increase from the atoms sodium to chlorine across period 3?
I. Electronegativity.
II. Nuclear charge.
III. Atomic radius.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The first four ionisation energies of beryllium and iron are shown.
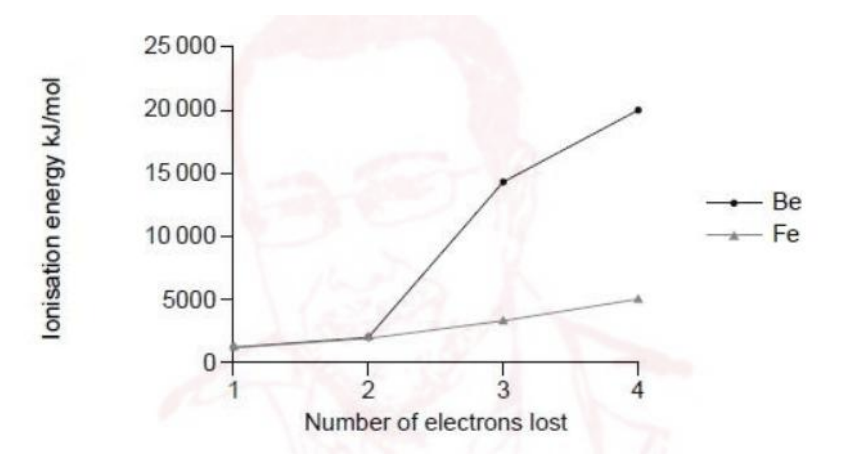
One common property of transition elements is that they have variable oxidation states. Discuss, referring to the graph, why iron, but not beryllium, displays this characteristic.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
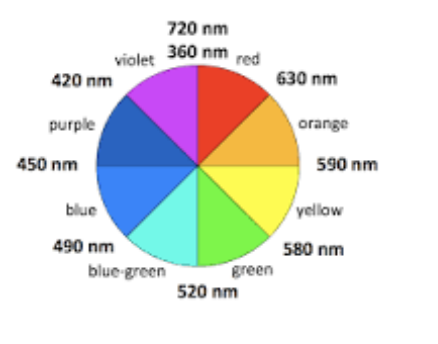
Potassium manganate(VII) is purple in colour. In which region of the visible spectrum does it mainly absorb?
A. Red.
B. Purple.
C. Blue.
D. Green.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which combination is correct for the complex ion in the coordination compound [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Br]Cl?
| Oxidation state of cobalt | Shape of the complex ion | Overall charge of the complex ion | |
| A. | +2 | Octahedral | +2 |
| B. | +3 | Square planar | –1 |
| C. | +2 | Octahedral | +1 |
| D. | +2 | Tetrahedral | +1 |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The following shows a series of reactions involving titanium compounds.
Concentrated HCl
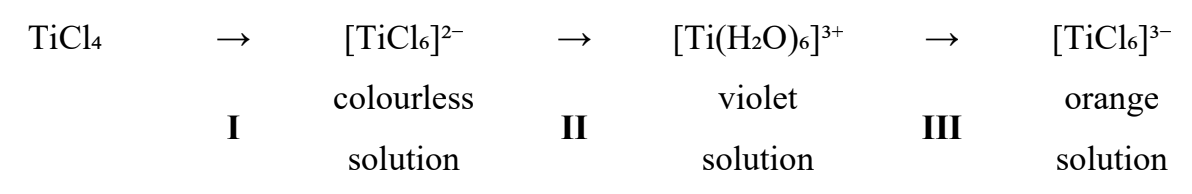
a. Suggest the type of reaction for II and III.
b. Explain why a solution of [TiCl₆]²⁻ is colourless but [TiCl₆]³⁻ is orange. The formula relating energy gap between d orbitals, ΔE, and wavelength, λ, is given as ΔE = hc / λ where h is the Planck’s constant and c is the speed of light.
c. Use Table 14 in the data booklet to deduce the colours absorbed by [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ and [TiCl₆]³⁻ and therefore identify which complex ion has the larger energy gap between the d orbitals.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal. Explain why a copper(II) solution is blue, using section 17 of the data booklet.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Explain, in terms of nuclear charge, electron subshells and the shielding provided by filled electron shells, why the first ionization energy increases from Li to Be, but decreases from Be to B.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
The electronegativities of four different elements are given below (the letters are not their chemical symbols).
| Element | W | X | Y | Z |
| Electronegativity | 0.9 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 4.0 |
Based on this information which statement is correct?
A. W is a non-metal.
B. W and X form an ionic compound.
C. Y is a metal.
D. Y and Z form a covalent compound.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
In which reaction does chromium undergo a change in oxidation state?
A. Cr2O3 + 6HCl → 2CrCl3 + 3H2O.
B. Cr2(SO4)3 + 6NaOH → 2Cr(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4.
C. 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O.
D. Na2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 + 6HCl → Cr2(SO4)3 + Na2SO4 + 7H2O + 3Cl2.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
What are the oxidation states of chlorine in the oxyacids HOCl, HClO3, and HClO4?
A. −1, +5 and +7.
B. −1, −5 and +7.
C. +1, +3 and +4.
D. +1, +5 and +7.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
Which compound is not a product of the reaction between an oxide of a period 3 element and water?
A. NaOH
B. Al(OH)3
C. H2SO3
D. H3PO4
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Explain why Cl₂ rather than Br₂ would react more vigorously with a solution of I⁻.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
Which oxide, when added to water, produces the solution with the highest pH?
A. Na2O
B. SO3
C. MgO
D. CO2
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
Which metal is in the f-block of the periodic table?
A. Sr.
B. Sm.
C. Pb.
D. Tc.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Which property generally decreases across period 3?
A. Atomic number.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. First ionization energy.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table?
A. Melting point.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. Ionic radius.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
Describe and explain the variation in the size (radius) of simple ions formed by the elements across period 3 from sodium (Na⁺) to chloride (Cl⁻).
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
Which statements about the periodic table are correct?
I. The elements Mg, Ca and Sr have similar chemical properties.
II. Elements in the same period have the same number of main energy levels.
III. The oxides of Na, Mg and P are basic.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
Element X is in group 5 and period 4 of the periodic table. Which statement is correct?
A. X has 5 occupied energy levels.
B. X can form ions with 3– charge.
C. X is a transition element.
D. X has 4 valence electrons.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
Tellurium is an element in the same group as sulfur.
Which of the following would be the correct formula for telluric(VI) acid?
A. H2Te
B. H2TeO2
C. H2TeO4
D. H2TeO3
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
Which element is in the p-block?
A. Pb.
B. Pm.
C. Pt.
D. Pu.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
How do the following properties change down group 18 of the periodic table?
| Ionization energy | Ionic radius | |
| A. | Increases | Increases |
| B. | Increases | Decreases |
| C. | Decreases | Increases |
| D. | Decreases | Decreases |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
An element M of mass number 40 has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2. Which statement regarding this element is not correct?
A. It belongs to Group 2 of the periodic table.
B. The nucleus of the atom has 20 neutrons.
C. It belongs to period 4 of the periodic table.
D. The formula of its oxide is MO₂.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
Which one of the following ion or atom has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5?
A. Mn.
B. Co²⁺.
C. Fe³⁺.
D. Cr²⁺.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
Which of the following electron configurations could represent a transition metal atom?
A. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2.
B. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5.
C. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p3.
D. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which of the following properties would increase from the atoms sodium to chlorine across period 3?
I. Electronegativity.
II. Nuclear charge.
III. Atomic radius.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: A. I and II only.
| Property | Trend | Reason |
| I. Electronegativity | Increases | The number of protons increases → stronger attraction for bonding electrons. |
| II. Nuclear charge | Increases | More protons are added to the nucleus. |
| III. Atomic radius | Decreases | Increased nuclear charge pulls electrons closer to the nucleus; no new energy level added. |
Question 2
The first four ionisation energies of beryllium and iron are shown.

One common property of transition elements is that they have variable oxidation states. Discuss, referring to the graph, why iron, but not beryllium, displays this characteristic.
• From the graph, Be shows a huge jump after the 2nd ionization (IE₃ is ~1.7×10⁴ kJ mol⁻¹). This means that after Be loses two 2s electrons it reaches a stable noble-gas core (1s²); removing a third electron would be from the core and is energetically prohibitive. Hence Be is essentially fixed at +2.
• Fe shows no large jump through the first 3–4 ionizations; the successive IEs rise only gradually. This shows that several outer electrons are of similar energy (the 4s and 3d electrons) and can be removed or used in bonding.
• Because these 4s/3d electrons are available to different extents, iron can form multiple oxidation states (e.g. +2, +3, etc.), whereas Be cannot.
Question 3
Potassium manganate(VII) is purple in colour. In which region of the visible spectrum does it mainly absorb?
A. Red.
B. Purple.
C. Blue.
D. Green.
Answer: D. Green.
Potassium manganate(VII), KMnO₄, appears deep purple because it transmits purple light.
The colour that a substance appears is the complementary colour of the light it absorbs.
● Purple (violet) is complementary to yellow-green (≈ 520–560 nm region).
● Therefore, KMnO₄ mainly absorbs green light.
Question 4
Which combination is correct for the complex ion in the coordination compound [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Br]Cl?
| Oxidation state of cobalt | Shape of the complex ion | Overall charge of the complex ion | |
| A. | +2 | Octahedral | +2 |
| B. | +3 | Square planar | –1 |
| C. | +2 | Octahedral | +1 |
| D. | +2 | Tetrahedral | +1 |
Answer: C.
Step 1: Find oxidation state of Co
Let oxidation state of Co = x
x + (4 × 0) + (0) + (−1) = +1
(since the compound has 1 Cl⁻ outside the coordination sphere)
x − 1 = +1 ⇒ x = +2
→ Oxidation state of Co = +2
Step 2: Determine the shape
Cobalt(II) forms six-coordinate complexes with ligands like NH₃, H₂O, and halides. → Coordination number = 6
→ octahedral shape
Step 3: Overall charge of the complex ion
Inside the brackets: [Co(NH₃)₄(H₂O)Br]⁺
Because the external Cl⁻ balances a +1 charge on the complex.
Question 5
The following shows a series of reactions involving titanium compounds.
Concentrated HCl

a. Suggest the type of reaction for II and III.
b. Explain why a solution of [TiCl₆]²⁻ is colourless but [TiCl₆]³⁻ is orange. The formula relating energy gap between d orbitals, ΔE, and wavelength, λ, is given as ΔE = hc / λ where h is the Planck’s constant and c is the speed of light.
c. Use Table 14 in the data booklet to deduce the colours absorbed by [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ and [TiCl₆]³⁻ and therefore identify which complex ion has the larger energy gap between the d orbitals.
a.
II: a redox step – Ti is reduced from +4 in [TiCl₆]²⁻ (d⁰) to +3 in [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ (d¹). III: a ligand-substitution (complex formation) step – water ligands are replaced by chloride to give [TiCl₆]³⁻; Ti remains +3.
b. Colour in these Ti complexes comes from d–d transitions between split d-orbitals. [TiCl₆]²⁻ has Ti(IV), d⁰ → no d electrons to promote → colourless. [TiCl₆]³⁻ has Ti(III), d¹ → an allowed d–d transition absorbs visible light, and the transmitted light appears orange.
c. A solution looks the complementary colour to what it absorbs.
[Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ is violet, so it absorbs yellow/green light (≈ 560–580 nm). [TiCl₆]³⁻ is orange, so it absorbs blue light (≈ 450–480 nm).
Since ΔE = `frac{hc}{lambda}`, the shorter wavelength (blue) corresponds to a larger ΔE.
Therefore, [TiCl₆]³⁻ has the larger d-orbital splitting (ΔE) compared with [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺.
Question 6
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal. Explain why a copper(II) solution is blue, using section 17 of the data booklet.
A copper(II) ion has an electron configuration of [Ar]3d⁹. In aqueous solution, the ligands (usually water molecules) form a complex ion with Cu²⁺, causing the 3d orbitals to split into two energy levels due to ligand field splitting. When visible light passes through the solution, electrons are promoted from the lower to the higher d-orbital by absorbing certain wavelengths of light. The remaining unabsorbed light is transmitted as blue, giving the solution its characteristic color.
Question 7
Explain, in terms of nuclear charge, electron subshells and the shielding provided by filled electron shells, why the first ionization energy increases from Li to Be, but decreases from Be to B.
• From Li to Be, the first ionization energy increases because the nuclear charge increases (more protons) while the electrons are being added to the same shell. The shielding effect remains approximately the same, so the increased nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer, making them harder to remove.
• From Be to B, the first ionization energy decreases because the electron removed from boron is in a 2p subshell, while in beryllium it is from a 2s subshell.
The 2p electron is at a higher energy level and is shielded slightly by the filled 2s subshell, making it easier to remove despite the increased nuclear charge.
Question 8
The electronegativities of four different elements are given below (the letters are not their chemical symbols).
| Element | W | X | Y | Z |
| Electronegativity | 0.9 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 4.0 |
Based on this information which statement is correct?
A. W is a non-metal.
B. W and X form an ionic compound.
C. Y is a metal.
D. Y and Z form a covalent compound.
Answer: D. Y and Z form a covalent compound.
A. Incorrect: W = 0.9 → very low → metal, not nonmetal.
B. Incorrect: Electronegativity difference = 1.2 – 0.9 = 0.3, which is very small. → This would be metallic bonding, not ionic.
C. Incorrect: Y = 3.4 → high electronegativity → nonmetal (similar to oxygen).
D. Correct: Electronegativity difference = 4.0 – 3.4 = 0.6, which is small, indicating covalent bonding between two nonmetals.
Question 9
In which reaction does chromium undergo a change in oxidation state?
A. Cr2O3 + 6HCl → 2CrCl3 + 3H2O.
B. Cr2(SO4)3 + 6NaOH → 2Cr(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4.
C. 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O.
D. Na2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 + 6HCl → Cr2(SO4)3 + Na2SO4 + 7H2O + 3Cl2.
Answer: D. Na2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 + 6HCl → Cr2(SO4)3 + Na2SO4 + 7H2O + 3Cl2.
A. Incorrect:
Cr₂O₃ + 6HCl → 2CrCl₃ + 3H₂O
• Cr in Cr₂O₃: O = –2 → total O = –6 → Cr₂ = +6 → each Cr = +3
• Cr in CrCl₃: Cl = –1 → Cr = +3
→ No oxidation state change
B. Incorrect:
Cr₂(SO₄)₃ + 6NaOH → 2Cr(OH)₃ + 3Na₂SO₄
• Cr in Cr₂(SO₄)₃: SO₄ = –2 → Cr = +3
• Cr in Cr(OH)₃: OH = –1 → Cr = +3
→ No oxidation state change
C. Incorrect:
2Na₂CrO₄ + H₂SO₄ → Na₂Cr₂O₇ + Na₂SO₄ + H₂O
• In both Na₂CrO₄ and Na₂Cr₂O₇, Cr = +6
→ No oxidation state change
D. Correct:
Na₂Cr₂O₇ + 4H₂SO₄ + 6HCl → Cr₂(SO₄)₃ + Na₂SO₄ + 7H₂O + 3Cl₂.
• Cr in Na₂Cr₂O₇ = +6
• Cr in Cr₂(SO₄)₃ = +3
Change: +6 → +3 → chromium is reduced
Also, Cl⁻ → Cl₂ (oxidized from –1 → 0)
Question 10
What are the oxidation states of chlorine in the oxyacids HOCl, HClO3, and HClO4?
A. −1, +5 and +7.
B. −1, −5 and +7.
C. +1, +3 and +4.
D. +1, +5 and +7.
Answer: D. +1, +5 and +7.
1. HOCl (hypochlorous acid)
Formula: H + Cl + O = 0
(+1) + (x) + (–2) = 0
x = +1
→ Oxidation state of Cl = +1
2. HClO₃ (chloric acid)
Formula: H + Cl + 3O = 0
(+1) + (x) + 3(–2) = 0
x = +5
→ Oxidation state of Cl = +5
3. HClO₄ (perchloric acid)
Formula: H + Cl + 4O = 0
(+1) + (x) + 4(–2) = 0
x = +7
→ Oxidation state of Cl = +7
Question 11
Which compound is not a product of the reaction between an oxide of a period 3 element and water?
A. NaOH
B. Al(OH)3
C. H2SO3
D. H3PO4
Answer: C. H2SO3
A. Incorrect: NaOH (Correct product)
• Oxide: Sodium oxide (Na₂O)
• Reaction: Na₂O + H₂O → 2NaOH
• Type: Basic oxide of a metal.
→ NaOH is indeed formed by a period 3 oxide reacting with water.
B. Incorrect: Al(OH)₃ (Correct product)
• Oxide: Aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃)
• Aluminium oxide is amphoteric, and when it reacts with water (under certain conditions), it can form Al(OH)₃.
→ Al(OH)₃ can be considered a product derived from a period 3 oxide.
C. Correct: H₂SO₃ (Not a product)
• Oxide: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
• Reaction: SO₂ + H₂O ⇌ H₂SO₃
• However, H₂SO₃ (sulfurous acid) is unstable and does not exist in a pure state— it decomposes back into SO₂ and water.
• The stable acid from a sulfur oxide is actually H₂SO₄, formed from SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄.
→ H₂SO₃ is not a stable or typical product of period 3 oxide + water.
D. Incorrect: H₃PO₄ (Correct product)
• Oxide: Phosphorus pentoxide (P₄O₁₀)
• Reaction: P₄O₁₀ + 6H₂O → 4H₃PO₄
→ Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄) is a true product of a period 3 oxide reacting with water.
Question 12
Explain why Cl₂ rather than Br₂ would react more vigorously with a solution of I⁻.
Chlorine reacts more vigorously with iodide ions than bromine because: Chlorine is a stronger oxidizing agent than bromine. This is because chlorine has a smaller atomic radius and higher electronegativity, so it more readily gains electrons to form Cl⁻ ions.
Question 13
Which oxide, when added to water, produces the solution with the highest pH?
A. Na2O
B. SO3
C. MgO
D. CO2
Answer: A. Na2O
When oxides react with water:
| Oxide | Reaction with water | Solution formed | pH | Type |
| Na₂O | Na₂O + H₂O → 2NaOH | Sodium hydroxide | ≈ 14 | Strongly basic |
| MgO | MgO + H₂O → Mg(OH)₂ | Magnesium hydroxide | ≈ 9–10 | Weakly basic |
| CO₂ | CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃ | Carbonic acid | ≈ 4–5 | Acidic |
| SO₃ | SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄ | Sulfuric acid | ≈ 1–2 | Strongly acidic |
Question 14
Which metal is in the f-block of the periodic table?
A. Sr.
B. Sm.
C. Pb.
D. Tc.
Answer: B. Sm.
A. Incorrect: Sr (s-block), group 2 element, electron configuration ends in 5s².
B. Correct: Sm (f-block), lanthanide element, electron configuration ends in 4f⁶ 6s².
C. Incorrect: Pb (p-block), group 14 element, electron configuration ends in 6p².
D. Incorrect: Tc (d-block), transition metal, electron configuration ends in 4d⁵ 5s².
Question 15
Which property generally decreases across period 3?
A. Atomic number.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. First ionization energy.
Answer: C. Atomic radius.
Across Period 3 (Na → Ar):
| Property | Trend | Reason |
| Atomic number | Increases | More protons and electrons are added. |
| Electronegativity | Increases | Greater nuclear charge attracts bonding electrons more strongly. |
| Atomic radius | Decreases | Nuclear charge increases while shielding stays nearly constant → electrons pulled closer to the nucleus. |
| First ionization energy | Generally increases | Harder to remove an electron due to stronger nuclear attraction. |
Question 16
Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table?
A. Melting point.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. Ionic radius.
Answer: B. Electronegativity.
Group 7 (the halogens) – F, Cl, Br, I, At
As we move down the group:
| Property | Trend | Explanation |
| Melting point | Increases | Molecules become larger → stronger van der Waals forces. |
| Electronegativity | Decreases | Atomic size increases → bonding electrons are farther from the nucleus → weaker attraction for electrons. |
| Atomic radius | Increases | More electron shells → larger atom. |
| Ionic radius | Increases | More electron shells → larger ions. |
Question 17
Describe and explain the variation in the size (radius) of simple ions formed by the elements across period 3 from sodium (Na⁺) to chloride (Cl⁻).
Across Period 3, from sodium (Na⁺) to chloride (Cl⁻), the size of the ions decreases from Na⁺ to Al³⁺, and then increases from P³⁻ to Cl⁻.
• From Na⁺ to Al³⁺:
o These are cations formed by the loss of electrons.
o The number of electron shells remains the same (all have 2 shells after ionization).
o However, the nuclear charge increases from +11 (Na⁺) to +13 (Al³⁺). o The greater nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus, causing the ionic radius to decrease.
o Hence, Na⁺ > Mg²⁺ > Al³⁺ in size.
• From P³⁻ to Cl⁻:
o These are anions formed by the gain of electrons.
o Each anion has the same number of electron shells (3 shells).
o As nuclear charge increases from P³⁻ to Cl⁻, the attraction between the nucleus and the extra electrons increases, pulling the electrons closer. o Therefore, the ionic radius decreases from P³⁻ > S²⁻ > Cl⁻.
• Across the entire period (Na⁺ to Cl⁻):
o Cations are much smaller than anions because cations lose an electron shell, while anions gain electrons and experience increased electron– electron repulsion.
o The smallest ion is Al³⁺ and the largest is P³⁻.
Question 18
Which statements about the periodic table are correct?
I. The elements Mg, Ca and Sr have similar chemical properties.
II. Elements in the same period have the same number of main energy levels.
III. The oxides of Na, Mg and P are basic.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: A. I and II only.
Statement I: True
• Mg, Ca, and Sr are all Group 2 (alkaline earth metals).
• Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons (2).
Statement II: True
• Elements in the same period have the same number of occupied electron shells (main energy levels).
• Example: Na, Mg, and Al are all in Period 3 → each has 3 energy levels.
Statement III: False
• Na₂O → basic oxide
• MgO → basic oxide
• P₄O₁₀ (oxide of phosphorus) → acidic oxide
→ Not all three are basic.
Question 19
Element X is in group 5 and period 4 of the periodic table. Which statement is correct?
A. X has 5 occupied energy levels.
B. X can form ions with 3– charge.
C. X is a transition element.
D. X has 4 valence electrons.
Answer: C. X is a transition element.
A. Incorrect: Period 4 → 4 energy levels, not 5.
B. Incorrect: Group 5 transition metals form positive ions (cations), not negative ions.
C. Correct: Group 5 elements are transition metal with partially filled 3d orbitals.
D. Incorrect: Group 5 → has 5 valence electrons (3d³ 4s²).
Question 20
Tellurium is an element in the same group as sulfur.
Which of the following would be the correct formula for telluric(VI) acid?
A. H2Te
B. H2TeO2
C. H2TeO4
D. H2TeO3
Answer: C. H2TeO4.
Tellurium (Te) is in Group 16, the same group as sulfur (S). The oxidation state is (+6)
A. Incorrect: Te oxidation state = −2
B. Incorrect: Te oxidation state = +2
C. Correct: Te oxidation state = +6
D. Incorrect: Te oxidation state = +4
Question 21
Which element is in the p-block?
A. Pb.
B. Pm.
C. Pt.
D. Pu.
Answer: A. Pb.
| Element | Symbol | Block | Reason |
| Pb (Lead) | Pb | p-block | Its outer electron configuration ends in 6p². Found in Group 14 (same group as C, Si, Sn). |
| Pm (Promethium) | Pm | f-block | A lanthanide (atomic number 61). |
| Pt (Platinum) | Pt | d-block | A transition metal (atomic number 78). |
| Pu (Plutonium) | Pu | f-block | An actinide (atomic number 94). |
Question 22
How do the following properties change down group 18 of the periodic table?
| Ionization energy | Ionic radius | |
| A. | Increases | Increases |
| B. | Increases | Decreases |
| C. | Decreases | Increases |
| D. | Decreases | Decreases |
Answer: C. Ionization energy: Decreases, Ionic radius: Increases
• As atomic number increases, the atomic radius increases, outer electrons are further from the nucleus, and shielding increases. Therefore, it is easier to remove an electron.
• Each element down the group has an extra electron shell, making the atoms (and ions, if formed) larger.
Question 23
An element M of mass number 40 has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2. Which statement regarding this element is not correct?
A. It belongs to Group 2 of the periodic table.
B. The nucleus of the atom has 20 neutrons.
C. It belongs to period 4 of the periodic table.
D. The formula of its oxide is MO₂.
Answer: D. The formula of its oxide is MO₂.
A. Incorrect:
This configuration ends in 4s², meaning the element is in Group 2 → Statement correct.
B. Incorrect:
40 (mass number) − 20 (protons) = 20 neutrons → Statement correct.
C. Incorrect:
Highest principal quantum number = 4 → Period 4 → Statement correct.
D. Correct:
Group 2 metals form oxides of the type MO because they have a +2 oxidation state and oxygen is −2 → Statement incorrect.
Question 24
Which one of the following ion or atom has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5?
A. Mn.
B. Co²⁺.
C. Fe³⁺.
D. Cr²⁺.
Answer: C. Fe³⁺.
This configuration ends with 3d⁵, which means the 3d subshell is half-filled and there are no 4s electrons — suggesting an ion formed by removing the 4s electrons from such an atom.
A. Incorrect: The neutral atom Mn has [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s², not exactly 3d⁵
B. Incorrect: [Ar] 3d⁷ 4s² → remove 2 electrons → [Ar] 3d⁷
C. Correct: [Ar] 3d⁶ 4s² → remove 3 electrons → [Ar] 3d⁵
D. Incorrect: [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹ → remove 2 electrons → [Ar] 3d⁴
Question 25
Which of the following electron configurations could represent a transition metal atom?
A. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2.
B. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5.
C. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p3.
D. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2.
Answer: A. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d³ 4s².
A transition metal is defined as an element that has an incomplete d sub-shell (partially filled d orbitals) in its atom or in one of its common ions.
| Option | Electron configuration | Element | Explanation |
| A. Correct | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d³ 4s² | Vanadium (V) | Has a partially filled 3d sub shell, so it’s a transition metal. |
| B. Incorrect | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁵ | Chlorine (Cl) | Nonmetal, p-block element. |
| C. Incorrect | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p³ | Arsenic (As) | p-block element (Group 15). |
| D. Incorrect | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² | Calcium (Ca) | s-block element, not a transition metal. |
Question 1
Which of the following properties would increase from the atoms sodium to chlorine across period 3?
I. Electronegativity.
II. Nuclear charge.
III. Atomic radius.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 2
The first four ionisation energies of beryllium and iron are shown.

One common property of transition elements is that they have variable oxidation states. Discuss, referring to the graph, why iron, but not beryllium, displays this characteristic.
Question 3
Potassium manganate(VII) is purple in colour. In which region of the visible spectrum does it mainly absorb?
A. Red.
B. Purple.
C. Blue.
D. Green.
Question 4
Which combination is correct for the complex ion in the coordination compound [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Br]Cl?
| Oxidation state of cobalt | Shape of the complex ion | Overall charge of the complex ion | |
| A. | +2 | Octahedral | +2 |
| B. | +3 | Square planar | –1 |
| C. | +2 | Octahedral | +1 |
| D. | +2 | Tetrahedral | +1 |
Question 5
The following shows a series of reactions involving titanium compounds.
Concentrated HCl

a. Suggest the type of reaction for II and III.
b. Explain why a solution of [TiCl₆]²⁻ is colourless but [TiCl₆]³⁻ is orange. The formula relating energy gap between d orbitals, ΔE, and wavelength, λ, is given as ΔE = hc / λ where h is the Planck’s constant and c is the speed of light.
c. Use Table 14 in the data booklet to deduce the colours absorbed by [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ and [TiCl₆]³⁻ and therefore identify which complex ion has the larger energy gap between the d orbitals.
Question 6
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal. Explain why a copper(II) solution is blue, using section 17 of the data booklet.
Question 7
Explain, in terms of nuclear charge, electron subshells and the shielding provided by filled electron shells, why the first ionization energy increases from Li to Be, but decreases from Be to B.
Question 8
The electronegativities of four different elements are given below (the letters are not their chemical symbols).
| Element | W | X | Y | Z |
| Electronegativity | 0.9 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 4.0 |
Based on this information which statement is correct?
A. W is a non-metal.
B. W and X form an ionic compound.
C. Y is a metal.
D. Y and Z form a covalent compound.
Question 9
In which reaction does chromium undergo a change in oxidation state?
A. Cr2O3 + 6HCl → 2CrCl3 + 3H2O.
B. Cr2(SO4)3 + 6NaOH → 2Cr(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4.
C. 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O.
D. Na2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 + 6HCl → Cr2(SO4)3 + Na2SO4 + 7H2O + 3Cl2.
Question 10
What are the oxidation states of chlorine in the oxyacids HOCl, HClO3, and HClO4?
A. −1, +5 and +7.
B. −1, −5 and +7.
C. +1, +3 and +4.
D. +1, +5 and +7.
Question 11
Which compound is not a product of the reaction between an oxide of a period 3 element and water?
A. NaOH
B. Al(OH)3
C. H2SO3
D. H3PO4
Question 12
Explain why Cl₂ rather than Br₂ would react more vigorously with a solution of I⁻.
Question 13
Which oxide, when added to water, produces the solution with the highest pH?
A. Na2O
B. SO3
C. MgO
D. CO2
Question 14
Which metal is in the f-block of the periodic table?
A. Sr.
B. Sm.
C. Pb.
D. Tc.
Question 15
Which property generally decreases across period 3?
A. Atomic number.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. First ionization energy.
Question 16
Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table?
A. Melting point.
B. Electronegativity.
C. Atomic radius.
D. Ionic radius.
Question 17
Describe and explain the variation in the size (radius) of simple ions formed by the elements across period 3 from sodium (Na⁺) to chloride (Cl⁻).
Question 18
Which statements about the periodic table are correct?
I. The elements Mg, Ca and Sr have similar chemical properties.
II. Elements in the same period have the same number of main energy levels.
III. The oxides of Na, Mg and P are basic.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 19
Element X is in group 5 and period 4 of the periodic table. Which statement is correct?
A. X has 5 occupied energy levels.
B. X can form ions with 3– charge.
C. X is a transition element.
D. X has 4 valence electrons.
Question 20
Tellurium is an element in the same group as sulfur.
Which of the following would be the correct formula for telluric(VI) acid?
A. H2Te
B. H2TeO2
C. H2TeO4
D. H2TeO3
Question 21
Which element is in the p-block?
A. Pb.
B. Pm.
C. Pt.
D. Pu.
Question 22
How do the following properties change down group 18 of the periodic table?
| Ionization energy | Ionic radius | |
| A. | Increases | Increases |
| B. | Increases | Decreases |
| C. | Decreases | Increases |
| D. | Decreases | Decreases |
Question 23
An element M of mass number 40 has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2. Which statement regarding this element is not correct?
A. It belongs to Group 2 of the periodic table.
B. The nucleus of the atom has 20 neutrons.
C. It belongs to period 4 of the periodic table.
D. The formula of its oxide is MO₂.
Question 24
Which one of the following ion or atom has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5?
A. Mn.
B. Co²⁺.
C. Fe³⁺.
D. Cr²⁺.
Question 25
Which of the following electron configurations could represent a transition metal atom?
A. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2.
B. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5.
C. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p3.
D. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2.