Question 1
Which metal has the strongest metallic bonding?
A. Li
B. K
C. Rb
D. Cs
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The melting point of calcium, 839°C, is much higher than the melting point of sodium, 98°C. Which statement is most relevant in explaining this difference?
A. The calcium atom has a larger radius than the sodium atom.
B. The calcium atom has a higher molar mass than the sodium atom.
C. The calcium ion has a higher charge than the sodium ion.
D. The calcium ion has more electrons than the sodium ion.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
In which of the following substances does metallic bonding predominate?
A. Graphene.
B. Brass.
C. Silicon.
D. Boron.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which statements are correct for metals?
I. They are good thermal conductors because they have free-moving cations.
II. They often consist of a close-packed lattice of cations with delocalized valence electrons.
III. They are malleable and ductile because the layers of cations can slide across each other and still remain bonded.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
a. Describe metallic bonding.
b. Explain why metals generally have high melting points, conduct electricity in both solid and liquid states and are good conductors of heat.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
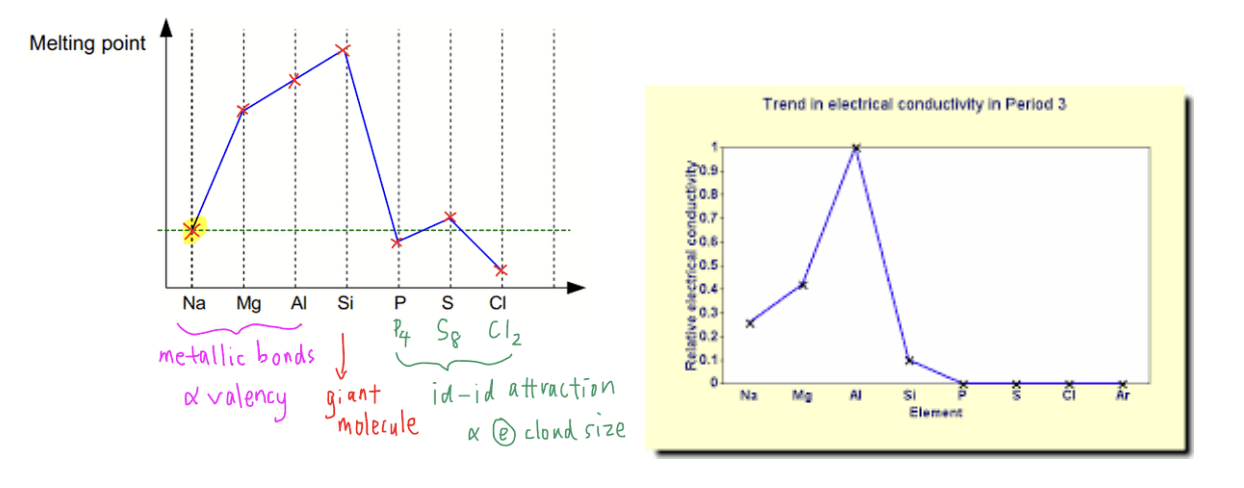
Describe the variation in melting points and electrical conductivities of the elements in period 3 (sodium to argon), and explain these variations in terms of their structures and bonding.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which statement best describes the attraction present in metallic bonding?
A. The attraction between metal nuclei and valence electrons.
B. The attraction between cations and valence electrons.
C. The attraction between cations and anions.
D. The attraction between protons and valence electrons.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
The table below shows part of the central block of the periodic table which displays transition metals found in periods 4, 5 and 6. The proton numbers and melting points of each of the metals are shown.
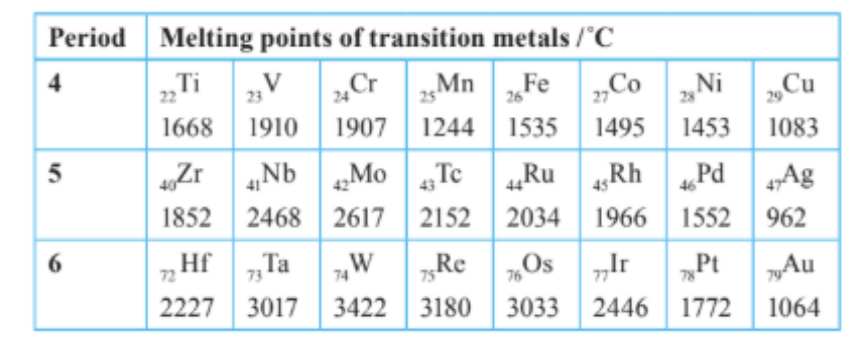
a. Use the information above to describe the trends in the melting points of transition metals down the groups and across the periods.
b. Evaluate the hypothesis that more unpaired electrons present in an atom tends to increase the bonding strength of a metal in the solid state.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
State and explain one difference in physical property between chromium (d-block metal) and strontium (a main group metal).
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which metal has the strongest metallic bonding?
A. Li
B. K
C. Rb
D. Cs
Answer: A. Li
Metallic bonding strength depends on:
1. Number of delocalized electrons per atom (same for all Group 1 metals — 1 electron).
2. Charge density (metal ion charge / size). → Smaller ions → stronger electrostatic attraction to the delocalized electrons → stronger metallic bonding. Lithium has the smallest atomic radius, so Li⁺ ions are close-packed and attract the delocalized electrons more strongly, giving it the strongest metallic bonding among the alkali metals.
Question 2
The melting point of calcium, 839°C, is much higher than the melting point of sodium, 98°C. Which statement is most relevant in explaining this difference?
A. The calcium atom has a larger radius than the sodium atom.
B. The calcium atom has a higher molar mass than the sodium atom.
C. The calcium ion has a higher charge than the sodium ion.
D. The calcium ion has more electrons than the sodium ion.
Answer: C. The calcium ion has a higher charge than the sodium ion.
A. Incorrect:
A larger radius would weaken metallic bonding, not strengthen it.
B. Incorrect:
Molar mass does not affect bond strength or melting point directly.
C. Correct:
Calcium forms 2⁺ ions, contributing two delocalized electrons per atom, leading to stronger metallic bonds and a much higher melting point.
D. Incorrect:
Though true, this is not the main reason for stronger metallic bonding; it’s the charge that matters.
Question 3
In which of the following substances does metallic bonding predominate?
A. Graphene.
B. Brass.
C. Silicon.
D. Boron.
Answer: B. Brass.
A. Incorrect:
Graphene consists of carbon atoms in a giant covalent lattice with delocalized π electrons above and below the plane. Although electrons are delocalized, the bonding is covalent, not metallic (since there are no positive metal ions).
B. Correct:
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, both metals. In brass, atoms exist in a lattice of positive metal ions surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons, the defining feature of metallic bonding.
C. Incorrect:
Silicon forms a giant covalent network (similar to diamond) with strong covalent bonds between Si atoms. It’s a semiconductor, not metallic in bonding nature.
D. Incorrect:
Boron also forms a covalent network solid (B₁₂ icosahedra), not a metallic lattice.
Question 4
Which statements are correct for metals?
I. They are good thermal conductors because they have free-moving cations.
II. They often consist of a close-packed lattice of cations with delocalized valence electrons.
III. They are malleable and ductile because the layers of cations can slide across each other and still remain bonded.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
A. Incorrect:
Statement II is correct, but statement I is incorrect. Metals conduct heat well, but not because of cations. The delocalized electrons (not cations) move freely and transfer kinetic energy throughout the lattice. Cations are fixed in position in the metallic lattice and only vibrate.
B. Incorrect: Statement III is correct, but statement I is not.
C. Correct: Both statements are correct.
D. Incorrect: Statement I is not correct.
Question 5
a. Describe metallic bonding.
b. Explain why metals generally have high melting points, conduct electricity in both solid and liquid states and are good conductors of heat.
a. Describe metallic bonding.
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions (cations) arranged in a regular lattice and a ‘sea’ of delocalized electrons that move freely throughout the structure. These delocalized electrons hold the metal lattice together. b. Explain why metals generally have high melting points, conduct electricity in both solid and liquid states, and are good conductors of heat.
1. High melting points:
o Metallic bonds are strong electrostatic attractions between metal cations
o A large amount of energy is required to break these strong bonds, resulting in high melting points.
2. Electrical conductivity (in both solid and liquid states):
o Metals contain delocalized electrons that are free to move throughout the structure.
o When a potential difference is applied, these electrons flow, allowing electric current to pass.
o In the liquid state, the metallic bonds are weakened but electrons remain mobile, so conduction continues.
3. Thermal conductivity:
o Delocalized electrons and vibrations of closely packed metal ions efficiently transfer kinetic energy through the lattice, making metals good conductors of heat.
Question 6
Describe the variation in melting points and electrical conductivities of the elements in period 3 (sodium to argon), and explain these variations in terms of their structures and bonding.
1. Metals (Na, Mg, Al):
• Melting point trend: increases from Na → Mg → Al
o Because the metallic bonding becomes stronger:
▪ Number of delocalized electrons per atom increases (Na: 1, Mg: 2, Al: 3).
▪ Charge on metal cation increases and ionic radius decreases, leading to stronger electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalized electrons.
• Electrical conductivity: also increases across Na → Mg → Al
o More delocalized electrons per atom are available for conduction. 2. Silicon (Si):
• Very high melting point
o Silicon has a giant covalent structure where each Si atom forms four strong covalent bonds in a 3D lattice.
o A large amount of energy is required to break these covalent bonds.
• Electrical conductivity: very low
o No free electrons, but limited conduction occurs due to excitation of electrons across the small band gap.
3. Nonmetals (P, S, Cl) and noble gas Ar:
• Melting points drop sharply after Si
o These elements have simple molecular structures with weak intermolecular (van der Waals) forces.
o The melting point depends on molecular size:
▪ S₈ (largest molecule) has the highest melting point among them.
▪ P₄ melts lower, Cl₂ and Ar (monatomic) melt at very low temperatures.
• Electrical conductivity: none, since there are no delocalized electrons.
Question 7
Which statement best describes the attraction present in metallic bonding?
A. The attraction between metal nuclei and valence electrons.
B. The attraction between cations and valence electrons.
C. The attraction between cations and anions.
D. The attraction between protons and valence electrons.
Answer: B. The attraction between cations and valence electrons.
A. Incorrect:
While this sounds close, metallic bonding involves attraction between positive metal ions (cations) - not just the nuclei - and the delocalized electrons.
B. Correct:
This is the definition of metallic bonding: The electrostatic attraction between positive metal cations and a ‘sea’ of delocalized valence electrons.
C. Incorrect: That describes ionic bonding, not metallic bonding.
D. Incorrect: Protons are inside nuclei and are not directly involved in metallic bonding interactions.
Question 8
The table below shows part of the central block of the periodic table which displays transition metals found in periods 4, 5 and 6. The proton numbers and melting points of each of the metals are shown.

a. Use the information above to describe the trends in the melting points of transition metals down the groups and across the periods.
b. Evaluate the hypothesis that more unpaired electrons present in an atom tends to increase the bonding strength of a metal in the solid state.
a. Trends in melting points
• Across a period (left → right): The melting points rise from Ti/Zr/Hf to a maximum at Cr–W (groups 6–7) and then fall toward the end (Ni → Cu; Pd → Ag; Pt → Au).
• Down a group (period 4 → 5 → 6): For most groups the melting point increases (e.g., Ti < Zr < Hf; V < Nb < Ta; Cr < Mo < W; Fe < Ru < Os; Co < Rh < Ir; Ni < Pd < Pt).
b. Evaluating the hypothesis: “More unpaired electrons → stronger metallic bonding.”.
• Largely supported across each period: the highest melting points occur for metals in the middle of the transition series (Cr/Mo/W; Re/Os) where there are many unpaired d electrons, giving strong metal – metal bonding.
• Falls toward the right as d electrons pair, reducing the number of unpaired electrons and weakening bonding.
• Not the only factor / some anomalies (e.g., Mn and the Cu/Ag/Au trio), and down group increases also reflect greater radial extent of 4d/5d orbitals improving overlap.
Conclusion: More unpaired electrons generally increase metallic bond strength, consistent with the observed melting-point trends, though other factors (orbital extent, specific electronic configurations) also play a role.
Question 9
State and explain one difference in physical property between chromium (d-block metal) and strontium (a main group metal).
Difference: Chromium has a much higher melting point and greater hardness than strontium.
Explanation:
• Chromium is a transition metal (d-block) - it has partially filled d orbitals that allow the presence of many delocalized electrons. These electrons form strong metallic bonds between closely packed metal cations.
• In contrast, strontium is a main-group (s-block) metal with only two delocalized electrons per atom, resulting in weaker metallic bonding. Therefore, chromium is harder, denser, and has a much higher melting point than strontium.
Question 1
Which metal has the strongest metallic bonding?
A. Li
B. K
C. Rb
D. Cs
Question 2
The melting point of calcium, 839°C, is much higher than the melting point of sodium, 98°C. Which statement is most relevant in explaining this difference?
A. The calcium atom has a larger radius than the sodium atom.
B. The calcium atom has a higher molar mass than the sodium atom.
C. The calcium ion has a higher charge than the sodium ion.
D. The calcium ion has more electrons than the sodium ion.
Question 3
In which of the following substances does metallic bonding predominate?
A. Graphene.
B. Brass.
C. Silicon.
D. Boron.
Question 4
Which statements are correct for metals?
I. They are good thermal conductors because they have free-moving cations.
II. They often consist of a close-packed lattice of cations with delocalized valence electrons.
III. They are malleable and ductile because the layers of cations can slide across each other and still remain bonded.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 5
a. Describe metallic bonding.
b. Explain why metals generally have high melting points, conduct electricity in both solid and liquid states and are good conductors of heat.
Question 6
Describe the variation in melting points and electrical conductivities of the elements in period 3 (sodium to argon), and explain these variations in terms of their structures and bonding.
Question 7
Which statement best describes the attraction present in metallic bonding?
A. The attraction between metal nuclei and valence electrons.
B. The attraction between cations and valence electrons.
C. The attraction between cations and anions.
D. The attraction between protons and valence electrons.
Question 8
The table below shows part of the central block of the periodic table which displays transition metals found in periods 4, 5 and 6. The proton numbers and melting points of each of the metals are shown.

a. Use the information above to describe the trends in the melting points of transition metals down the groups and across the periods.
b. Evaluate the hypothesis that more unpaired electrons present in an atom tends to increase the bonding strength of a metal in the solid state.
Question 9
State and explain one difference in physical property between chromium (d-block metal) and strontium (a main group metal).