Question 1
Which is the best description of ionic bonding?
A. Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
B. Electrostatic attraction between positive ions and electrons.
C. Electrostatic attraction of nuclei towards shared electrons in the bond between the nuclei.
D. Electrostatic attraction between nuclei.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which statement best describes the lattice structure of solid sodium chloride?
A. Each sodium ion is surrounded by one chloride ion.
B. Each chloride ion is surrounded by two sodium ions.
C. Each chloride ion is surrounded by four sodium ions.
D. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which compounds have an ionic lattice structure in the solid state?
I. Silicon dioxide
II. Sodium fluoride
III. Ammonium nitrate
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A group 1 element, X, bonds with a group 17 element, Y. What is the most likely formula and type of bonding in this compound?
A. X2Y ionic.
B. XY ionic.
C. XY7 covalent.
D. XY covalent.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
What is the formula for the ionic compound formed when barium reacts with nitrogen?
A. BaN.
B. Ba2N.
C. Ba3N2.
D. Ba2N3.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The diagram shows the arrangement of the ions in an ionic crystal.
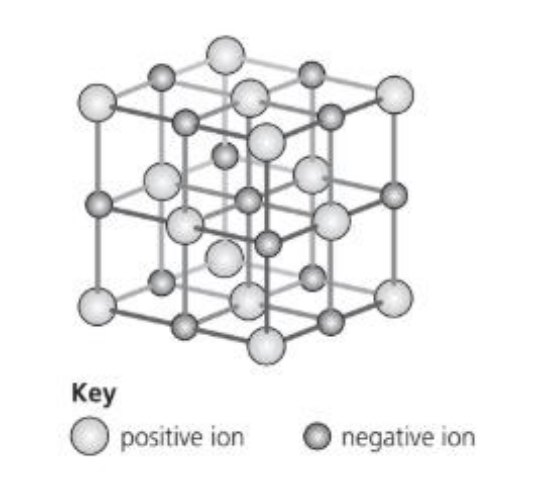
Which compound cannot have this lattice?
A. Magnesium oxide.
B. Calcium chloride.
C. Iron(II) sulfate.
D. Lithium chloride.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The formula for samarium(III) chloride is SmCl3. What is the formula for samarium(III) sulfate(VI)?
A. Sm2(SO4)3.
B. Sm(SO4)3.
C. Sm3(SO4)2.
D. Sm2SO4.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What are the correct formulas of the following ions?
| Nitrate | Sulfate | Phosphate | Hydrogencarbonate | |
| A. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| B. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
| C. | NO₂⁻ | SO₄⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| D. | NO₂⁻ | SO₃²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which statement is a correct description of electron loss in this redox reaction?
2Al + 3Se → Al2Se3
A. Each aluminium atom loses two valence electrons.
B. Each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons.
C. Each selenium atom loses two valence electrons.
D. Each selenium atom loses three valence electrons.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Which of the following ionic compounds is expected to have the most positive value of lattice enthalpy?
A. NaF.
B. NaBr.
C. LiI.
D. LiF.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
Magnesium sulfate is used as an electrolyte to treat brain injury patients in hospitals.
Magnesium sulfate contains both covalent bonds and ionic bonding.
a. State the formulas of the ions present and the nature of the force operating between the oppositely charged ions.
b. State which atoms are covalently bonded.
c. A metal atom has the electron configuration of 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹. Identify element and predict the charge on the cation.
d. Deduce the formula of its sulfate which finds use as a blood coagulant.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Silver reacts with fluorine to form silver fluoride, AgF. Silver fluoride has a high melting point and has a simple cubic structure similar to that of sodium chloride.
a. Explain why the formula, AgF, is an empirical formula.
b. State the equation showing the synthesis of silver fluoride from its elements.
c. State the type of reaction involved.
d. State and describe the type of bonding involved in silver fluoride.
e. State four properties typical of compounds with this type of bonding.
f. Draw a diagram to show how the particles are arranged in a silver fluoride lattice and show the charges on the particles.
g. Silver fluoride is insoluble in organic solvents, but lithium bromide shows significant solubility in organic solvents. Suggest a reason for this behaviour of lithium bromide.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
Which compound has the largest value of lattice enthalpy?
A. Al2O3.
B. MgS.
C. NaF.
D. MgO.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
Halogens react readily with lead to form lead halides.
The melting points of some of the lead halides are given in the table below.
| Compound | Melting point / °C |
| PbF₂ | 824 |
| PbCl₂ | 501 |
| PbBr₂ | 373 |
| PbCl₄ | –15 |
a. Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why the melting points of the lead(II) halides decrease from lead(II) fluoride to lead(II) bromide.
b. Explain why PbCl4 is a covalent compound and account for its low melting point.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Which element forms more than one stable cation?
A. Ca.
B. Mn.
C. Zn.
D. Al.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which is the best description of ionic bonding?
A. Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
B. Electrostatic attraction between positive ions and electrons.
C. Electrostatic attraction of nuclei towards shared electrons in the bond between the nuclei.
D. Electrostatic attraction between nuclei.
Answer: A. Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
A. Correct: This directly describes the nature of ionic bonding (e.g., Na+ and Cl− in NaCl).
B. Incorrect: That describes metallic bonding, where delocalized electrons attract metal cations.
C. Incorrect: That describes covalent bonding, where atoms share electrons.
D. Incorrect: Nuclei repel each other because both are positively charged.
Question 2
Which statement best describes the lattice structure of solid sodium chloride?
A. Each sodium ion is surrounded by one chloride ion.
B. Each chloride ion is surrounded by two sodium ions.
C. Each chloride ion is surrounded by four sodium ions.
D. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions.
Answer: D. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions.
Solid sodium chloride (NaCl) forms a giant ionic lattice structure known as a face-centered cubic (FCC) or rock-salt structure. In this lattice:
Each Na+ ion is surrounded by six Cl− ions.
Each Cl− ion is also surrounded by six Na+ ions.
A. Incorrect: Ionic bonding extends in all directions, not just one-to-one.
B. Incorrect: Coordination number is 6, not 2.
C. Incorrect: Four coordination applies to other structures (like ZnS), not NaCl.
D. Correct: This correctly describes the cubic lattice structure of NaCl.
Question 3
Which compounds have an ionic lattice structure in the solid state?
I. Silicon dioxide
II. Sodium fluoride
III. Ammonium nitrate
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
I. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) → Not ionic
• SiO2 is a giant covalent (network) structure, not ionic.
• Each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
→ Not an ionic lattice.
II. Sodium fluoride (NaF) → Ionic
• Na+ and F− ions form a giant ionic lattice similar to NaCl.
• Strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
→ Ionic lattice structure.
III. Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) → Ionic
• Contains `""NH_4^+` (ammonium cations) and `""NO_3^-` (nitrate anions).
• These ions are held together by ionic bonds in a lattice.
→ Ionic lattice structure (though each ion itself contains covalent bonds internally).
Question 4
A group 1 element, X, bonds with a group 17 element, Y. What is the most likely formula and type of bonding in this compound?
A. X2Y ionic.
B. XY ionic.
C. XY7 covalent.
D. XY covalent.
Answer: B. XY ionic.
• Group 1 element (X) → metals such as Li, Na, K → Forms X+ ions (loses one electron).
• Group 17 element (Y) → halogens such as F, Cl, Br → Forms Y− ions (gains one electron).
When X and Y combine:
X++Y− → XY
→ The compound formed is ionic, consisting of oppositely charged ions held by electrostatic attraction.
A. Incorrect: Would imply X has a `frac{+1}{2}` charge or Y has a –2 charge, which doesn’t fit Group 1 and 17.
B. Correct: Fits the ratio 1:1 between X+ and Y− ions (e.g., NaCl, KBr).
C. Incorrect: Group 1 metals don’t form covalent compounds like this.
D. Incorrect: Group 1 and 17 elements form ionic, not covalent, bonds.
Question 5
What is the formula for the ionic compound formed when barium reacts with nitrogen?
A. BaN.
B. Ba2N.
C. Ba3N2.
D. Ba2N3.
Answer: C. Ba3N2.
When barium (Ba) reacts with nitrogen (N), they form an ionic compound.
• Barium (Ba) is a Group 2 element → forms Ba2+ ions.
• Nitrogen (N) is a Group 15 element → forms N3− ions.To form a neutral compound, the total positive and negative charges must balance:
3(Ba2+) = +6 and 2(N3−) = −6
`=>` The correct formula is: Ba3N2.
A. Incorrect: Charges not balanced (+2 vs –3).
B. Incorrect: Still not balanced (+4 vs –3).
C. Correct: Balanced (+6 and –6).
D. Incorrect: (+4 vs –9, not balanced).
Question 6
The diagram shows the arrangement of the ions in an ionic crystal.

Which compound cannot have this lattice?
A. Magnesium oxide.
B. Calcium chloride.
C. Iron(II) sulfate.
D. Lithium chloride.
Answer: C. Iron(II) sulfate.
The diagram shows a simple cubic ionic lattice with alternating positive and negative ions — just like sodium chloride (NaCl) structure.
This type of lattice has:
• 1:1 ratio of positive to negative ions
• Each ion surrounded by six oppositely charged ions (coordination number 6:6)
Check each compound:
| Compound | Ion ratio | Lattice type | Compatible |
| A. Magnesium oxide | 1:1 (Mg²⁺ : O²⁻) | NaCl-type (ionic) | Yes |
| B. Calcium chloride | 1:2 (Ca²⁺ : Cl⁻) | Not 1:1, but still ionic | Does not match 1:1 lattice |
| C. Iron(II) sulfate | 1:1 (Fe²⁺ : SO₄²⁻), but SO₄²⁻ is a complex polyatomic ion | Structure is not a simple cubic lattice; it has ionic + covalent bonding | Cannot have this lattice |
| D. Lithium chloride | 1:1 (Li⁺ : Cl⁻) | NaCl-type (ionic) | Yes |
Question 7
The formula for samarium(III) chloride is SmCl3. What is the formula for samarium(III) sulfate(VI)?
A. Sm2(SO4)3.
B. Sm(SO4)3.
C. Sm3(SO4)2.
D. Sm2SO4.
Answer: A. Sm2(SO4)3.
We are forming samarium(III) sulfate(VI).
Step 1: Balance charges
To make the compound neutral, total positive = total negative.
Sm³⁺ and SO₄²⁻
Find the lowest common multiple (LCM) of 3 and 2 → 6
→ To get total charge = 0:
Step 2: Write the formula: Sm2(SO4)3.
Question 8
What are the correct formulas of the following ions?
| Nitrate | Sulfate | Phosphate | Hydrogencarbonate | |
| A. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| B. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
| C. | NO₂⁻ | SO₄⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| D. | NO₂⁻ | SO₃²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
Answer: A. Nitrate: NO₃⁻; Sulfate: SO₄²⁻; Phosphate: PO₄³⁻; Hydrogencarbonate: HCO₃⁻
A. Correct
B. Incorrect: Phosphate is PO₄³⁻.
C. Incorrect: SO₄⁻ should be SO₄²⁻.
D. Incorrect: NO₂⁻ is nitrite and SO₃²⁻ is sulfite, not nitrate and sulfate.
Question 9
Which statement is a correct description of electron loss in this redox reaction?
2Al + 3Se → Al2Se3
A. Each aluminium atom loses two valence electrons.
B. Each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons.
C. Each selenium atom loses two valence electrons.
D. Each selenium atom loses three valence electrons.
Answer: B. Each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons.
The reaction is: 2Al + 3Se → Al2Se3
Step 1: Identify oxidation states
o Starts as an element → oxidation state = 0
o In Al2Se3, it becomes Al³⁺
o Starts as an element → oxidation state = 0
o In Al2Se3, it becomes Se²⁻
Step 2: Determine electron transfer
⇒ Each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons.
Question 10
Which of the following ionic compounds is expected to have the most positive value of lattice enthalpy?
A. NaF.
B. NaBr.
C. LiI.
D. LiF.
Answer: D. LiF.
Factors affecting lattice enthalpy:
| Compound | Cation radius | Anion radius | Ionic size (r) | Lattice enthalpy |
| NaF | Larger (Na⁺, F⁻) | Small | Medium | High |
| NaBr | Larger (Na⁺, Br⁻) | Larger | Larger | Lower |
| LiI | Small (Li⁺, I⁻) | Large | Large | Lower |
| LiF | Small (Li⁺, F⁻) | Small | Smallest | Highest |
⇒ LiF has the most positive (largest magnitude) lattice enthalpy → Strongest ionic bonding.
Question 11
Magnesium sulfate is used as an electrolyte to treat brain injury patients in hospitals.
Magnesium sulfate contains both covalent bonds and ionic bonding.
a. State the formulas of the ions present and the nature of the force operating between the oppositely charged ions.
b. State which atoms are covalently bonded.
c. A metal atom has the electron configuration of 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹. Identify element and predict the charge on the cation.
d. Deduce the formula of its sulfate which finds use as a blood coagulant.
a. Ions present: Mg²⁺ and SO₄²⁻
Nature of force: The force between oppositely charged ions is electrostatic attraction (ionic bond).
b. Within the sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻), the sulfur and oxygen atoms are joined by covalent bonds.
c. Given electron configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹
→ This is aluminium (Al) (atomic number 13).
When it forms a cation, it loses its three valence electrons (3s²3p¹) → Forms Al³⁺.
d. The sulfate of aluminium is formed by combining Al³⁺ and SO₄²⁻ ions. To balance charges:
2(Al³⁺) = +6, 3(SO₄²⁻) = −6
→ Formula: Al2(SO4)3
Question 12
Silver reacts with fluorine to form silver fluoride, AgF. Silver fluoride has a high melting point and has a simple cubic structure similar to that of sodium chloride.
a. Explain why the formula, AgF, is an empirical formula.
b. State the equation showing the synthesis of silver fluoride from its elements.
c. State the type of reaction involved.
d. State and describe the type of bonding involved in silver fluoride.
e. State four properties typical of compounds with this type of bonding.
f. Draw a diagram to show how the particles are arranged in a silver fluoride lattice and show the charges on the particles.
g. Silver fluoride is insoluble in organic solvents, but lithium bromide shows significant solubility in organic solvents. Suggest a reason for this behaviour of lithium bromide.
a. AgF is an empirical formula because ionic solids are represented by the simplest whole-number ratio of ions (no discrete molecules) - here Ag⁺:F⁻ = 1:1.
b. Balanced equation: 2Ag(s) + F₂(g) → 2AgF(s)
c. Combination (synthesis) reaction; also redox (Ag 0 → +1, F 0 → –1)
d. Ionic bonding: a giant lattice of Ag⁺ and F⁻ held by electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
e. Any four typical ionic properties:
• High melting/boiling point.
• Brittle crystalline solid.
• Does not conduct electricity as a solid but does conduct when molten or in aqueous solution.
• Generally soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents.
f. Rock-salt (NaCl-type) lattice: ions alternate in 3D; each Ag⁺ is surrounded by six F⁻ and each F⁻ by six Ag⁺.
Show charges Ag⁺ and F⁻ on the spheres in the diagram.
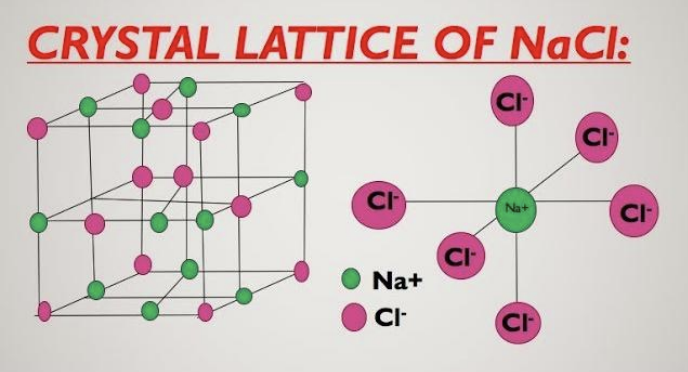
g. Lithium bromide dissolves in organic solvents because it has significant covalent character (Fajans’ rules): Li⁺ is small and strongly polarizing, and Br⁻ is large and highly polarizable → more covalent, hence more soluble in non-polar/organic media. AgF is comparatively more ionic (hard F⁻ with Ag⁺), so it remains insoluble in organic solvents.
Question 13
Which compound has the largest value of lattice enthalpy?
A. Al2O3.
B. MgS.
C. NaF.
D. MgO.
Answer: A. Al2O3.
Compare each compound:
| Compound | Ions | Charges | Ionic radius trend | Expected lattice enthalpy |
| NaF | Na⁺, F⁻ | +1/−1 | relatively large | small |
| MgS | Mg²⁺, S²⁻ | +2/−2 | moderate | large |
| MgO | Mg²⁺, O²⁻ | +2/−2 | smaller ions than S²⁻ | very large |
| Al₂O₃ | Al³⁺, O²⁻ | +3/−2 | high charges, small ions | largest |
Al³⁺ and O²⁻ have high charges and small radii, leading to very strong electrostatic attraction.
⇒ Al₂O₃ has the largest (most positive) lattice enthalpy among the options.
Question 14
Halogens react readily with lead to form lead halides.
The melting points of some of the lead halides are given in the table below.
| Compound | Melting point / °C |
| PbF₂ | 824 |
| PbCl₂ | 501 |
| PbBr₂ | 373 |
| PbCl₄ | –15 |
a. Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why the melting points of the lead(II) halides decrease from lead(II) fluoride to lead(II) bromide.
b. Explain why PbCl4 is a covalent compound and account for its low melting point.
a. PbF₂, PbCl₂ are ionic lattices. Down Group 17 the anion radius increases (F⁻ < Cl⁻), so the distance between ions increases and the lattice enthalpy decreases. Weaker electrostatic attraction ⇒ Lower melting point, hence PbF₂ > PbCl₂.
b. In PbCl₄ lead is Pb⁴⁺, a very small, highly charged cation that strongly polarizes Cl⁻ (Fajans’ rules), giving covalent Pb–Cl bonds. PbCl₄ therefore consists of discrete molecular units (tetrachloride) held together only by weak intermolecular forces, so it has a very low melting point (–15 °C).
Question 15
Which element forms more than one stable cation?
A. Ca.
B. Mn.
C. Zn.
D. Al.
Answer: B. Mn.
A. Incorrect: only Ca²⁺
B. Correct: Forms multiple stable cations: Mn²⁺, Mn³⁺, Mn⁴⁺, Mn⁶⁺, Mn⁷⁺, etc.
C. Incorrect: only Zn²⁺
D. Incorrect: only Al³⁺
Question 1
Which is the best description of ionic bonding?
A. Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
B. Electrostatic attraction between positive ions and electrons.
C. Electrostatic attraction of nuclei towards shared electrons in the bond between the nuclei.
D. Electrostatic attraction between nuclei.
Question 2
Which statement best describes the lattice structure of solid sodium chloride?
A. Each sodium ion is surrounded by one chloride ion.
B. Each chloride ion is surrounded by two sodium ions.
C. Each chloride ion is surrounded by four sodium ions.
D. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions.
Question 3
Which compounds have an ionic lattice structure in the solid state?
I. Silicon dioxide
II. Sodium fluoride
III. Ammonium nitrate
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 4
A group 1 element, X, bonds with a group 17 element, Y. What is the most likely formula and type of bonding in this compound?
A. X2Y ionic.
B. XY ionic.
C. XY7 covalent.
D. XY covalent.
Question 5
What is the formula for the ionic compound formed when barium reacts with nitrogen?
A. BaN.
B. Ba2N.
C. Ba3N2.
D. Ba2N3.
Question 6
The diagram shows the arrangement of the ions in an ionic crystal.

Which compound cannot have this lattice?
A. Magnesium oxide.
B. Calcium chloride.
C. Iron(II) sulfate.
D. Lithium chloride.
Question 7
The formula for samarium(III) chloride is SmCl3. What is the formula for samarium(III) sulfate(VI)?
A. Sm2(SO4)3.
B. Sm(SO4)3.
C. Sm3(SO4)2.
D. Sm2SO4.
Question 8
What are the correct formulas of the following ions?
| Nitrate | Sulfate | Phosphate | Hydrogencarbonate | |
| A. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| B. | NO₃⁻ | SO₄²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
| C. | NO₂⁻ | SO₄⁻ | PO₄³⁻ | HCO₃⁻ |
| D. | NO₂⁻ | SO₃²⁻ | PO₃³⁻ | HCO₃²⁻ |
Question 9
Which statement is a correct description of electron loss in this redox reaction?
2Al + 3Se → Al2Se3
A. Each aluminium atom loses two valence electrons.
B. Each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons.
C. Each selenium atom loses two valence electrons.
D. Each selenium atom loses three valence electrons.
Question 10
Which of the following ionic compounds is expected to have the most positive value of lattice enthalpy?
A. NaF.
B. NaBr.
C. LiI.
D. LiF.
Question 11
Magnesium sulfate is used as an electrolyte to treat brain injury patients in hospitals.
Magnesium sulfate contains both covalent bonds and ionic bonding.
a. State the formulas of the ions present and the nature of the force operating between the oppositely charged ions.
b. State which atoms are covalently bonded.
c. A metal atom has the electron configuration of 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹. Identify element and predict the charge on the cation.
d. Deduce the formula of its sulfate which finds use as a blood coagulant.
Question 12
Silver reacts with fluorine to form silver fluoride, AgF. Silver fluoride has a high melting point and has a simple cubic structure similar to that of sodium chloride.
a. Explain why the formula, AgF, is an empirical formula.
b. State the equation showing the synthesis of silver fluoride from its elements.
c. State the type of reaction involved.
d. State and describe the type of bonding involved in silver fluoride.
e. State four properties typical of compounds with this type of bonding.
f. Draw a diagram to show how the particles are arranged in a silver fluoride lattice and show the charges on the particles.
g. Silver fluoride is insoluble in organic solvents, but lithium bromide shows significant solubility in organic solvents. Suggest a reason for this behaviour of lithium bromide.
Question 13
Which compound has the largest value of lattice enthalpy?
A. Al2O3.
B. MgS.
C. NaF.
D. MgO.
Question 14
Halogens react readily with lead to form lead halides.
The melting points of some of the lead halides are given in the table below.
| Compound | Melting point / °C |
| PbF₂ | 824 |
| PbCl₂ | 501 |
| PbBr₂ | 373 |
| PbCl₄ | –15 |
a. Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why the melting points of the lead(II) halides decrease from lead(II) fluoride to lead(II) bromide.
b. Explain why PbCl4 is a covalent compound and account for its low melting point.
Question 15
Which element forms more than one stable cation?
A. Ca.
B. Mn.
C. Zn.
D. Al.