Question 1
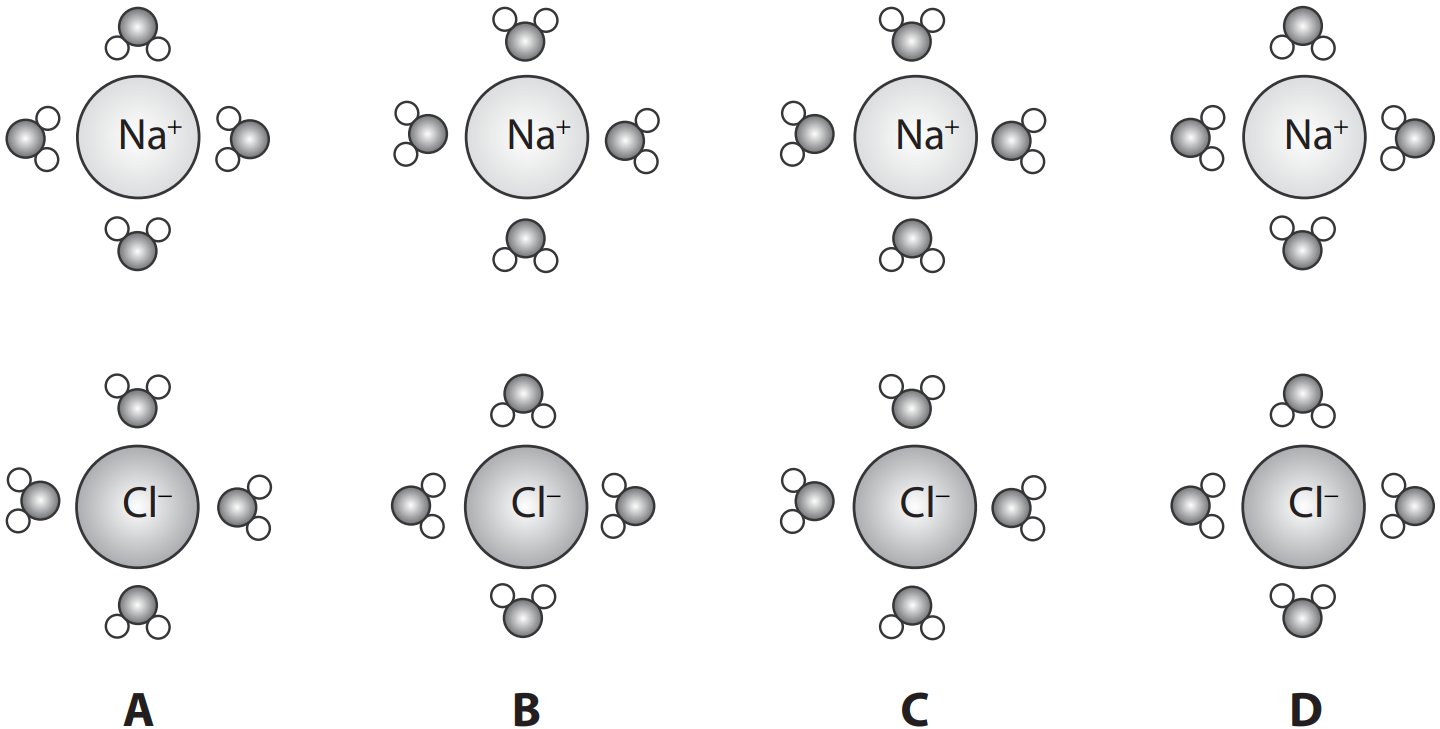
Which diagram best represents the arrangement of water molecules around sodium (`Na^+`) and chloride (`Cl^−`) ions in solution?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which properties of water reduce temperature changes inside cells?
1. cohesion
2. latent heat of vaporisation
3. specific heat capacity
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
When a lake begins to freeze, which properties of water are needed for fish to survive?
1. Water has a high surface tension.
2. Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation.
3. Water has a high thermal capacity.
4. Water has its maximum density at 4°C.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| A. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| B. | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| C. | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D. | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
Key:
✓ = needed
✗ = not needed
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Polar molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other. Which properties of water result from its molecules being polar?
1. good solvent
2. high specific heat capacity
3. high surface tension
4. cohesive
A. 1, 2, 3 and 4
B. 1, 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 3 and 4 only
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
a. Water has many significant roles to play in cells and living organisms. Complete Table 1 below by stating the property of water that allows each of the following to take place.
| role of water | property of water |
| solvent for glucose and ions | |
| movement in xylem | |
| helps to decrease body temperature in mammals |
b. The table below includes statements about the roles of water
• in living organisms
• as an environment for living organisms.
Complete the table by indicating with a tick (✓) which one of the properties of water is responsible for each role. You should put only one tick in each row.
| roles of water | properties of water | |||
| high specific heat capacity | strong cohesive forces between water molecules | high heat of vaporisation | solvent for polar molecules and ions | |
| transport medium in blood plasma and phloem | ||||
| surface for small insects to walk on | ||||
| major component of sweat used in heat loss | ||||
| transpiration pull in xylem | ||||
| preventing wide variations in body temperature |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Distinguish between ionic and covalent bonding.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
State the property of water that allows each of the following (a, b and c) to take place. Explain the importance of a, b and c:
a. The cooling of skin during sweating
b. The transport of glucose and ions in a mammal
c. Much smaller temperature fluctuations in lakes and oceans than in terrestrial (land-based) habitats.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Water has a relative molecular mass of only 18 yet it is a liquid at room temperature. This contrasts with other small molecules which are gases. (For example, methane (`"CH"_4`) with a relative molecular mass of 16; ammonia (`"NH"_3`) with a relative molecular mass of 17 and carbon dioxide (`"CO"_2`) with a relative molecular mass of 44.)
What property of water molecules may account for this?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Water is one of the most important biochemicals to organisms as, despite its simple structure, it has many important functions.
a. Describe how the structure of water results in high latent heat of vapourisation.
b. Suggest how sweating helps to lower body temperature.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
a. The angle between the oxygen–hydrogen bonds in water is about 1508. By means of a fully annotated diagram only, explain why the existence of this angle causes the water molecule to be polar (although overall it is electrically neutral).
b. Outline four of the unusual properties of water that can be ascribed to the effect of hydrogen bonds and summarise the significance of each for living things.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which diagram best represents the arrangement of water molecules around sodium (`Na^+`) and chloride (`Cl^−`) ions in solution?

Answer: B
A water molecule (H₂O) is made of one oxygen atom joined to two hydrogen atoms by shared electrons. Because the shared negative hydrogen electrons are pulled towards the oxygen atom, the oxygen atom has a slight negative charge (δ⁻), and the hydrogen atoms have a slight positive charge (δ⁺). This unequal distribution of charge makes water a polar molecule, or a dipole.
Water is a powerful solvent for polar substances, including ionic substances like sodium chloride (Na⁺ and Cl⁻). As water is polar, the slightly negatively charged end of a water molecule (oxygen) will be attracted to the positive ion (Na⁺). Similarly, the slightly positively charged end of a water molecule (hydrogen) will be attracted to the negative ion (Cl⁻). This attraction causes the ions to get totally surrounded by water molecules, allowing them to dissolve.
Only option B accurately represents this arrangement, showing the oxygen atoms (δ⁻) of the water molecules facing inwards towards the positive Na⁺ ion, and the hydrogen atoms (δ⁺) of the water molecules facing inwards towards the negative Cl⁻ ion.
Question 2
Which properties of water reduce temperature changes inside cells?
1. cohesion
2. latent heat of vaporisation
3. specific heat capacity
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only
Answer: D
Water possesses several unique properties that are essential for life, particularly in mitigating temperature fluctuations within living organisms and their cells.
Specific heat capacity is the primary property of water that directly reduces temperature changes inside cells. Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it requires a relatively large amount of energy to raise its temperature. This property is attributed to the many hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules, which restrict their movement and thus require significant thermal energy to break. As organisms, and the cells from which they are made, are largely
composed of water, this high specific heat capacity provides thermal cushioning, enabling them to absorb or lose a great deal of heat energy without their temperature changing very much. This helps maintain a stable internal temperature, which is crucial for optimal enzyme activity and overall biological reactions.
While other properties are also important for temperature regulation in organisms:
Water also has a high latent heat of vaporisation, meaning a large amount of energy is absorbed when it changes from a liquid to a gas. This property is vital for cooling organisms through processes like sweating in animals and transpiration in plants, as the evaporating water carries away excess heat from the body's surface. This process actively reduces temperature, especially preventing overheating, thereby reducing temperature changes.
Cohesion refers to the attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding. This property allows water to form droplets, creates surface tension, and enables the continuous transport of water in plants. However, it is not directly responsible for reducing temperature changes within cells in the same way as specific heat capacity or latent heat of vaporization.
Therefore, the property most directly responsible for reducing temperature changes inside cells by allowing the water content to resist temperature shifts is its high specific heat capacity.
Question 3
When a lake begins to freeze, which properties of water are needed for fish to survive?
1. Water has a high surface tension.
2. Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation.
3. Water has a high thermal capacity.
4. Water has its maximum density at 4°C.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| A. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| B. | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| C. | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D. | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
Key:
✓ = needed
✗ = not needed
Answer: D
When a lake begins to freeze, several unique properties of water play crucial roles in the survival of fish.
Surface tension is a property of water caused by cohesive forces (hydrogen bonds) between water molecules, especially at the surface where water meets the air. This allows some small organisms, such as pond skaters, to walk or rest on the water's surface. However, this property is primarily relevant for organisms that live on the surface and is not directly needed for the survival of fish that live below the surface when a lake freezes. Hence, high surface tension is not needed (✗) for fish survival.
Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation, meaning it requires a significant amount of energy for it to change from a liquid to a gas (evaporate). This property is primarily important for cooling organisms through processes like sweating in animals or transpiration in plants, as the evaporating water carries away excess heat. While the strong hydrogen bonds that cause high latent heat of vaporisation also contribute to water's general resistance to phase changes, the property most directly relevant to preventing a lake from freezing is the high latent heat of fusion (the energy required to change from liquid to solid). In the context of "a lake begins to freeze" and fish survival within the lake, latent heat of vaporisation (evaporation) is not the most direct or primary property that ensures their survival. Hence, high latent heat of vaporisation is not needed (✗) for fish survival.
Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it requires a relatively large amount of energy to change its temperature. This property is crucial because it allows large bodies of water, like lakes, to absorb or release significant amounts of heat energy without their temperature changing drastically. This provides a thermally stable habitat for aquatic organisms, including fish, preventing rapid temperature fluctuations that would be detrimental to their survival. Therefore, high specific heat capacity is needed (✓) for fish survival.
Unlike most substances, water reaches its maximum density at 4°C. As water cools further below 4°C and freezes, it becomes less dense and forms a hexagonal open structure, causing ice to float on the surface. This floating layer of ice acts as an insulating barrier, protecting the liquid water below from freezing solid and allowing aquatic plants and animals, such as fish, to survive in the slightly warmer water beneath the ice. Therefore, water having its maximum density at 4°C is needed (✓) for fish survival.
Question 4
Polar molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other. Which properties of water result from its molecules being polar?
1. good solvent
2. high specific heat capacity
3. high surface tension
4. cohesive
A. 1, 2, 3 and 4
B. 1, 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 3 and 4 only
Answer: A
Water's unique properties, essential for life, largely stem from its polar nature and the resulting ability to form hydrogen bonds between its molecules. All four listed properties are properties of water that result from its molecules being polar and forming hydrogen bonds.
Water is a good solvent because its polar nature allows it to surround other charged or polar molecules, preventing them from clumping together. Positively charged ions are surrounded by the negative ends of water molecules, while negatively charged ions are surrounded by the positive ends. The formation of intermolecular bonds, including hydrogen bonds, between water and ions keeps them in solution.
Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it requires a relatively large amount of energy to raise its temperature. This property is a direct consequence of the many hydrogen bonds that must be broken to increase the water molecules' movement and thus its temperature. Water's polarity is the basis for these hydrogen bonds.
Water exhibits high surface tension because, at the surface where water meets the air, there is a greater attraction (due to hydrogen bonds) between water molecules than to air particles. This strong attraction forms a "strong surface" that can support some small organisms. This property is an emergent property resulting from the interactions of water's polar molecules.
Water is cohesive because hydrogen bonds form between its molecules, holding them together. This cohesion allows water to travel in continuous columns, such as in the xylem of plants. This property is a direct result of water's polarity.
Question 5
a. Water has many significant roles to play in cells and living organisms. Complete Table 1 below by stating the property of water that allows each of the following to take place.
| role of water | property of water |
| solvent for glucose and ions | |
| movement in xylem | |
| helps to decrease body temperature in mammals |
b. The table below includes statements about the roles of water
• in living organisms
• as an environment for living organisms.
Complete the table by indicating with a tick (✓) which one of the properties of water is responsible for each role. You should put only one tick in each row.
| roles of water | properties of water | |||
| high specific heat capacity | strong cohesive forces between water molecules | high heat of vaporisation | solvent for polar molecules and ions | |
| transport medium in blood plasma and phloem | ||||
| surface for small insects to walk on | ||||
| major component of sweat used in heat loss | ||||
| transpiration pull in xylem | ||||
| preventing wide variations in body temperature |
a.
| role of water | property of water |
| solvent for glucose and ions | dipolar/polar |
| movement in xylem | hydrogen bonding |
| helps to decrease body temperature in mammals | high latent heat of vapourisation/ high specific heat (capacity)/ high enthalpy heat of vapourisation/ lots of energy required for evaporation |
b.
| roles of water | properties of water | |||
| high specific heat capacity | strong cohesive forces between water molecules | high heat of vaporisation | solvent for polar molecules and ions | |
| transport medium in blood plasma and phloem | ✓ | |||
| surface for small insects to walk on | ✓ | |||
| major component of sweat used in heat loss | ✓ | |||
| transpiration pull in xylem | ✓ | |||
| preventing wide variations in body temperature | ✓ |
Question 6
Distinguish between ionic and covalent bonding.
In ionic bonding, atoms gain or lose electrons to form positive or negative ions. An atom with a positive charge is called a cation, and an atom with a negative charge is called an anion. Ionic bonding transforms atoms into stable ions. Strong forces of attraction, called ionic bonds, hold these oppositely charged ions together.
In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between atoms. These are often described as strong bonds. For example, in a water molecule, two hydrogen atoms each share a pair of electrons with an oxygen atom, forming covalent bonds.
The key difference is that in ionic bonding, electrons are transferred to form charged ions that attract each other, whereas in covalent bonding, electrons are shared betweenatoms. This contrasts with the process of ionisation and ion formation seen in ionic bonding.
Question 7
State the property of water that allows each of the following (a, b and c) to take place. Explain the importance of a, b and c:
a. The cooling of skin during sweating
b. The transport of glucose and ions in a mammal
c. Much smaller temperature fluctuations in lakes and oceans than in terrestrial (land-based) habitats.
a. The cooling of skin during sweating
Property: high latent heat of vaporisation (as water requires a relatively large amount of heat energy to evaporate)
Explanation: Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation, meaning it requires a relatively large amount of energy to change from a liquid to a gas (evaporate). This is because many hydrogen bonds between water molecules must be broken for evaporation to occur, and breaking these bonds requires significant energy.
When the body overheats, the hypothalamus stimulates sweat glands to secrete sweat onto the skin's surface. This sweat (mainly water) absorbs a great deal of heat energy from the body, particularly from blood flowing close to the surface due to vasodilation of arterioles in the skin. As the water evaporates, it carries this excess heat away from the body, thereby cooling the skin and helping to prevent the body from overheating. This process is highly efficient as only a small volume of water is needed to dissipate a large amount of heat.
b. The transport of glucose and ions in a mammal
Property: good solvent
Explanation: Water's polar nature means it has a slightly negative oxygen end and slightly positive hydrogen ends. This polarity allows water molecules to form intermolecular bonds (hydrogen bonds or ion-dipole forces) with other charged or polar molecules, such as glucose and ions (like `"Na"^+` and `"Cl"^–`). Water molecules surround these solutes, preventing them from clumping together and thus keeping them in solution.
As the primary component (over 90%) of blood plasma, water acts as an excellent transport medium for these dissolved substances. Soluble solutes like glucose, amino acids, and various ions can be efficiently transported from the digestive system to other organs and cells of the body where they are needed for metabolism and function. This ensures that biochemical reactions can take place in an aqueous environment.
c. Much smaller temperature fluctuations in lakes and oceans than in terrestrial (land-based) habitats.
Property: high specific heat capacity
Explanation: Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it requires a large amount of heat energy to raise its temperature. This property results from the many hydrogen bonds between water molecules that restrict their movement; a significant amount of thermal energy is needed to break these bonds to increase the water's temperature.
Consequently, large bodies of water like lakes and oceans can absorb or release a great deal of heat without their temperature changing drastically. This provides a thermally stable habitat for aquatic organisms. A stable temperature is crucial for living things because biological reactions, including enzyme activity, occur efficiently only within a narrow range of temperatures. This thermal cushioning protects aquatic organisms from extreme temperature fluctuations that would be detrimental to their survival and metabolism.
Question 8
Water has a relative molecular mass of only 18 yet it is a liquid at room temperature. This contrasts with other small molecules which are gases. (For example, methane (`"CH"_4`) with a relative molecular mass of 16; ammonia (`"NH"_3`) with a relative molecular mass of 17 and carbon dioxide (`"CO"_2`) with a relative molecular mass of 44.)
What property of water molecules may account for this?
Water (`"H"_2"O"`), despite having a relative molecular mass of only 18, is a liquid at room temperature, which contrasts with other small molecules like methane (`"CH"_4`, relative molecular mass 16), ammonia (`"NH"_3`, relative molecular mass 17), and carbon dioxide (`"CO"_2`, relative molecular mass 44), which are gases. This unique property of water is primarily due to its polarity and the resulting ability to form hydrogen bonds.
In gases, molecules are widely spaced and free to move about independently. In liquids, molecules are closer together. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds pull the molecules very close to each other, which is why water is a liquid at the temperatures and pressure that exists over much of the Earth’s surface. As a result, we have a liquid medium which life exploits.
This property of water is crucial for life, as it provides a liquid medium for living things and for the vast array of chemical reactions (metabolism) that occur within cells and organisms.
Question 9
Water is one of the most important biochemicals to organisms as, despite its simple structure, it has many important functions.
a. Describe how the structure of water results in high latent heat of vapourisation.
b. Suggest how sweating helps to lower body temperature.
a.
Water molecules are polar, with a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charges on hydrogens, due to unequal sharing of electrons in covalent bonds. This polarity causes hydrogen bonds to form between water molecules, which are relatively strong intermolecular forces. Many hydrogen bonds must be broken for water molecules to evaporate (change from liquid to gas).
Because breaking these hydrogen bonds requires a large amount of energy, water has a high latent heat of vaporisation—it absorbs a lot of heat before evaporating. This property helps water absorb heat energy without a large temperature increase.
b. Sweat is mostly water; when it evaporates from the skin, it absorbs a large amount of heat energy from the body to break hydrogen bonds (due to water’s high latent heat of vaporisation). This removes heat from the skin, cooling the body down. Sweating is therefore an effective cooling mechanism that helps maintain a stable internal temperature.
Question 10
a. The angle between the oxygen–hydrogen bonds in water is about 1508. By means of a fully annotated diagram only, explain why the existence of this angle causes the water molecule to be polar (although overall it is electrically neutral).
b. Outline four of the unusual properties of water that can be ascribed to the effect of hydrogen bonds and summarise the significance of each for living things.
a.
Water has a bent shape with an angle of about 104.5° between the hydrogen atoms. Oxygen is more electronegative, pulling electrons toward itself, giving it a partial negative charge (`δ^–`) and the hydrogens partial positive charges (`δ^+`). Because of the bent shape, these charges do not cancel out, making water a polar molecule with distinct positive and negative poles, though overall electrically neutral.
b.
| Property | Explanation | Significance for living things |
| High latent heat of vaporisation | A large amount of energy is required to break the numerous hydrogen bonds that hold water molecules together for water to change from a liquid to a gas (evaporate). | This property allows water to act as an effective coolant. For instance, when sweat (primarily water) evaporates from the skin of mammals, it absorbs a large amount of heat energy from the body, thereby cooling it down and preventing overheating. In plants, transpiration similarly dissipates heat. |
| High specific heat capacity | Water has a high specific heat capacity because a large amount of energy is needed to break the many hydrogen bonds to increase its temperature. This means water can absorb or give out a great deal of heat energy without its temperature changing significantly. | This property allows water to resist changes in temperature, providing a thermally stable environment. This is vital for aquatic organisms, which experience much smaller temperature fluctuations than those in terrestrial habitats. It also helps organisms, which are largely composed of water, to maintain a constant internal body temperature (homeostasis), as stable temperatures are crucial for enzyme function. |
| Cohesion | Water molecules are strongly attracted to each other due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between them. This strong attraction allows water to form droplets and is responsible for its high surface tension. |
|
| Solvent properties | Water is known as a "universal solvent" due to its polar nature. It can interact with and surround other charged (ionic) molecules (like Na+ and Cl–) and polar organic molecules (like glucose and amino acids) by forming hydrogen bonds or ion-dipole forces, preventing them from clumping together and allowing them to dissolve. | Water acts as an excellent transport medium. Most biochemical reactions (metabolism) take place in an aqueous (water) solution. This enables efficient transport of vital substances like glucose, amino acids, and ions in bodily fluids such as blood plasma in animals and sap in plants. |
Question 1
Which diagram best represents the arrangement of water molecules around sodium (`Na^+`) and chloride (`Cl^−`) ions in solution?

Question 2
Which properties of water reduce temperature changes inside cells?
1. cohesion
2. latent heat of vaporisation
3. specific heat capacity
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only
Question 3
When a lake begins to freeze, which properties of water are needed for fish to survive?
1. Water has a high surface tension.
2. Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation.
3. Water has a high thermal capacity.
4. Water has its maximum density at 4°C.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| A. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| B. | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| C. | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D. | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
Key:
✓ = needed
✗ = not needed
Question 4
Polar molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other. Which properties of water result from its molecules being polar?
1. good solvent
2. high specific heat capacity
3. high surface tension
4. cohesive
A. 1, 2, 3 and 4
B. 1, 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 3 and 4 only
Question 5
a. Water has many significant roles to play in cells and living organisms. Complete Table 1 below by stating the property of water that allows each of the following to take place.
| role of water | property of water |
| solvent for glucose and ions | |
| movement in xylem | |
| helps to decrease body temperature in mammals |
b. The table below includes statements about the roles of water
• in living organisms
• as an environment for living organisms.
Complete the table by indicating with a tick (✓) which one of the properties of water is responsible for each role. You should put only one tick in each row.
| roles of water | properties of water | |||
| high specific heat capacity | strong cohesive forces between water molecules | high heat of vaporisation | solvent for polar molecules and ions | |
| transport medium in blood plasma and phloem | ||||
| surface for small insects to walk on | ||||
| major component of sweat used in heat loss | ||||
| transpiration pull in xylem | ||||
| preventing wide variations in body temperature |
Question 6
Distinguish between ionic and covalent bonding.
Question 7
State the property of water that allows each of the following (a, b and c) to take place. Explain the importance of a, b and c:
a. The cooling of skin during sweating
b. The transport of glucose and ions in a mammal
c. Much smaller temperature fluctuations in lakes and oceans than in terrestrial (land-based) habitats.
Question 8
Water has a relative molecular mass of only 18 yet it is a liquid at room temperature. This contrasts with other small molecules which are gases. (For example, methane (`"CH"_4`) with a relative molecular mass of 16; ammonia (`"NH"_3`) with a relative molecular mass of 17 and carbon dioxide (`"CO"_2`) with a relative molecular mass of 44.)
What property of water molecules may account for this?
Question 9
Water is one of the most important biochemicals to organisms as, despite its simple structure, it has many important functions.
a. Describe how the structure of water results in high latent heat of vapourisation.
b. Suggest how sweating helps to lower body temperature.
Question 10
a. The angle between the oxygen–hydrogen bonds in water is about 1508. By means of a fully annotated diagram only, explain why the existence of this angle causes the water molecule to be polar (although overall it is electrically neutral).
b. Outline four of the unusual properties of water that can be ascribed to the effect of hydrogen bonds and summarise the significance of each for living things.