Question 1
Which term describes both collagen and haemoglobin?
A. macromolecules
B. enzymes
C. fibrous proteins
D. globular proteins
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What type of chemical reaction is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds?
A. condensation
B. hydrolysis
C. oxidation
D. reduction
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The diagram shows the structure of four amino acids in solution.
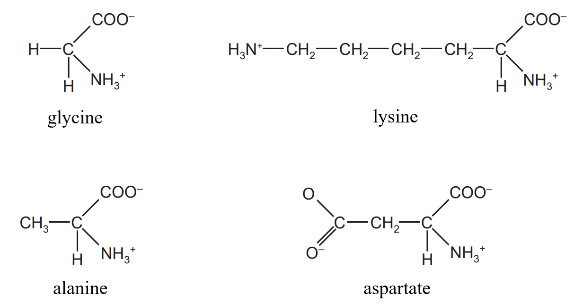
Which amino acids have no overall charge?
A. alanine and aspartate
B. alanine and glycine
C. aspartate and lysine
D. glycine and lysine
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Sketch the general structure of an amino acid.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
X and Y represent two different amino acids.
a. Write down the sequences of all the possible tripeptides that could be made with just these two amino acids.
b. From your answer to a, what is the formula for calculating the number of different tripeptides that can be formed from two different amino acids?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Explain why polysaccharides and proteins are described as macromolecules but lipids are not.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
a. Describe the structure of a collagen molecule.
b. Describe how the arrangement of collagen molecules in a collagen fibre relates to its function
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
a. Copy and complete the table to summarise some differences between collagen and haemoglobin.
| Collagen | Haemoglobin | |
| Globular or fibrous? | ||
| Entirely or partly helical? | ||
| Type of helix | ||
| Prosthetic group present? | ||
| Soluble in water? |
b. State one way in which the structure of haemoglobin is related to its function.
c. Haemoglobin possesses a quaternary structure. What does this mean?
d. Name the five elements found in haemoglobin.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
The p53 gene is a tumour suppressor gene. The gene codes for the p53 protein which binds to other cellular proteins to regulate cell division. Tumour cells often contain mutated p53 protein where an amino acid called arginine is replaced by a different amino acid called proline. The figure below shows the structures of arginine and proline.
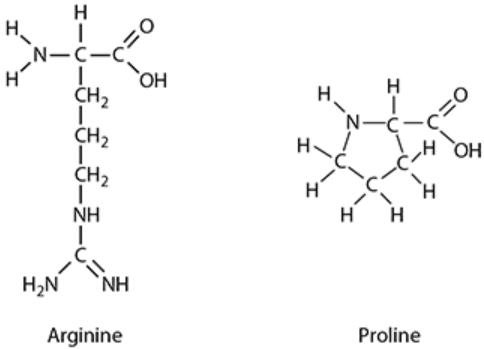
Arginine is a hydrophilic amino acid that has a net positive charge. Proline is a hydrophobic uncharged amino acid.
a. Draw the R-group of arginine.
b. Using the example above, explain how changing the primary sequence of a polypeptide could affect its function.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
The primary structure of a protein is the unique sequence of amino acids, which determines the location of the bonds in the tertiary structure.
a. How many different naturally occurring amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
b. What are the four bonds that help to keep proteins folded in the tertiary structure?
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which term describes both collagen and haemoglobin?
A. macromolecules
B. enzymes
C. fibrous proteins
D. globular proteins
Answer: A
A. Correct: Both proteins and polysaccharides are described as macromolecules. A macromolecule is a giant molecule, often described as a polymer made from many similar repeating subunits called monomers. Proteins are polymers made from amino acids. Both collagen and haemoglobin are proteins, and therefore both are macromolecules.
B. Incorrect: Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. While enzymes are globular proteins, neither collagen nor haemoglobin is primarily described as functioning as an enzyme. Proteins have various functions, including enzymes, hormones, transport proteins, and structural proteins. Haemoglobin transports oxygen, and collagen provides structural support. They are not primarily enzymes.
C. Incorrect: Fibrous proteins are generally insoluble and have structural roles. Collagen is an example of a fibrous protein. However, haemoglobin is not a fibrous protein.
D. Globular proteins fold into a roughly spherical shape, are generally soluble, and often have physiological roles. Haemoglobin is an example of a globular protein. However, collagen is not a globular protein.
Question 2
What type of chemical reaction is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds?
A. condensation
B. hydrolysis
C. oxidation
D. reduction
Answer: C
The type of chemical reaction involved in the formation of disulfide bonds is oxidation.
Disulfide bonds are strong covalent bonds that form between two cysteine amino acid molecules (as this is the only amino acid with an available sulphur atom in its side chain, specifically in –SH groups).
The formation of a disulfide bond is a process involving the loss of hydrogen atoms or electrons, which is oxidation.
Conversely, the breakage of a disulfide bond is a reduction reaction (where a molecule gains electrons), involving the addition of hydrogen.
Question 3
The diagram shows the structure of four amino acids in solution.

Which amino acids have no overall charge?
A. alanine and aspartate
B. alanine and glycine
C. aspartate and lysine
D. glycine and lysine
Answer: B
Each amino acid has a carboxyl group (–COOH → deprotonated as –COO⁻ in solution → –1 charge), an amino group (`"–NH"_2` → protonated as `"–NH3"^+` in solution → +1 charge), and a side chain (R group) that may be neutral, positive, or negative depending on the amino acid
Glycine has a simple hydrogen atom as its R group. This is a neutral R group, and Glycine is considered a neutral amino acid with no overall charge in solution (`"NH3"^+` = +1, `"COO"^–` = –1 → Net charge = 0).
Alanine has a methyl (`"–CH"_3`) group as its R group. This is also a neutral R group, and Alanine is considered a neutral amino acid with no overall charge in solution (`"NH"_3^+` = +1, `"COO"^–` = –1 → Net charge = 0).
Aspartate (derived from aspartic acid) has an acidic R group containing an extra carboxyl group. This additional carboxyl group can lose a proton, resulting in an extra negative charge. Thus, Aspartate
typically carries a net negative charge in solution (NH3+ = +1, two COO– = –2 → Net charge = –1).
Lysine has a basic R group containing an extra amino group. This additional amino group can gain a proton, resulting in an extra positive charge. Thus, Lysine typically carries a net positive charge in solution. Basic amino acids like Lysine have a net positive charge in solution (two `"NH"_3^+` = +2, `"COO"^–` = –1 → Net charge = +1).
So only B (alanine and glycine) is incorrect.
Question 4
Sketch the general structure of an amino acid.
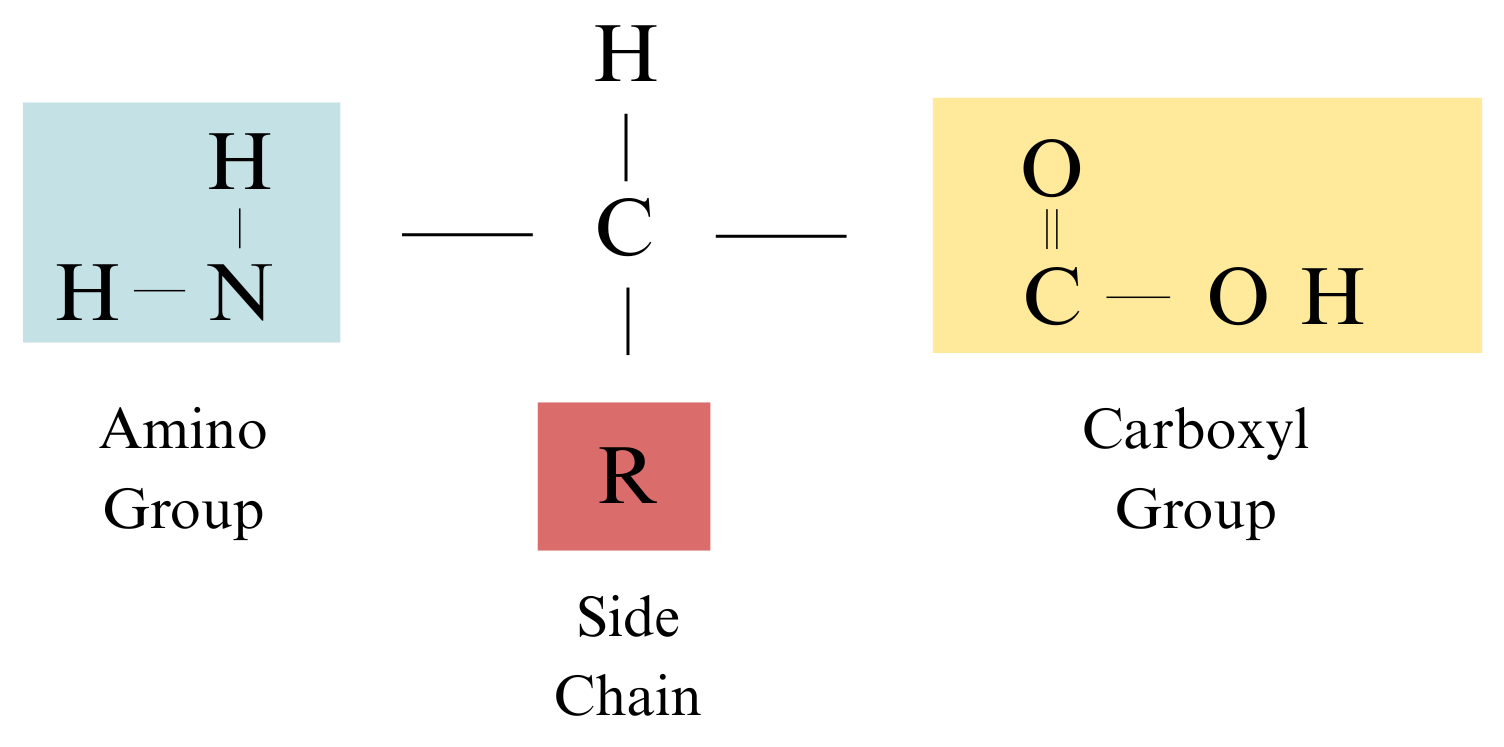
Question 5
X and Y represent two different amino acids.
a. Write down the sequences of all the possible tripeptides that could be made with just these two amino acids.
b. From your answer to a, what is the formula for calculating the number of different tripeptides that can be formed from two different amino acids?
a. The possible tripeptides that can be formed using only two different amino acids (X and Y) are XXX, XXY, XYY, XYX, YYY, YYX, YXX, YXY.
b. The formula for calculating the number of different tripeptides that can be formed from two different amino acids is `2^3`.
More generally, the possible number of different polypeptides (P) that can be assembled is given by the formula `P=A^n`. In this formula:
Therefore, for tripeptides made from two different amino acids, the calculation is `2^3=8` possible tripeptides.
Question 6
Explain why polysaccharides and proteins are described as macromolecules but lipids are not.
Macromolecules are "giant molecules", which are very large, complex molecules typically formed from vast numbers of repeating smaller molecules joined together as polymers.
Polysaccharides (like cellulose) and proteins (like lysozyme) are considered macromolecules because they fit this description. Polysaccharides are polymers made up of vast numbers of repeating smaller molecules called monosaccharides (such as glucose). They are formed from very many monosaccharide molecules condensed together. Proteins are also polymers formed from many amino acids combined in a long chain. Sources note that typically hundreds or even thousands of amino acid molecules are combined to make a protein.
Lipids, on the other hand, although important biological molecules, are generally not described as macromolecules in the same way. While they are composed of components like glycerol and fatty acids, molecules such as triglycerides are relatively much smaller molecules compared to the giant polymeric structures of polysaccharides and proteins. They are not structured as long chains of repeating monomers in the same sense as polymers like polysaccharides and proteins.
Although lipids are hydrophobic and may clump together and give the appearance of being huge molecules, this clumping is due to their properties and behavior in water (e.g., forming insoluble droplets or bilayers) and is not because they are single, giant polymeric molecules themselves. Therefore, the definition of macromolecule based on being a very large polymer of numerous repeating units applies to polysaccharides and proteins but not typically to lipids.
Question 7
a. Describe the structure of a collagen molecule.
b. Describe how the arrangement of collagen molecules in a collagen fibre relates to its function
a. A collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains. Each chain forms a helix, but it is not a typical alpha-helix; instead, the three helices twist around each other forming a triple helix (like a three-stranded rope). The three chains are held together by many hydrogen bonds and some covalent bonds. Glycine, the smallest amino acid, appears at every third position in the chains, allowing the helices to pack tightly together. Other amino acids like proline and hydroxyproline contribute to the molecule’s stability.
b. Many collagen triple helices align side-by-side in parallel to form fibrils. These fibrils are linked by covalent cross-links between amino acid side chains, which greatly increase the strength of the fibre. The collagen molecules within fibrils are arranged in a staggered pattern, preventing weak points along the fibre. Multiple fibrils bundle together to form collagen fibres, which provide high tensile strength and structural support. This arrangement allows collagen fibres to resist stretching and tearing forces, making them essential in tissues like skin, tendons, cartilage, bone, and blood vessel walls. The fibres’ insolubility and layered structure also contribute to their durability and function in maintaining tissue integrity.
Question 8
a. Copy and complete the table to summarise some differences between collagen and haemoglobin.
| Collagen | Haemoglobin | |
| Globular or fibrous? | ||
| Entirely or partly helical? | ||
| Type of helix | ||
| Prosthetic group present? | ||
| Soluble in water? |
b. State one way in which the structure of haemoglobin is related to its function.
c. Haemoglobin possesses a quaternary structure. What does this mean?
d. Name the five elements found in haemoglobin.
a.
| Collagen | Haemoglobin | |
| Globular or fibrous? | fibrous | globular |
| Entirely or partly helical? | entirely | partly |
| Type of helix | triple helix / extended helix / three-stranded | alpha |
| Prosthetic group present? | no | yes |
| Soluble in water? | no / insoluble | yes / soluble |
b. One way the structure of haemoglobin is related to its function is that each polypeptide chain has a haem group containing an iron ion (Fe2+); this iron ion is able to combine reversibly with oxygen, allowing haemoglobin to transport oxygen throughout the body.
c. Haemoglobin has a quaternary structure, which means it is made up of more than one polypeptide chain. Haemoglobin is a molecule has more than one polypeptide chain (consists of four polypeptide subunits) arranged together to form a functional protein complex. This quaternary arrangement allows the subunits to interact and work cooperatively, such as binding oxygen molecules more efficiently. In general, quaternary structure refers to the way multiple folded protein subunits are organized and held together in a multi-subunit protein complex, distinguishing it from proteins composed of a single polypeptide chain.
d. Five elements found in haemoglobin are:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, iron
Question 9
The p53 gene is a tumour suppressor gene. The gene codes for the p53 protein which binds to other cellular proteins to regulate cell division. Tumour cells often contain mutated p53 protein where an amino acid called arginine is replaced by a different amino acid called proline. The figure below shows the structures of arginine and proline.

Arginine is a hydrophilic amino acid that has a net positive charge. Proline is a hydrophobic uncharged amino acid.
a. Draw the R-group of arginine.
b. Using the example above, explain how changing the primary sequence of a polypeptide could affect its function.
a.
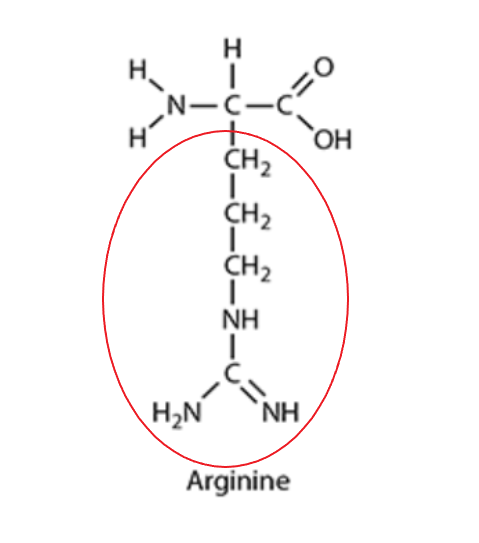
b. Arginine is described as a hydrophilic amino acid with a net positive charge. This means it would typically be found on the surface of a soluble protein, interacting with water molecules (hydrophilic) and forming ionic bonds with negatively charged R-groups.
Proline is described as a hydrophobic and uncharged amino acid. Hydrophobic R-groups tend to orient towards the interior of the protein molecule, shielding themselves from the watery environment, and forming hydrophobic interactions.
When arginine is replaced by proline:
The loss of the positive charge from arginine means that any ionic bonds it normally formed within the protein's structure would be lost.
The introduction of a hydrophobic proline in a position previously occupied by a hydrophilic arginine would likely disrupt the normal folding pattern. This new hydrophobic residue might try to orient itself towards the protein's interior, disturbing the existing arrangement of amino acids and breaking other crucial bonds that stabilize the tertiary structure.
The p53 protein normally binds to other cellular proteins to regulate cell division. If its tertiary structure is altered, the specific region responsible for binding to other proteins (its "active site" or binding interface) will likely change shape. This means the p53 protein would no longer be able to bind effectively with its target proteins or carry out its normal function.
Since p53 is a tumour suppressor gene, its normal function is to slow down cell division or cause damaged cells to self-destruct (apoptosis). A mutation that inactivates this gene, by changing its protein's structure and function, can lead to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of a tumour, which is characteristic of cancer.
Question 10
The primary structure of a protein is the unique sequence of amino acids, which determines the location of the bonds in the tertiary structure.
a. How many different naturally occurring amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
b. What are the four bonds that help to keep proteins folded in the tertiary structure?
a. Regarding the number of naturally occurring amino acids: All living things share a bank of only 20 amino acids. These 20 amino acids are the smaller units from which proteins are made. The twenty amino acids that are common in all organisms differ only in their R group (also known as a side group or variable side group).
b. The three-dimensional shape of a protein's tertiary structure is held in place by several types of bonds or interactions. The four main types of bonds that help to keep proteins folded in the tertiary structure are hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions:
Hydrogen bonds: These are relatively weak bonds that form between a hydrogen atom and other atoms like nitrogen or oxygen. In tertiary structure, they form between different parts of the polypeptide chain and between R groups. While also important in secondary structure, they are crucial for the overall 3D fold.
• Ionic bonds: These are attractions between negative and positive charges on different parts of the molecule. They form between charged R groups.
• Disulfide bonds: These are covalent bonds formed whenever two molecules of the amino acid cysteine come close together, bonding the sulfur atom in one cysteine to the sulfur atom in the other. They are considered strong covalent bonds. These bonds are important in maintaining protein structure.
• Hydrophobic interactions: These occur between non-polar R groups. Hydrophobic (water-repelling) groups tend to clump together in the interior of the protein when it's in a watery environment, affecting how the protein folds. These are sometimes mentioned alongside van der Waals forces and are described as weak interactions.
Question 1
Which term describes both collagen and haemoglobin?
A. macromolecules
B. enzymes
C. fibrous proteins
D. globular proteins
Question 2
What type of chemical reaction is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds?
A. condensation
B. hydrolysis
C. oxidation
D. reduction
Question 3
The diagram shows the structure of four amino acids in solution.

Which amino acids have no overall charge?
A. alanine and aspartate
B. alanine and glycine
C. aspartate and lysine
D. glycine and lysine
Question 4
Sketch the general structure of an amino acid.
Question 5
X and Y represent two different amino acids.
a. Write down the sequences of all the possible tripeptides that could be made with just these two amino acids.
b. From your answer to a, what is the formula for calculating the number of different tripeptides that can be formed from two different amino acids?
Question 6
Explain why polysaccharides and proteins are described as macromolecules but lipids are not.
Question 7
a. Describe the structure of a collagen molecule.
b. Describe how the arrangement of collagen molecules in a collagen fibre relates to its function
Question 8
a. Copy and complete the table to summarise some differences between collagen and haemoglobin.
| Collagen | Haemoglobin | |
| Globular or fibrous? | ||
| Entirely or partly helical? | ||
| Type of helix | ||
| Prosthetic group present? | ||
| Soluble in water? |
b. State one way in which the structure of haemoglobin is related to its function.
c. Haemoglobin possesses a quaternary structure. What does this mean?
d. Name the five elements found in haemoglobin.
Question 9
The p53 gene is a tumour suppressor gene. The gene codes for the p53 protein which binds to other cellular proteins to regulate cell division. Tumour cells often contain mutated p53 protein where an amino acid called arginine is replaced by a different amino acid called proline. The figure below shows the structures of arginine and proline.

Arginine is a hydrophilic amino acid that has a net positive charge. Proline is a hydrophobic uncharged amino acid.
a. Draw the R-group of arginine.
b. Using the example above, explain how changing the primary sequence of a polypeptide could affect its function.
Question 10
The primary structure of a protein is the unique sequence of amino acids, which determines the location of the bonds in the tertiary structure.
a. How many different naturally occurring amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
b. What are the four bonds that help to keep proteins folded in the tertiary structure?