Question 1
The value of quantity `X` has a percentage uncertainty of 2%.
The value of quantity `Y` has a percentage uncertainty of 4%.
The value of a quantity `W` is calculated from the values of `X` and `Y`.
What could be the relationship between `W`, `X` and `Y`?
A. `W=XY`
B. `W=2XY`
C. `W=X/Y^2`
D. `W=Y/X^2`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A solid bar has a square cross-section. Its length is measured as `50+-0.2 " cm"` and its width is measured as `20.0+-0.01 " cm"`
These values are used to calculate the volume of the bar.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the calculated volume?
A. ± 0.21%
B. ± 0.22%
C. ± 0.90%
D. ± 1.4%
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A physical quantity consists of a magnitude and a unit.
Which row does not show a correct combination of a quantity and its unit?
| Quantity | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| A | mass | gram |
| B | length | metre |
| C | charge | ampere |
| D | temperature | kelvin |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
What is the effect of a systematic error on the measurement of a physical quantity?
A. It limits the precision of the measured value.
B. It limits the range of values obtained in repeated measurements.
C. It results in repeated measurements having different values from each other.
D. It results in the measured value being different from the correct value.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Which quantity is a scalar quantity?
A. Force
B. Momentum
C. Velocity
D. Work
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The relationship between the variables `D` and `T` is given by the equation `1/T = b/sqrt(D) + c`
Where `b` and `C` are constants.
The unit of `D` is `"m"^2` and the unit of `T` is `"s"`.
What are the units of `b` and `c`?
| Unit of b | Unit of c | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `"m"."s"` | `"s"` |
| B | `"m"."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
| C | `"m"^-1."s"` | `"s"` |
| D | `"m"^-1."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
What represents a physical quantity?
A. 3.0
B. Kilogram
C. 7.0 N
D. 40%
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
A student estimates the maximum speed of some different moving objects.
Which maximum speed is not a reasonable estimate?
A. Container ship: `"10 m"."s"^-1`
B. Olympic sprinter: `"0.1 km"."s"^-1`
C. Racing car: `"9000 cm"."s"^-1`
D. Snail: `"0.01 km"."h"^-1`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A student takes measurements to determine the constant acceleration of a model car moving from rest in a straight line. The measured values with their absolute uncertainties are shown.
| Quantity | Measured value | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| displacement | 16.5 m | ± 0.1 m |
| time | 15.0 s | ± 1.0 s |
The student uses the equation `s = 1/2 a t^2` to calculate the acceleration of the car.
What is the acceleration and its absolute uncertainty?
A. `0.11 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
B. `0.11 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
C. `0.15 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
D. `0.15 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A desk has a true width of 50.0 cm.
Two students, X and Y, measure the width of the desk.
Student X uses a tape measure and records a width of (49.5 ± 0.5) cm.
Student Y uses a metre rule and records a width of (51.4 ± 0.1) cm.
Which statement about the measurement of student X is correct?
A. It is less accurate and less precise than the measurement of student Y.
B. It is less accurate but more precise than the measurement of student Y.
C. It is more accurate and more precise than the measurement of student Y.
D. It is more accurate but less precise than the measurement of student Y.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
What is a power of 3.7 MW when expressed in kilowatts?
A. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " kW"`
B. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " KW"`
C. `3.7 xx 10^3 " kW"`
D. `3.7 xx 10^3 " KW"`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
A spring is suspended from a fixed point and a force is applied. The position of a pointer attached to the bottom of the spring against a vertical ruler is recorded.
Before the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (225 ± 2) mm.
After the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (250 ± 2) mm.
The extension of the spring is determined.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the extension?
A. 1.6%
B. 1.8%
C. 8.0%
D. 16%
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
The drag coefficient `C_d` is a number with no units. It is used to compare the drag on different cars at different speeds. `C_d` is given by the equation `C_d = (2F) / (v^n rho A)`
Where `F` is the drag force on the car, `rho` is the density of the air, `A` is the cross-sectional area of the car and `v` is the speed of the car.
What is the value of `n`?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
A set of repeated measurements is made of a fixed quantity. An average of these measurements is calculated.
What is the effect of averaging on the random error and the systematic error in the measurements?
A. Random error and systematic error are both reduced.
B. Random error and systematic error are both unaffected.
C. Random error is reduced but systematic error is unaffected.
D. Random error is unaffected but systematic error is reduced.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Which two units are identical when expressed in terms of SI base units?
A. `"J"."C"^-1`, `"kg"."m"^2."A"^-1."s"^-2`
B. `"J"."s"`, `"kg"."m"^2."s"^-1`
C. `"N"."m"`, `"kg"."m"^3."s"^-2`
D. `"N"."s"`, `"kg"."m"."s"^-3`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
a. Explain what is meant by the accuracy of a measured value.
b. Two solid cubes, A and B, are measured to determine the density of their materials.
Table shows the measurements for cube A.
| Quantity | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Length of side | (1.53 ± 0.01) cm |
| Mass | (31.3 ± 0.5) g |
i. Show that the calculated density of the material of cube A is 8.7 × 103 kg.m−3
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the density of the material of cube A.
iii. The density of the material of cube B is determined to be 9.2 × 103 kg.m−3 ± 6%
State and explain whether cube A and cube B could be made from the same material.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
a. State what is meant by work done.
b. Use your answer in a. to show that the SI base units of energy are kg.m2.s−2
c. A metal rod is heated at one end so that thermal energy flows to the other end.
The thermal energy EE that flows through the rod in time tt is given by `E =(cA (T_1 - T_2) t) / (L)`
Where
`A` is the cross-sectional area of the rod.
`T_1` and `T_2` are the temperatures of the ends of the rod.
`L` is the length of the rod.
`c` is a constant.
Determine the SI base units of `c`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
a. The list below shows some SI quantities.
Underline the quantity that is not an SI base quantity.
charge current length time
b. A square solar panel with sides of length 1300 mm is shown in figure.
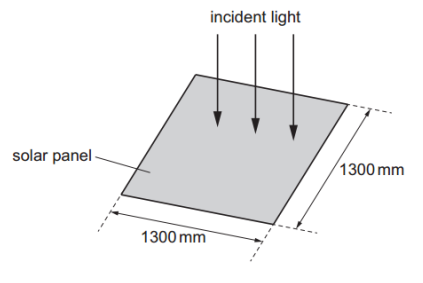 Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
i. The power of the light incident on the solar panel is 750 W.
Calculate the intensity of the light.
ii. The percentage uncertainty in the incident power is ± 3%.
The uncertainty in the length of each side is ± 5 mm.
Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the intensity of the light.
iii. The useful power output of the solar panel is 160 W.
Calculate the percentage efficiency of the solar panel.
iv. Another square solar panel is placed so that light of the same intensity is incident normally on it.
The new panel has shorter sides than the original panel. The new panel has the same power output as the original panel.
State and explain whether the efficiency of the new panel is greater than, less than, or the same as the efficiency of the original panel.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
a. In the following list, underline all quantities that are SI base quantities.
charge electric current force time
b. Under certain conditions, the distance `s` moved in a straight line by an object in time `t` is given by:
`s = 1/2 a t^2`, where `a` is the acceleration of the object.
State two conditions under which the above expression applies to the motion of the object.
c. The variation with time `t` of the velocity `v` of a car that is moving in a straight line is shown in figure.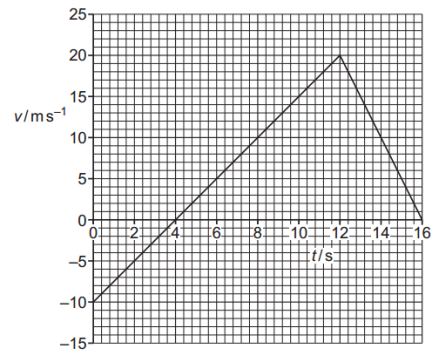 i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
ii. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car at time `t="4 s"`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
a. Define density.
b. A smooth pebble, made from uniform rock, has the shape of an elongated sphere as shown in figure.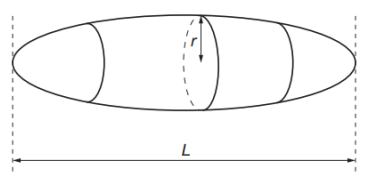 The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
A student investigating the density of the rock makes measurements to determine the values of `L`, `r`, and the mass `M` of the pebble as follows:
`L=(0.1242±0.0001) " m"`
`r=(0.0420±0.0004) " m"`
`M=(1.072±0.001) " kg"`
i. State the name of a measuring instrument suitable for making this measurement of `L`.
ii. Determine the percentage uncertainty in the measurement of `r`.
c. The density `rho` of the rock from which the pebble in b. is composed is given by `rho = (M r^n) / (k L)`
where `n` is an integer and `k` is a constant, with no units, that is equal to 2.094.
i. Use SI base units to show that `n` is equal to −2.
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in `rho`.
iii. Determine `rho` with its absolute uncertainty. Give your values to the appropriate number of significant figures.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The value of quantity `X` has a percentage uncertainty of 2%.
The value of quantity `Y` has a percentage uncertainty of 4%.
The value of a quantity `W` is calculated from the values of `X` and `Y`.
What could be the relationship between `W`, `X` and `Y`?
A. `W=XY`
B. `W=2XY`
C. `W=X/Y^2`
D. `W=Y/X^2`
Answer: D
A. Incorrect:
If `W=XY` the percentage uncertainty of `W` is the sum of the percentage uncertainties of `X` and `Y`:
`"2%" + "4%" = "6%"`
This is less than 8%, so it cannot be the correct answer.
B. Incorrect:
If `W=2XY`, the coefficient 2 does not affect the percentage uncertainty. The calculation is still:
`"2%" + "4%" = "6%"`
This is not equal to 8%.
C. Incorrect:
If `W=X/Y^2`, the percentage uncertainty of `W` is:
`"2%" + 2 xx "4%" = "2%" + "8%" = "10%"`
This is greater than 8%.
D. Correct:
If `W=Y/X^2`, the percentage uncertainty of `W` is:
`"4%" + 2 xx "2%" = "4%" + "4%" = "8%"`
This exactly matches the required 8%.
Question 2
A solid bar has a square cross-section. Its length is measured as `50+-0.2 " cm"` and its width is measured as `20.0+-0.01 " cm"`
These values are used to calculate the volume of the bar.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the calculated volume?
A. ± 0.21%
B. ± 0.22%
C. ± 0.90%
D. ± 1.4%
Answer: D
The percentage uncertainty for length: `0.2/50.0 xx "100%" = "0.4%"`
The percentage uncertainty for width: `0.01/2.00 xx "100%" = "0.5%"`
Volume formula: `V = "width"^2 xx "length"`
The percentage uncertainty in volume: `"0.4%" + 2 xx "0.5%" = "1.4%"`
Question 3
A physical quantity consists of a magnitude and a unit.
Which row does not show a correct combination of a quantity and its unit?
| Quantity | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| A | mass | gram |
| B | length | metre |
| C | charge | ampere |
| D | temperature | kelvin |
A. Incorrect: Gram is a unit of mass (although not SI base unit, it is still a unit of mass).
B. Incorrect: Meter is the SI base unit for length.
C. Correct: Ampere is the unit of current, not charge. The correct SI unit for charge is coulomb.
D. Incorrect: Kelvin is the SI base unit for temperature.
Question 4
What is the effect of a systematic error on the measurement of a physical quantity?
A. It limits the precision of the measured value.
B. It limits the range of values obtained in repeated measurements.
C. It results in repeated measurements having different values from each other.
D. It results in the measured value being different from the correct value.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Systematic error affects accuracy, not precision.
B. Incorrect: Systematic error does not limit the range of values; it causes all measurements to shift in the same direction.
C. Incorrect: Systematic error makes repeated measurements consistently offset, but does not cause them to differ from each other.
D. Correct: Systematic error causes all measured values to be offset from the true (correct) value.
The measured value is different from the correct value by a constant amount.
Question 5
Which quantity is a scalar quantity?
A. Force
B. Momentum
C. Velocity
D. Work
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Force is a vector quantity (has both magnitude and direction).
B. Incorrect: Momentum is a vector quantity.
C. Incorrect: Velocity is a vector quantity.
D. Correct: Work is a scalar quantity (only has magnitude, no direction).
Question 6
The relationship between the variables `D` and `T` is given by the equation `1/T = b/sqrt(D) + c`
Where `b` and `C` are constants.
The unit of `D` is `"m"^2` and the unit of `T` is `"s"`.
What are the units of `b` and `c`?
| Unit of b | Unit of c | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `"m"."s"` | `"s"` |
| B | `"m"."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
| C | `"m"^-1."s"` | `"s"` |
| D | `"m"^-1."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
Answer: B
The unit of `T` is s.
The unit of `1/T` is `"s"^-1`
The unit of c must be the same as the left side, so c has unit `"s"^-1`
The term `b/sqrt(D)` must have the same unit as c, which is `"s"^-1`
The unit of `sqrt(D)` is `"m"`
The unit of must be `"m"."s"^-1`
Question 7
What represents a physical quantity?
A. 3.0
B. Kilogram
C. 7.0 N
D. 40%
Answer: C
A. Incorrect:
3.0 is just a numerical value, no unit.
Not a physical quantity.
B. Incorrect:
Kilogram is a unit only, no magnitude.
Not a physical quantity.
C. Correct:
7.0 N has both a magnitude and a unit.
Represents a physical quantity (force).
D. Incorrect: 40% is a ratio or percentage, not a physical quantity.
Question 8
A student estimates the maximum speed of some different moving objects.
Which maximum speed is not a reasonable estimate?
A. Container ship: `"10 m"."s"^-1`
B. Olympic sprinter: `"0.1 km"."s"^-1`
C. Racing car: `"9000 cm"."s"^-1`
D. Snail: `"0.01 km"."h"^-1`
Answer: B
0.1 km.s-1 = 100 m.s-1, which is much too fast for an Olympic sprinter (world record ~12 m.s-1).
Question 9
A student takes measurements to determine the constant acceleration of a model car moving from rest in a straight line. The measured values with their absolute uncertainties are shown.
| Quantity | Measured value | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| displacement | 16.5 m | ± 0.1 m |
| time | 15.0 s | ± 1.0 s |
The student uses the equation `s = 1/2 a t^2` to calculate the acceleration of the car.
What is the acceleration and its absolute uncertainty?
A. `0.11 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
B. `0.11 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
C. `0.15 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
D. `0.15 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
Answer: D
Percentage uncertainty of displacement: `0.1/16.5 xx 100% = 0.61%`
Percentage uncertainty of time: `2xx1.0/15.0 xx 100% = 13.34%`
Total percentage uncertainty:`0.61% + 13.34% = 13.95%`
Absolute uncertainty: `0.15 xx 0.1395 = 0.021`
Calculate acceleration: `a = (2 s) / t^2 = (2 xx 16.5 )/ (15.0)^2 = 0.15 " m"."s"^-2`
The acceleration and its absolute uncertainty: `0.15 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
Question 10
A desk has a true width of 50.0 cm.
Two students, X and Y, measure the width of the desk.
Student X uses a tape measure and records a width of (49.5 ± 0.5) cm.
Student Y uses a metre rule and records a width of (51.4 ± 0.1) cm.
Which statement about the measurement of student X is correct?
A. It is less accurate and less precise than the measurement of student Y.
B. It is less accurate but more precise than the measurement of student Y.
C. It is more accurate and more precise than the measurement of student Y.
D. It is more accurate but less precise than the measurement of student Y.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect:
Accuracy: Student X’s measurement (49.5 cm) is closer to the true value (50.0 cm) than student Y’s (51.4 cm).
Precision: Student X’s uncertainty (±0.5 cm) is larger than student Y’s (±0.1 cm).
B. Incorrect: Student X is more accurate (closer to true value), but less precise (greater uncertainty).
C. Incorrect: Student X is not more precise.
D. Correct: Student X is more accurate (closer to true value), but less precise (greater uncertainty) than student Y.
Question 11
What is a power of 3.7 MW when expressed in kilowatts?
A. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " kW"`
B. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " KW"`
C. `3.7 xx 10^3 " kW"`
D. `3.7 xx 10^3 " KW"`
Answer: C
`"3.7 MW"=3.7×10^3 " kW"`
Question 12
A spring is suspended from a fixed point and a force is applied. The position of a pointer attached to the bottom of the spring against a vertical ruler is recorded.
Before the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (225 ± 2) mm.
After the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (250 ± 2) mm.
The extension of the spring is determined.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the extension?
A. 1.6%
B. 1.8%
C. 8.0%
D. 16%
Answer: D
Extension: `250 - 225 = 25 " mm"`
Combine absolute uncertainties: 2 mm + 2 mm = 4 mm
Percentage uncertainty: `4/25 xx "100%" = "16%"`
Question 13
The drag coefficient `C_d` is a number with no units. It is used to compare the drag on different cars at different speeds. `C_d` is given by the equation `C_d = (2F) / (v^n rho A)`
Where `F` is the drag force on the car, `rho` is the density of the air, `A` is the cross-sectional area of the car and `v` is the speed of the car.
What is the value of `n`?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: B
Unit of physical quantities:
Force: `"kg"."m"."s"^-2`
Density: `"kg"."m"^-3`
Area: `"m"^2`
Speed: `"m"."s"^-1`
Substitute into the equation: `C_d = ("kg"."m"."s"^-2) / (( "m"."s"^-1 )^n xx "kg"."m"^-3 xx "m"^2 )`
`C_d = ("kg"."m"."s"^-2) / ("kg"."m"^(n-1)."s"^-n)`
`C_d = "m"^(2-n)."s"^(n-2)`
Since `C_d` has no unit, `2-n` and `n-2` must be equal to zero.
`2-n=0rightarrown=2`
Question 14
A set of repeated measurements is made of a fixed quantity. An average of these measurements is calculated.
What is the effect of averaging on the random error and the systematic error in the measurements?
A. Random error and systematic error are both reduced.
B. Random error and systematic error are both unaffected.
C. Random error is reduced but systematic error is unaffected.
D. Random error is unaffected but systematic error is reduced.
Answer C
A. Incorrect:
Averaging reduces random error because random variations can cancel out, leading to a more precise result.
However, systematic error shifts all results by a fixed amount, so averaging does not reduce it.
B. Incorrect:
Averaging does affect random error (reduces it), so this statement is not correct.
Systematic error, though, is indeed unaffected.
C. Correct:
Averaging multiple measurements reduces the effect of random error, making the mean value more precise.
Systematic error is a constant bias affecting all measurements equally, so it remains unchanged even after averaging.
D. Incorrect:
Averaging cannot reduce systematic error, because it affects all measurements in the same way.
Random error, however, is reduced by averaging.
Question 15
Which two units are identical when expressed in terms of SI base units?
A. `"J"."C"^-1`, `"kg"."m"^2."A"^-1."s"^-2`
B. `"J"."s"`, `"kg"."m"^2."s"^-1`
C. `"N"."m"`, `"kg"."m"^3."s"^-2`
D. `"N"."s"`, `"kg"."m"."s"^-3`
Answer: B
Work is defined as force times distance: `W = F xx d`
Unit of force (newton, N): `F = m xx a`
Where `m` is mass (kg), `a` is acceleration (`"m"."s"^-2"`).
Therefore, `"N" = "kg"."m"."s"^-2`
Substitute into work: `"J" = "N"."m" = "kg"."m"."s"^-2."m"`
`"J" = "kg"."m"^2."s"^-2`
Now, `"J"."s" = "kg"."m"^2."s"^-2."s" = "kg"."m"^2."s"^-1`
Question 16
a. Explain what is meant by the accuracy of a measured value.
b. Two solid cubes, A and B, are measured to determine the density of their materials.
Table shows the measurements for cube A.
| Quantity | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Length of side | (1.53 ± 0.01) cm |
| Mass | (31.3 ± 0.5) g |
i. Show that the calculated density of the material of cube A is 8.7 × 103 kg.m−3
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the density of the material of cube A.
iii. The density of the material of cube B is determined to be 9.2 × 103 kg.m−3 ± 6%
State and explain whether cube A and cube B could be made from the same material.
a. Accuracy is a measure of how close the measured value is to the true value of the quantity.
b. i. `rho = m/V=(31.3) / (3.58) = 8.75 " g"."cm"^-3=8.7 xx 10^3 " kg"."m"^-3`
ii. Percentage uncertainty in mass: `0.5/31.3 xx "100%" = "1.6%"`
Percentage uncertainty in length: `3xx0.01/1.53 xx "100%" = "1.95%"`
Percentage uncertainty in density: `"1.6%" + "1.95%" = "3.55%" ~~ "3.6%"`
iii. The possible range for cube A:
Lower limit = `8.7 xx 10^3 xx (1 - 0.036) = 8.4 xx 10^3`
Upper limit = `8.7 xx 10^3 xx (1 + 0.036) = 9.0 xx 10^3`
The calculated density for cube B (9.2 × 103 kg.m−3) does not lie within the range of cube A.
Therefore, cube A and cube B are unlikely to be made from the same material.
Question 17
a. State what is meant by work done.
b. Use your answer in a. to show that the SI base units of energy are kg.m2.s−2
c. A metal rod is heated at one end so that thermal energy flows to the other end.
The thermal energy EE that flows through the rod in time tt is given by `E =(cA (T_1 - T_2) t) / (L)`
Where
`A` is the cross-sectional area of the rod.
`T_1` and `T_2` are the temperatures of the ends of the rod.
`L` is the length of the rod.
`c` is a constant.
Determine the SI base units of `c`
a. Work done is the product of force and displacement in the direction of the force: `W = F xx d`
b. The SI unit for work done (and energy):
`W = F xx d = ("kg"."m"."s"^-2) xx "m" = "kg"."m"^2."s"^-2`
c. `c = (E L) / (A (T_1 - T_2) t)`
SI units for each quantity:
Energy: `"kg"."m"^2."s"^-2`
Length: `"m"`
Area: `"m"^2`
Temperature difference: `K`
Time: `s`
Substitute into c: `c = ( "kg"."m"^2."s"^-2 xx "m" ) / ( "m"^2 xx "K" xx "s" )`
`c = ("kg"."m"^3."s"^-2) / ("m"^2."K"."s") = "kg"."m"."s"^-3."K"^-1`
Question 18
a. The list below shows some SI quantities.
Underline the quantity that is not an SI base quantity.
charge current length time
b. A square solar panel with sides of length 1300 mm is shown in figure.
 Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
i. The power of the light incident on the solar panel is 750 W.
Calculate the intensity of the light.
ii. The percentage uncertainty in the incident power is ± 3%.
The uncertainty in the length of each side is ± 5 mm.
Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the intensity of the light.
iii. The useful power output of the solar panel is 160 W.
Calculate the percentage efficiency of the solar panel.
iv. Another square solar panel is placed so that light of the same intensity is incident normally on it.
The new panel has shorter sides than the original panel. The new panel has the same power output as the original panel.
State and explain whether the efficiency of the new panel is greater than, less than, or the same as the efficiency of the original panel.
a. charge
b. i. `I = P/A=750/1.69 = 444 " W"."m"^-2= 440 " W"."m"^-2`
ii. Uncertainty in length of one side: `5/1300 xx "100%" = "0.38%"`
Uncertainty in area: `2 xx "0.38%" = "0.76%"`
Percentage uncertainty in intensity: `"3%" + "0.76%" = "3.76%" ~~ "4%"`
iii. `"Efficiency" = ("output power")/("input power") xx "100%"= 160/750 xx "100%" = "21%"`
iv. The new panel has shorter sides, so its area is less.
Input power (`P=IxxA`) for the new panel is less, since intensity `I` is the same but `A` is smaller.
Useful power output is the same (160 W).
Since the input power is smaller but the useful output power is unchanged, the efficiency of the new panel is greater than the original panel.
Question 19
a. In the following list, underline all quantities that are SI base quantities.
charge electric current force time
b. Under certain conditions, the distance `s` moved in a straight line by an object in time `t` is given by:
`s = 1/2 a t^2`, where `a` is the acceleration of the object.
State two conditions under which the above expression applies to the motion of the object.
c. The variation with time `t` of the velocity `v` of a car that is moving in a straight line is shown in figure. i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
ii. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car at time `t="4 s"`.
a. electric current, time
b. Initial speed or velocity is zero.
Acceleration is constant and the motion is in a straight line.
c. i. The magnitude of the acceleration at `t="8 s"` is less than that at `t="14 s"`.
The direction of acceleration at `t="8 s"` is opposite to the direction at `t="14 s"`.
ii. Acceleration is the gradient of the velocity-time graph: `a = (Delta v) / (Delta t)`
`a = (20 - (-10))/(12 - 0) = 30/12 = 2.5 " m"."s"^-2`
Question 20
a. Define density.
b. A smooth pebble, made from uniform rock, has the shape of an elongated sphere as shown in figure. The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
A student investigating the density of the rock makes measurements to determine the values of `L`, `r`, and the mass `M` of the pebble as follows:
`L=(0.1242±0.0001) " m"`
`r=(0.0420±0.0004) " m"`
`M=(1.072±0.001) " kg"`
i. State the name of a measuring instrument suitable for making this measurement of `L`.
ii. Determine the percentage uncertainty in the measurement of `r`.
c. The density `rho` of the rock from which the pebble in b. is composed is given by `rho = (M r^n) / (k L)`
where `n` is an integer and `k` is a constant, with no units, that is equal to 2.094.
i. Use SI base units to show that `n` is equal to −2.
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in `rho`.
iii. Determine `rho` with its absolute uncertainty. Give your values to the appropriate number of significant figures.
a. Density is the mass per unit volume.
b. i. A suitable measuring instrument is caliper.
ii. Percentage uncertainty in the measurement of `r`: `0.0004/0.0420 xx "100%" = "0.95%"`
c. i. Given `rho = (M r^n) / (k L)`
Unit: `rho = (M r^n) / (k L)=( "kg" xx "m"^n ) / "m" = "kg"."m"^(n-1)`
Set equal to kg.m−3
`"kg"."m"^(n−1) ="kg"."m"^(−3)`
`n - 1 = -3rightarrown=-2`
ii. Uncertainty in mass: `0.001/1.072 xx "100%" = "0.09%"`
Uncertainty in radius:`2xx0.0004/0.0420 xx "100%" = "1.9%"`
Uncertainty in length: `0.0001/0.1242 xx "100%" = "0.08%"`
Percentage uncertainty of `rho`: `"0.09%" + "1.9%" + "0.08%" = "2.07%" ~~ "2%"`
iii. `rho =(M r^-2) / (k L)= (1.072 xx 567) / (2.094 xx 0.1242) = 607.824 / 0.2601 = 2337 " kg"."m"^-3`
Absolute uncertainty: `Delta rho = 0.021 xx 2337 = 49 " kg"."m"^-3`
`rho = 2340 +- 50 " kg"."m"^-3`
Question 1
The value of quantity `X` has a percentage uncertainty of 2%.
The value of quantity `Y` has a percentage uncertainty of 4%.
The value of a quantity `W` is calculated from the values of `X` and `Y`.
What could be the relationship between `W`, `X` and `Y`?
A. `W=XY`
B. `W=2XY`
C. `W=X/Y^2`
D. `W=Y/X^2`
Question 2
A solid bar has a square cross-section. Its length is measured as `50+-0.2 " cm"` and its width is measured as `20.0+-0.01 " cm"`
These values are used to calculate the volume of the bar.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the calculated volume?
A. ± 0.21%
B. ± 0.22%
C. ± 0.90%
D. ± 1.4%
Question 3
A physical quantity consists of a magnitude and a unit.
Which row does not show a correct combination of a quantity and its unit?
| Quantity | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| A | mass | gram |
| B | length | metre |
| C | charge | ampere |
| D | temperature | kelvin |
Question 4
What is the effect of a systematic error on the measurement of a physical quantity?
A. It limits the precision of the measured value.
B. It limits the range of values obtained in repeated measurements.
C. It results in repeated measurements having different values from each other.
D. It results in the measured value being different from the correct value.
Question 5
Which quantity is a scalar quantity?
A. Force
B. Momentum
C. Velocity
D. Work
Question 6
The relationship between the variables `D` and `T` is given by the equation `1/T = b/sqrt(D) + c`
Where `b` and `C` are constants.
The unit of `D` is `"m"^2` and the unit of `T` is `"s"`.
What are the units of `b` and `c`?
| Unit of b | Unit of c | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `"m"."s"` | `"s"` |
| B | `"m"."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
| C | `"m"^-1."s"` | `"s"` |
| D | `"m"^-1."s"^-1` | `"s"^-1` |
Question 7
What represents a physical quantity?
A. 3.0
B. Kilogram
C. 7.0 N
D. 40%
Question 8
A student estimates the maximum speed of some different moving objects.
Which maximum speed is not a reasonable estimate?
A. Container ship: `"10 m"."s"^-1`
B. Olympic sprinter: `"0.1 km"."s"^-1`
C. Racing car: `"9000 cm"."s"^-1`
D. Snail: `"0.01 km"."h"^-1`
Question 9
A student takes measurements to determine the constant acceleration of a model car moving from rest in a straight line. The measured values with their absolute uncertainties are shown.
| Quantity | Measured value | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| displacement | 16.5 m | ± 0.1 m |
| time | 15.0 s | ± 1.0 s |
The student uses the equation `s = 1/2 a t^2` to calculate the acceleration of the car.
What is the acceleration and its absolute uncertainty?
A. `0.11 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
B. `0.11 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
C. `0.15 +- 0.01 " m"."s"^-2`
D. `0.15 +- 0.02 " m"."s"^-2`
Question 10
A desk has a true width of 50.0 cm.
Two students, X and Y, measure the width of the desk.
Student X uses a tape measure and records a width of (49.5 ± 0.5) cm.
Student Y uses a metre rule and records a width of (51.4 ± 0.1) cm.
Which statement about the measurement of student X is correct?
A. It is less accurate and less precise than the measurement of student Y.
B. It is less accurate but more precise than the measurement of student Y.
C. It is more accurate and more precise than the measurement of student Y.
D. It is more accurate but less precise than the measurement of student Y.
Question 11
What is a power of 3.7 MW when expressed in kilowatts?
A. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " kW"`
B. `3.7 xx 10^-3 " KW"`
C. `3.7 xx 10^3 " kW"`
D. `3.7 xx 10^3 " KW"`
Question 12
A spring is suspended from a fixed point and a force is applied. The position of a pointer attached to the bottom of the spring against a vertical ruler is recorded.
Before the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (225 ± 2) mm.
After the force is applied, the position of the pointer is (250 ± 2) mm.
The extension of the spring is determined.
What is the percentage uncertainty in the extension?
A. 1.6%
B. 1.8%
C. 8.0%
D. 16%
Question 13
The drag coefficient `C_d` is a number with no units. It is used to compare the drag on different cars at different speeds. `C_d` is given by the equation `C_d = (2F) / (v^n rho A)`
Where `F` is the drag force on the car, `rho` is the density of the air, `A` is the cross-sectional area of the car and `v` is the speed of the car.
What is the value of `n`?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Question 14
A set of repeated measurements is made of a fixed quantity. An average of these measurements is calculated.
What is the effect of averaging on the random error and the systematic error in the measurements?
A. Random error and systematic error are both reduced.
B. Random error and systematic error are both unaffected.
C. Random error is reduced but systematic error is unaffected.
D. Random error is unaffected but systematic error is reduced.
Question 15
Which two units are identical when expressed in terms of SI base units?
A. `"J"."C"^-1`, `"kg"."m"^2."A"^-1."s"^-2`
B. `"J"."s"`, `"kg"."m"^2."s"^-1`
C. `"N"."m"`, `"kg"."m"^3."s"^-2`
D. `"N"."s"`, `"kg"."m"."s"^-3`
Question 16
a. Explain what is meant by the accuracy of a measured value.
b. Two solid cubes, A and B, are measured to determine the density of their materials.
Table shows the measurements for cube A.
| Quantity | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Length of side | (1.53 ± 0.01) cm |
| Mass | (31.3 ± 0.5) g |
i. Show that the calculated density of the material of cube A is 8.7 × 103 kg.m−3
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the density of the material of cube A.
iii. The density of the material of cube B is determined to be 9.2 × 103 kg.m−3 ± 6%
State and explain whether cube A and cube B could be made from the same material.
Question 17
a. State what is meant by work done.
b. Use your answer in a. to show that the SI base units of energy are kg.m2.s−2
c. A metal rod is heated at one end so that thermal energy flows to the other end.
The thermal energy EE that flows through the rod in time tt is given by `E =(cA (T_1 - T_2) t) / (L)`
Where
`A` is the cross-sectional area of the rod.
`T_1` and `T_2` are the temperatures of the ends of the rod.
`L` is the length of the rod.
`c` is a constant.
Determine the SI base units of `c`
Question 18
a. The list below shows some SI quantities.
Underline the quantity that is not an SI base quantity.
charge current length time
b. A square solar panel with sides of length 1300 mm is shown in figure.
 Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
Light is incident normally on the solar panel.
i. The power of the light incident on the solar panel is 750 W.
Calculate the intensity of the light.
ii. The percentage uncertainty in the incident power is ± 3%.
The uncertainty in the length of each side is ± 5 mm.
Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the intensity of the light.
iii. The useful power output of the solar panel is 160 W.
Calculate the percentage efficiency of the solar panel.
iv. Another square solar panel is placed so that light of the same intensity is incident normally on it.
The new panel has shorter sides than the original panel. The new panel has the same power output as the original panel.
State and explain whether the efficiency of the new panel is greater than, less than, or the same as the efficiency of the original panel.
Question 19
a. In the following list, underline all quantities that are SI base quantities.
charge electric current force time
b. Under certain conditions, the distance `s` moved in a straight line by an object in time `t` is given by:
`s = 1/2 a t^2`, where `a` is the acceleration of the object.
State two conditions under which the above expression applies to the motion of the object.
c. The variation with time `t` of the velocity `v` of a car that is moving in a straight line is shown in figure. i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
i. Compare, qualitatively, the acceleration of the car at time `t="8 s"` and at time `t="14 s"` in terms of magnitude and direction.
ii. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car at time `t="4 s"`.
Question 20
a. Define density.
b. A smooth pebble, made from uniform rock, has the shape of an elongated sphere as shown in figure. The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
The length of the pebble is `L`. The cross-section of the pebble, in the plane perpendicular to `L`, is circular with a maximum radius `r`.
A student investigating the density of the rock makes measurements to determine the values of `L`, `r`, and the mass `M` of the pebble as follows:
`L=(0.1242±0.0001) " m"`
`r=(0.0420±0.0004) " m"`
`M=(1.072±0.001) " kg"`
i. State the name of a measuring instrument suitable for making this measurement of `L`.
ii. Determine the percentage uncertainty in the measurement of `r`.
c. The density `rho` of the rock from which the pebble in b. is composed is given by `rho = (M r^n) / (k L)`
where `n` is an integer and `k` is a constant, with no units, that is equal to 2.094.
i. Use SI base units to show that `n` is equal to −2.
ii. Calculate the percentage uncertainty in `rho`.
iii. Determine `rho` with its absolute uncertainty. Give your values to the appropriate number of significant figures.