Question 1
Calculate the angles at which the first and second maxima are formed when a monochromatic light of wavelength 7.2 × 10−7 is shone perpendicularly onto a grating with 5000 lines per cm.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A diffraction grating has 12,500 lines per centimetre.
When monochromatic light is shone on the grating, the first maximum is found to be at an angle of 30∘ to the central maximum. Calculate the wavelength of the light.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
This diagram shows the experimental setup (left) used to analyse the spectrum of a sodium discharge lamp with a diffraction grating with 500 lines mm-1, and the spectral lines observed (right) in the developed photographic film.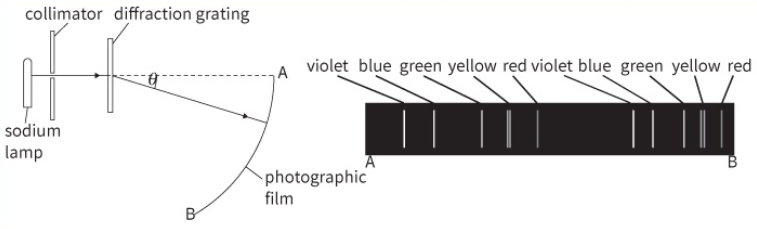 a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
b. Describe two differences between these two spectra.
c. The green maximum near end A is at an angle θ of 19.5°.
i. Calculate the wavelength of the green light.
ii. Calculate the angle produced by the second green line.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A diffraction grating and a screen are used to determine the single wavelength λ of the light from a source.
What is an essential feature of this experiment?
A. A curved screen must be used.
B. The diffraction angle θ must be measured for at least two interference maxima.
C. The light waves incident on the grating must be coherent.
D. The third order intensity maximum must be produced.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Light of a single unknown wavelength and blue light of a single wavelength are both incident normally on a diffraction grating. Two diffraction patterns are produced, one for each wavelength of light.
The third-order maximum for the blue light occurs at the same angle as the second-order maximum for the light of unknown wavelength. The wavelength of the blue light is 480 nm.
What is the unknown wavelength?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A parallel beam of light consists of light of wavelength 420 nm and light of wavelength 630 nm.
The light is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The diffraction maxima for the two wavelengths overlap only at an angle of 31° from the direction of the incident light beam.
What could be the line spacing of the diffraction grating?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Light of wavelength `5.4 × 10⁻⁷` m is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The separation between adjacent lines in the grating is `2.0 × 10⁻⁶ " m"`. The light that emerges from the grating falls on a semicircular screen, as shown in the view from above.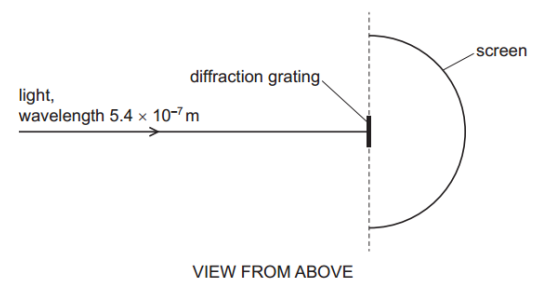 The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
How many bright dots are formed on the screen?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
The diagram shows a diffraction grating and a monochromatic source of light with wavelength.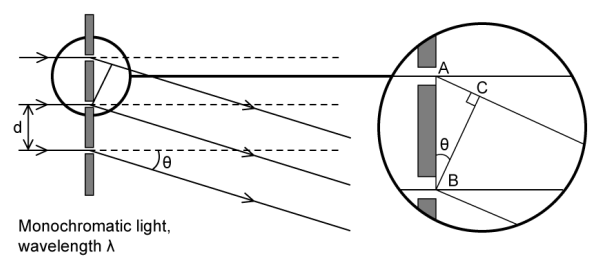 What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
A. The angle of diffraction remains the same.
B. The angle of diffraction is decreased.
C. The angle of diffraction is increased.
D. There is not enough information to know what will happen.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
What is a diffraction grating?
A. Two slits created as two gaps within a material through which waves can be diffracted.
B. A plate consisting of a very large number of parallel, identical, closely-spaced slits.
C. A circular aperture through which light can be diffracted and then images resolved.
D. A photographic filter that allows light in only one plane to pass through.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A beam of monochromatic light with a wavelength of 690 nm is directed at a diffraction grating with 300 lines per mm as shown in the diagram.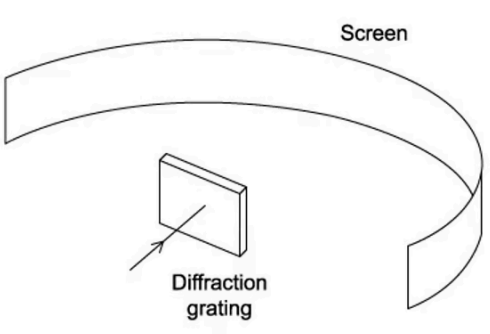 This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?
This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Calculate the angles at which the first and second maxima are formed when a monochromatic light of wavelength 7.2 × 10−7 is shone perpendicularly onto a grating with 5000 lines per cm.
`d = 1 / 5000 " cm" = 2 xx 10^-4 " cm" = 2 xx 10^-6 " m"`
For the first maximum:
`lambda = d sin theta`
`sin theta = lambda / d = 7.2 xx 10^-7 / (2 xx 10^-6) = 0.36`
`theta = 21^@`
For the second maximum:
`2 lambda = d sin theta`
`sin theta = (2 xx 7.2 xx 10^-7) / (2 xx 10^-6) = 0.72`
`theta = 46^@`
Question 2
A diffraction grating has 12,500 lines per centimetre.
When monochromatic light is shone on the grating, the first maximum is found to be at an angle of 30∘ to the central maximum. Calculate the wavelength of the light.
Since there are 12,500 lines per centimeter:
`d = 1 / 12500 " cm" = 8.0 xx 10^-5 " cm" = 8.0 xx 10^-7 " m"`
Rearranging the diffraction equation: `lambda = d sin theta`
`lambda = (8.0 xx 10^-7 " m") sin 30^@`
`lambda = (8.0 xx 10^-7) xx 0.5 = 4.0 xx 10^-7 " m"`
Question 3
This diagram shows the experimental setup (left) used to analyse the spectrum of a sodium discharge lamp with a diffraction grating with 500 lines mm-1, and the spectral lines observed (right) in the developed photographic film. a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
b. Describe two differences between these two spectra.
c. The green maximum near end A is at an angle θ of 19.5°.
i. Calculate the wavelength of the green light.
ii. Calculate the angle produced by the second green line.
a. First order produced by waves with path difference of one wavelength.
Second order produced by waves with path difference of two wavelengths.
b. Lines at end A are further apart or lines at end B are closer together.
Lines at end A are thinner or lines at end B are wider.
c.
i. `n xx lambda = d xx sin theta`
`n = 1, lambda = (sin 19.5^@) / (5000 xx 10^2)`
`lambda = 6.68 xx 10^-7 approx 6.7 xx 10^-7 " m"`
ii. `sin theta = (n xx lambda) / D`
`sin theta = 2 xx 6.68 xx 10^-7 xx 5000 xx 10^2`
`theta = 41.8^@ approx 42^@`
Question 4
A diffraction grating and a screen are used to determine the single wavelength λ of the light from a source.
What is an essential feature of this experiment?
A. A curved screen must be used.
B. The diffraction angle θ must be measured for at least two interference maxima.
C. The light waves incident on the grating must be coherent.
D. The third order intensity maximum must be produced.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: a flat screen is typically sufficient.
B. Incorrect: measuring even a single order maximum (first-order) can be enough to determine λ.
C. Correct:
To determine the wavelength of light using a diffraction grating, the setup relies on constructive interference of light waves at specific angles. For this interference pattern to be stable and measurable, the light source must emit coherent waves. This coherence ensures that the interference fringes (bright and dark spots) are clear, stable, and predictable, which is crucial for accurate measurement of the diffraction angles.
D. Incorrect: higher-order maxima (like third-order) are not necessary.
Question 5
Light of a single unknown wavelength and blue light of a single wavelength are both incident normally on a diffraction grating. Two diffraction patterns are produced, one for each wavelength of light.
The third-order maximum for the blue light occurs at the same angle as the second-order maximum for the light of unknown wavelength. The wavelength of the blue light is 480 nm.
What is the unknown wavelength?
Since both maxima occur at the same angle θ, we equate the path differences:
`n_("blue") xx lambda_("blue") = n_("unknown") xx lambda_("unknown")`
`3 xx 480 = 2 xx lambda_("unknown")`
`lambda_("unknown") = 1440 / 2 = 720 " nm"`
Question 6
A parallel beam of light consists of light of wavelength 420 nm and light of wavelength 630 nm.
The light is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The diffraction maxima for the two wavelengths overlap only at an angle of 31° from the direction of the incident light beam.
What could be the line spacing of the diffraction grating?
Two different wavelengths (420 nm and 630 nm) produce maxima at the same angle (31°), so we find integers n1, n2 such that: `n_1 xx lambda_1 = n_2 xx lambda_2 = d xx sin theta`
Let’s test the lowest possible integer ratio:
`630 / 420 = 3 / 2 => n_1 = 2, n_2 = 3`
`d = (2 xx 630) / sin(31^@) approx 2446 " nm" = 2.4 " "mu m`
Question 7
Light of wavelength `5.4 × 10⁻⁷` m is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The separation between adjacent lines in the grating is `2.0 × 10⁻⁶ " m"`. The light that emerges from the grating falls on a semicircular screen, as shown in the view from above. The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
How many bright dots are formed on the screen?
since light can't diffract beyond this angle (semicircular screen).
Solve for the maximum order nn where :
`n <= d / lambda = (2.0 xx 10^-6) / (5.4 xx 10^-7) approx 3.7`
So the maximum integer order is `3`; `n=0, ±1, ±2, ±3`
This gives 7 total bright spots.
Question 8
The diagram shows a diffraction grating and a monochromatic source of light with wavelength. What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
A. The angle of diffraction remains the same.
B. The angle of diffraction is decreased.
C. The angle of diffraction is increased.
D. There is not enough information to know what will happen.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: The angle of diffraction increases, so does not remain the same.
B. Incorrect: the angle of diffraction increases, so does not decrease.
C. Correct:
When the wavelength of the light is increased, it must diffract through a gap that is much smaller in relation to its length.
This means it “bends” or diffracts more, creating a larger angle of diffraction θ. This can also be seen from the diffraction grating equation. Sinθ is directly proportional to λ. This means that if λ increases then so does sinθ. If sinθ is increasing then so is θ.
D. Incorrect: There is enough information to know that the angle of diffraction will increase because of an increase in wavelength λ.
Question 9
What is a diffraction grating?
A. Two slits created as two gaps within a material through which waves can be diffracted.
B. A plate consisting of a very large number of parallel, identical, closely-spaced slits.
C. A circular aperture through which light can be diffracted and then images resolved.
D. A photographic filter that allows light in only one plane to pass through.
Answer: B
Diffraction gratings are made up of hundreds of slits per mm of their width.
The slits must all be: In the same direction (therefore parallel to each other), having the same width and height (identical to each other), very close together.
Question 10
A beam of monochromatic light with a wavelength of 690 nm is directed at a diffraction grating with 300 lines per mm as shown in the diagram. This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?
This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?
Slit separation: `d = 1 / 300 = 3.33 xx 10^-3 " mm" = 3.33 xx 10^-6 " m"`
`n = (d xx sin theta) / lambda = ((3.33 xx 10^-6) xx sin 90^@^) / (690 xx 10^-9) = 4.8`
This means, the 4th bright fringe can be observed but not the 5th bright fringe.
Since 4.8 < 5, there are 4 bright fringes on the other side and one central fringe.
The total number of fringes`= 4 + 1 + 4 = 9`.
Question 1
Calculate the angles at which the first and second maxima are formed when a monochromatic light of wavelength 7.2 × 10−7 is shone perpendicularly onto a grating with 5000 lines per cm.
Question 2
A diffraction grating has 12,500 lines per centimetre.
When monochromatic light is shone on the grating, the first maximum is found to be at an angle of 30∘ to the central maximum. Calculate the wavelength of the light.
Question 3
This diagram shows the experimental setup (left) used to analyse the spectrum of a sodium discharge lamp with a diffraction grating with 500 lines mm-1, and the spectral lines observed (right) in the developed photographic film. a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
a. Explain why two spectra are observed.
b. Describe two differences between these two spectra.
c. The green maximum near end A is at an angle θ of 19.5°.
i. Calculate the wavelength of the green light.
ii. Calculate the angle produced by the second green line.
Question 4
A diffraction grating and a screen are used to determine the single wavelength λ of the light from a source.
What is an essential feature of this experiment?
A. A curved screen must be used.
B. The diffraction angle θ must be measured for at least two interference maxima.
C. The light waves incident on the grating must be coherent.
D. The third order intensity maximum must be produced.
Question 5
Light of a single unknown wavelength and blue light of a single wavelength are both incident normally on a diffraction grating. Two diffraction patterns are produced, one for each wavelength of light.
The third-order maximum for the blue light occurs at the same angle as the second-order maximum for the light of unknown wavelength. The wavelength of the blue light is 480 nm.
What is the unknown wavelength?
Question 6
A parallel beam of light consists of light of wavelength 420 nm and light of wavelength 630 nm.
The light is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The diffraction maxima for the two wavelengths overlap only at an angle of 31° from the direction of the incident light beam.
What could be the line spacing of the diffraction grating?
Question 7
Light of wavelength `5.4 × 10⁻⁷` m is incident normally on a diffraction grating.
The separation between adjacent lines in the grating is `2.0 × 10⁻⁶ " m"`. The light that emerges from the grating falls on a semicircular screen, as shown in the view from above. The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
The grating is at the centre of the semicircle, and the lines of the grating are vertical.
How many bright dots are formed on the screen?
Question 8
The diagram shows a diffraction grating and a monochromatic source of light with wavelength. What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
What happens to the angle of diffraction when the wavelength of light is increased, but all the other equipment remains the same?
A. The angle of diffraction remains the same.
B. The angle of diffraction is decreased.
C. The angle of diffraction is increased.
D. There is not enough information to know what will happen.
Question 9
What is a diffraction grating?
A. Two slits created as two gaps within a material through which waves can be diffracted.
B. A plate consisting of a very large number of parallel, identical, closely-spaced slits.
C. A circular aperture through which light can be diffracted and then images resolved.
D. A photographic filter that allows light in only one plane to pass through.
Question 10
A beam of monochromatic light with a wavelength of 690 nm is directed at a diffraction grating with 300 lines per mm as shown in the diagram. This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?
This set up produces a series of maxima on the screen, what is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed?