Question 1
In a double-slit experiment using light from a helium–neon laser, a student obtained the following results:
Width of 10 fringes 10x = 1.5 cm.
Separation of slits a = 1.0 mm.
Slit-to-screen distance D = 2.40 m.
Calculate the wavelength of the light in nm.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Use the equation to explain the following observations:
a. With the slits closer together, the fringes are further apart.
b. Interference fringes for blue light are closer together than for red light.
c. In an experiment to measure the wavelength of light, it is desirable to have the screen as far from the slits as possible.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
a. Explain what is meant by the term superposition.
b. In a double-slit experiment, yellow light of wavelength 590 nm from a sodium discharge tube is used. A student sets up a screen 1.8 m from the double-slit. The distance between 12 bright fringes is measured to be 16.8 mm.
Calculate the separation of the slits.
c. Describe the effect of:
i. Using slits of narrower width, but with the same separation.
ii. Using slits with a smaller separation, but of the same width.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The diagram shows an arrangement for demonstrating two-source interference using coherent light of a single wavelength λ.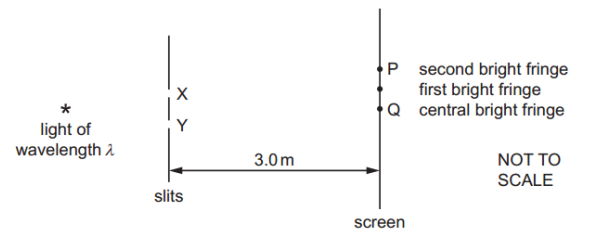 An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
The central bright fringe is at Q, and the second bright fringe from the center is at P.
What is the distance between Q and P?
A. 6 × 103
B. 3 × 103 λ.
C. 6.7 × 10−4 λ.
D. 3.3 × 10−4 λ.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Two identical waves are produced by sources at points P and Q. The waves travel along different paths to reach point R, as shown.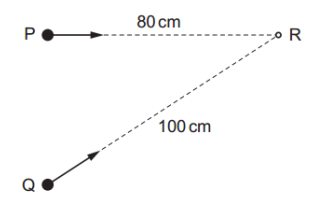 Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
What is the phase difference between the waves as they leave points P and Q?
A. 0∘.
B. 60∘.
C. 90∘.
D. 120∘.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A teacher sets up the apparatus shown to demonstrate a double-slit interference pattern on a screen. Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
A. Decrease the distance p.
B. Decrease the distance q.
C. Decrease the distance r.
D. Decrease the wavelength of the light.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
In a two-source interference experiment, light of a single frequency is incident on a double slit.
The light waves emerging from the slits are coherent.
What is meant by coherent?
A. The waves are in phase.
B. The waves have a constant phase difference.
C. The waves have the same amplitude.
D. The waves interfere constructively wherever they overlap.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
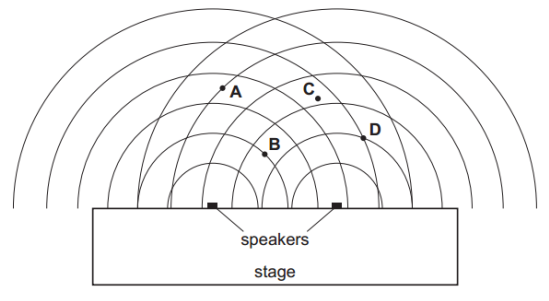
An outdoor concert has two large speakers beside the stage for broadcasting music.
In order to test the speakers, they are made to emit sound of the same wavelength and the same amplitude.
The curved lines in the diagram represent wavefronts.
Where is the loudest sound heard?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A beam of light from a laser is incident normally on a double slit. Interference fringes are seen on a screen placed parallel to the double slit.
The separation of the two slits is . The distance between the slits and the screen is . The distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes is x.
and are both halved.
What is the distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes after these changes?
A. `x/2`
B. `x`
C. `2x`
D. `4x`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Light from a laser is used to produce an interference pattern on a screen, as shown in figure.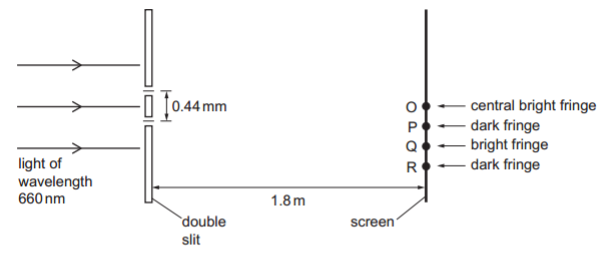 The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The central bright fringe on the screen is formed at point O. The next dark fringe below point O is formed at point P. The next bright fringe and the next dark fringe below point P are formed at points Q and R respectively.
a. The light waves from the two slits are coherent.
State what is meant by coherent.
b. For the two light waves superposing at R, calculate:
i. The difference in their path lengths, in nm, from the slits.
ii. Their phase difference.
c. Calculate the distance OQ.
d. The intensity of the light incident on the double slit is increased without changing the frequency.
Describe how the appearance of the fringes after this change is different from, and similar to, their appearance before the change.
e. The light of wavelength 660 nm is now replaced by blue light from a laser.
State and explain the change, if any, that must be made to the separation of the two slits so that the fringe separation on the screen is the same as it was for light of wavelength 660 nm.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
In a double-slit experiment using light from a helium–neon laser, a student obtained the following results:
Width of 10 fringes 10x = 1.5 cm.
Separation of slits a = 1.0 mm.
Slit-to-screen distance D = 2.40 m.
Calculate the wavelength of the light in nm.
Fringe seperation: `x=(1.5xx10^2)/10=1.5xx10^-3 " m"`
Wavelength:
`lambda = (a xx x) / D = (1 xx 10^-3 xx 1.5 xx 10^-3) / 2.4 = 6.25 xx 10^-7 " m"`
Therefore, `lambda = "625 nm"`
Question 2
Use the equation to explain the following observations:
a. With the slits closer together, the fringes are further apart.
b. Interference fringes for blue light are closer together than for red light.
c. In an experiment to measure the wavelength of light, it is desirable to have the screen as far from the slits as possible.
a. `x = (lambda xx D) / a`, therefore `x prop 1/a`, so decreasing a gives increased x.
b. Blue light has shorter wavelength; x ∝ λ so x is less.
c. x is directly proportional to D. For larger D, x is greater, so there is a smaller percentage uncertainty in x.
Question 3
a. Explain what is meant by the term superposition.
b. In a double-slit experiment, yellow light of wavelength 590 nm from a sodium discharge tube is used. A student sets up a screen 1.8 m from the double-slit. The distance between 12 bright fringes is measured to be 16.8 mm.
Calculate the separation of the slits.
c. Describe the effect of:
i. Using slits of narrower width, but with the same separation.
ii. Using slits with a smaller separation, but of the same width.
a. Superposition is the algebraic summing of the displacements of two (or more) waves.
b. `lambda = (a xx x) / D`
Leading to `a = (lambda xx D) / x = (590 xx 10^-9 xx 1.8 xx 12) / (16.8 xx 10^-3)= 6.3 xx 10^-4 " m"`
c.
i. More fringes seen on screen or fringe brightness decreases less from middle to edge of screen.
Less bright.
ii. Fringes wider/farther apart.
Same brightness.
Question 4
The diagram shows an arrangement for demonstrating two-source interference using coherent light of a single wavelength λ. An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
The central bright fringe is at Q, and the second bright fringe from the center is at P.
What is the distance between Q and P?
A. 6 × 103
B. 3 × 103 λ.
C. 6.7 × 10−4 λ.
D. 3.3 × 10−4 λ.
Answer: A
In a double-slit interference pattern, the position yn of the -th bright fringe from the center is given by:
`y_n = (n xx lambda xx D) / a`
`y_2 = (2 xx lambda xx 3) / (1 xx 10^-3)`
`y_2 = (6.0 xx lambda) / (10^-3)`
`y_2 = 6 xx 10^3 " " lambda`
Question 5
Two identical waves are produced by sources at points P and Q. The waves travel along different paths to reach point R, as shown. Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
What is the phase difference between the waves as they leave points P and Q?
A. 0∘.
B. 60∘.
C. 90∘.
D. 120∘.
Path difference : `Delta x = "100 cm" - "80 cm" = "20 cm"`
Phase difference is related to path difference
`Delta phi = (360^@ / lambda) xxDelta x`
`Delta phi = (360^@ / 6 ) xx20`
`Delta phi = 60^@ xx 20 = 1200^@`
`1200^@ - 3 xx 360^@ = 120^@`
Explanation of the calculation:
represents the total raw phase difference calculated based on the path difference.
Every 360∘ corresponds to one full cycle of a wave (one complete wavelength).
Since phase is cyclic (repeats every 360∘), we can subtract multiples of 360 without changing the physical meaning:
3 × 360∘ = 1080∘ corresponds to 3 full wave cycles.
Subtracting 1080∘ from 1200∘ leaves 120∘, which is the effective phase difference that actually matters.
Question 6
A teacher sets up the apparatus shown to demonstrate a double-slit interference pattern on a screen. Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
A. Decrease the distance p.
B. Decrease the distance q.
C. Decrease the distance r.
D. Decrease the wavelength of the light.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: is distance from source to single slit; does not affect fringe spacing directly.
B. Correct:
Formula for fringe separation (x) in a double-slit experiment: `x = (lambdaxx r) / q`
To increase x, we can:
Increase λ (wavelength),
Increase r (distance to screen),
Decrease q (slit separation).
C. Incorrect: Decreases distance to screen → decreases fringe separation.
D. Incorrect: Decreases λ\lambda → decreases fringe separation.
Question 7
In a two-source interference experiment, light of a single frequency is incident on a double slit.
The light waves emerging from the slits are coherent.
What is meant by coherent?
A. The waves are in phase.
B. The waves have a constant phase difference.
C. The waves have the same amplitude.
D. The waves interfere constructively wherever they overlap.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Coherent waves can have any fixed phase difference, not necessarily 0°.
B. Correct:
Coherence between two waves means:
They maintain a constant phase difference over time.
They must have the same frequency (but not necessarily the same amplitude).
C. Incorrect: Coherence is about phase, not amplitude. Waves can have different amplitudes and still be coherent.
D. Incorrect: They can interfere constructively or destructively depending on their phase at the overlap point.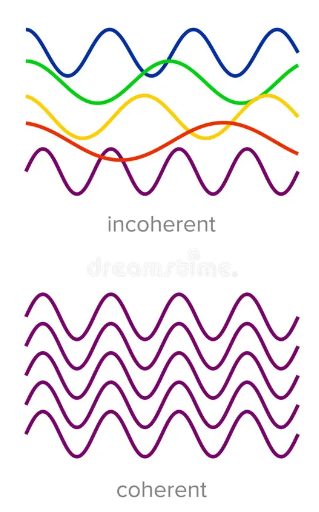
Question 8
An outdoor concert has two large speakers beside the stage for broadcasting music.
In order to test the speakers, they are made to emit sound of the same wavelength and the same amplitude.
The curved lines in the diagram represent wavefronts.
Where is the loudest sound heard?

Answer: D
Look at the wavefronts:
At D, the wavefronts from both speakers perfectly align (crest meets crest).
At A, B, and C, the wavefronts do not align perfectly - meaning partial or destructive interference happens.
Thus:
At D, constructive interference occurs → loudest sound.
Question 9
A beam of light from a laser is incident normally on a double slit. Interference fringes are seen on a screen placed parallel to the double slit.
The separation of the two slits is . The distance between the slits and the screen is . The distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes is x.
and are both halved.
What is the distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes after these changes?
A. `x/2`
B. `x`
C. `2x`
D. `4x`
Answer: B
Formula for fringe separation `x` in a double-slit experiment:
`x = (lambdaxx D) / a`
New fringe spacing `x'`: `x' = (lambdaxx D) / a`
Thus: `x'=x`
The fringe separation is constant.
Question 10
Light from a laser is used to produce an interference pattern on a screen, as shown in figure. The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The central bright fringe on the screen is formed at point O. The next dark fringe below point O is formed at point P. The next bright fringe and the next dark fringe below point P are formed at points Q and R respectively.
a. The light waves from the two slits are coherent.
State what is meant by coherent.
b. For the two light waves superposing at R, calculate:
i. The difference in their path lengths, in nm, from the slits.
ii. Their phase difference.
c. Calculate the distance OQ.
d. The intensity of the light incident on the double slit is increased without changing the frequency.
Describe how the appearance of the fringes after this change is different from, and similar to, their appearance before the change.
e. The light of wavelength 660 nm is now replaced by blue light from a laser.
State and explain the change, if any, that must be made to the separation of the two slits so that the fringe separation on the screen is the same as it was for light of wavelength 660 nm.
a. Coherent waves have a constant phase difference between them.
b.
i. Since R is a dark fringe, and it is the second dark fringe from the center (O → P → Q → R), the path difference is:
Path difference for dark fringe:
`Delta x = (n + 0.5) lambda`
At R:
From O to P: 1st dark fringe → `n` = 0From P to R: another half-wavelength → `n` = 1Thus, total path difference: `Delta x = (1.5) xx660 = "990 nm"`
ii. Phase difference `Delta phi` is related to path difference `Deltax`
`Delta phi = (360^@ / lambda) xx Delta x=(360^@/660)xx990=540^@`
c. `x = (lambda xxD) / a=x = (660 xx 10^-9 xx1.8) / (0.44 xx 10^-3)=2.7 xx10^-3 " m"`
d. Bright fringes are brighter.
No change to dark fringes.
No change to fringe separation or fringe separation.
Explanation:
The intensity `I` of a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude A: `I prop A^2`
Increasing the intensity means the amplitude of the light waves increases.
In constructive interference (where the bright fringes form), the amplitudes add up, so the maximum amplitude is higher.
As a result, the bright fringes appear brighter.
Dark fringes occur where the two waves are completely out of phase (destructive interference).
Even if the amplitudes are bigger, the waves still cancel each other out perfectly at dark fringes.
Thus, there is no light intensity at those points.
No change to dark fringes.
The fringe separation `x` depends only on the wavelength `lamda`, the distance to the screen `D`, and the slit separation : `x = (lambda xxD) / a`
Since the problem says that the frequency (and thus wavelength) remains unchanged.
And `D` and `a` are also unchanged.
Therefore, the fringe separation remains the same.
e. Blue light has shorter wavelength than 660 nm.
From the formula: `x prop lambda`
If `lambda` decreases, to keep `x` constant, we must also decrease slit separation `a`.
Question 1
In a double-slit experiment using light from a helium–neon laser, a student obtained the following results:
Width of 10 fringes 10x = 1.5 cm.
Separation of slits a = 1.0 mm.
Slit-to-screen distance D = 2.40 m.
Calculate the wavelength of the light in nm.
Question 2
Use the equation to explain the following observations:
a. With the slits closer together, the fringes are further apart.
b. Interference fringes for blue light are closer together than for red light.
c. In an experiment to measure the wavelength of light, it is desirable to have the screen as far from the slits as possible.
Question 3
a. Explain what is meant by the term superposition.
b. In a double-slit experiment, yellow light of wavelength 590 nm from a sodium discharge tube is used. A student sets up a screen 1.8 m from the double-slit. The distance between 12 bright fringes is measured to be 16.8 mm.
Calculate the separation of the slits.
c. Describe the effect of:
i. Using slits of narrower width, but with the same separation.
ii. Using slits with a smaller separation, but of the same width.
Question 4
The diagram shows an arrangement for demonstrating two-source interference using coherent light of a single wavelength λ. An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
An interference pattern is observed on a screen 3 m away from the slits X and Y, which have a seperation of 1 mm.
The central bright fringe is at Q, and the second bright fringe from the center is at P.
What is the distance between Q and P?
A. 6 × 103
B. 3 × 103 λ.
C. 6.7 × 10−4 λ.
D. 3.3 × 10−4 λ.
Question 5
Two identical waves are produced by sources at points P and Q. The waves travel along different paths to reach point R, as shown. Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
Both waves have a wavelength of 6.0 cm. The waves are in phase at point R.
What is the phase difference between the waves as they leave points P and Q?
A. 0∘.
B. 60∘.
C. 90∘.
D. 120∘.
Question 6
A teacher sets up the apparatus shown to demonstrate a double-slit interference pattern on a screen. Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
Which change to the apparatus will increase the fringe spacing?
A. Decrease the distance p.
B. Decrease the distance q.
C. Decrease the distance r.
D. Decrease the wavelength of the light.
Question 7
In a two-source interference experiment, light of a single frequency is incident on a double slit.
The light waves emerging from the slits are coherent.
What is meant by coherent?
A. The waves are in phase.
B. The waves have a constant phase difference.
C. The waves have the same amplitude.
D. The waves interfere constructively wherever they overlap.
Question 8
An outdoor concert has two large speakers beside the stage for broadcasting music.
In order to test the speakers, they are made to emit sound of the same wavelength and the same amplitude.
The curved lines in the diagram represent wavefronts.
Where is the loudest sound heard?

Question 9
A beam of light from a laser is incident normally on a double slit. Interference fringes are seen on a screen placed parallel to the double slit.
The separation of the two slits is . The distance between the slits and the screen is . The distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes is x.
and are both halved.
What is the distance between the centres of two adjacent bright fringes after these changes?
A. `x/2`
B. `x`
C. `2x`
D. `4x`
Question 10
Light from a laser is used to produce an interference pattern on a screen, as shown in figure. The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The light of wavelength 660 nm is incident normally on two slits that have a separation of 0.44 mm. The double slit is parallel to the screen. The perpendicular distance between the double slit and the screen is 1.8 m.
The central bright fringe on the screen is formed at point O. The next dark fringe below point O is formed at point P. The next bright fringe and the next dark fringe below point P are formed at points Q and R respectively.
a. The light waves from the two slits are coherent.
State what is meant by coherent.
b. For the two light waves superposing at R, calculate:
i. The difference in their path lengths, in nm, from the slits.
ii. Their phase difference.
c. Calculate the distance OQ.
d. The intensity of the light incident on the double slit is increased without changing the frequency.
Describe how the appearance of the fringes after this change is different from, and similar to, their appearance before the change.
e. The light of wavelength 660 nm is now replaced by blue light from a laser.
State and explain the change, if any, that must be made to the separation of the two slits so that the fringe separation on the screen is the same as it was for light of wavelength 660 nm.