Question 1
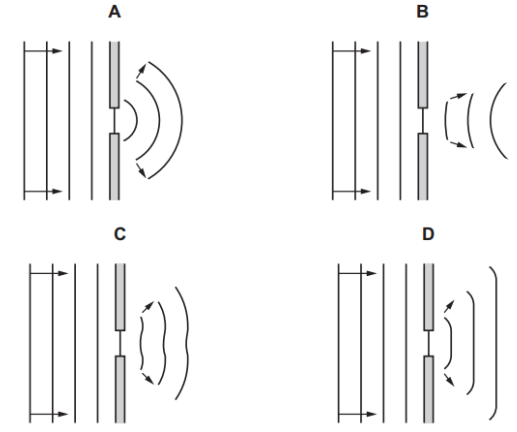
Water waves in a ripple tank are made to pass through a small gap as shown.
Which diagram shows the waves after they have passed through the gap?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which wave behaviour is shown in the diagram?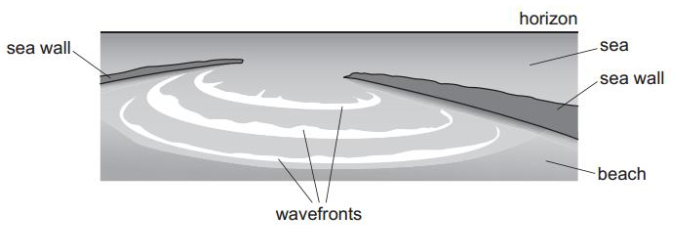 A. Diffraction.
A. Diffraction.
B. Doppler shift.
C. Interference.
D. Superposition.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which diagram best shows how water waves diffract when they pass through a gap in a barrier?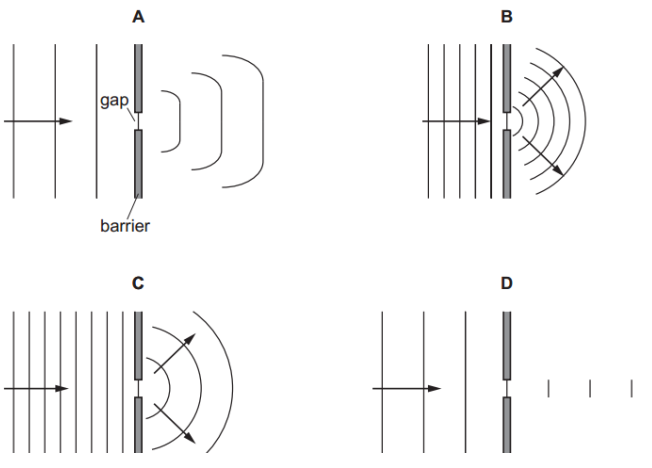
A. Gap causes straight lines to shift slightly.
B. Gap causes waves to spread in circular arcs.
C. Waves curve too soon before reaching the gap.
D. Gap does not affect the waves at all.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Water waves of wavelength λ are incident normally on an obstacle with a narrow gap. The width of the gap is equal to λ. The waves from the gap emerge over an angle , as shown.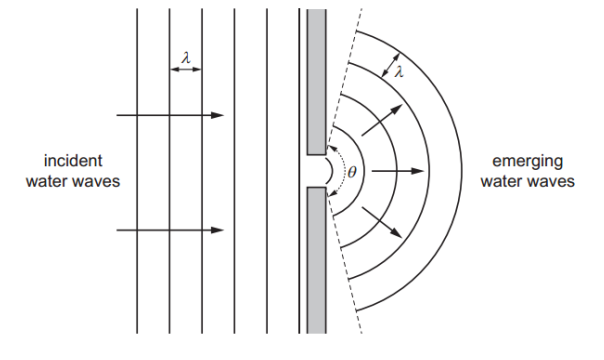 Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
| θ | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | decreases | remains the same |
| B | increases | remains the same |
| C | remains the same | decreases |
| D | remains the same | increases |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A bar vibrates with frequency to produce water waves in a ripple tank.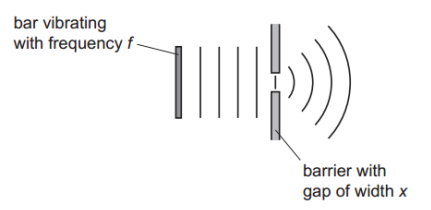
The waves pass through a gap of width in a barrier so that diffraction occurs.
Which combination of vibration frequency and gap width will produce the smallest angle of diffraction?
| vibration frequency | gap width | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `f/2` | `x/2` |
| B | `f/2` | `2x` |
| C | `2f` | `x/2` |
| D | `2f` | `2x` |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which of the following is the definition of diffraction?
A. Change of direction when waves cross the boundary between one medium and another.
B. Splitting of white light into colours.
C. Addition of two coherent waves to produce a stationary wave pattern.
D. Bending of waves around an obstacle.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
For which types of wave does diffraction occur?
A. In all waves.
B. In soundwaves only.
C. In transverse waves only.
D. In light waves only.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Wavefront diagrams can be used to indicate the frequency of waves.
Which wave has the lowest frequency?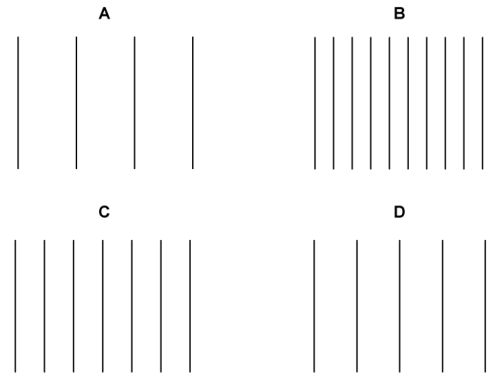
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
An atomic lattice has a spacing of around 10-10 m, which electromagnetic wave would cause the most significant diffraction effect?
A. X-ray.
B. Infrared.
C. Microwave.
D. Ultraviolet.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Which property would be different at S compared to T?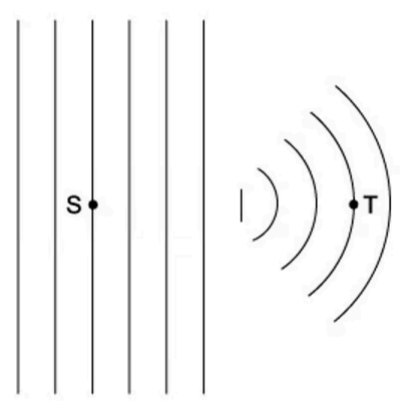 A. Frequency.
A. Frequency.
B. Amplitude.
C. Wavelength.
D. Velocity.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Water waves in a ripple tank are made to pass through a small gap as shown.
Which diagram shows the waves after they have passed through the gap?

Answer: A
A. Correct:
Waves spread widely in semicircular arcs after passing through a small gap.
Consistent with the physics of wave diffraction.
B. Incorrect:
Waves show very little spreading.
In reality, when the gap is small, significant spreading occurs, not narrow wavefronts like in (B).
C. Incorrect:
The waves appear to change shape strangely and look uneven (wavy pattern), not spread out smoothly.
Diffraction after a small gap should create smooth circular arcs, not strange or uneven shapes.
D. Incorrect:
The waves are curved but the spreading is too limited.
Also, the wavefronts look compressed rather than spreading out.
Question 2
Which wave behaviour is shown in the diagram? A. Diffraction.
A. Diffraction.
B. Doppler shift.
C. Interference.
D. Superposition.
Answer: A
A. Correct: Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves when they pass through a small opening.
B. Incorrect: Doppler effect happens when the source or observer moves, causing a change in wave frequency. Here, the waves change shape because of a barrier, not because of motion.
C. Incorrect: Interference is when two or more waves overlap and combine. In the diagram, only one wavefront is shown passing through the gap - no overlapping wave sources.
D. Incorrect: Superposition is a general principle where multiple waves add together. The diagram only shows single waves, not overlapping ones.
Question 3
Which diagram best shows how water waves diffract when they pass through a gap in a barrier?
A. Gap causes straight lines to shift slightly.
B. Gap causes waves to spread in circular arcs.
C. Waves curve too soon before reaching the gap.
D. Gap does not affect the waves at all.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: The waves stay mostly straight after the gap with minimal spreading.
B. Correct:
Waves pass through the small gap and spread into perfect semicircular arcs.
This is exactly what diffraction predicts for waves passing a narrow opening.
C. Incorrect: Waves begin curving before reaching the gap.
D. Incorrect: Waves pass straight through without any noticeable bending or spreading.
Question 4
Water waves of wavelength λ are incident normally on an obstacle with a narrow gap. The width of the gap is equal to λ. The waves from the gap emerge over an angle , as shown. Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
| θ | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | decreases | remains the same |
| B | increases | remains the same |
| C | remains the same | decreases |
| D | remains the same | increases |
Answer: A
A. Correct:
decreases (less spreading because gap is larger).
Wavelength remains the same (medium does not change).
B. Incorrect: increasing the gap reduces diffraction, so θ must decrease, not increase.
C. Incorrect: Wavelength depends only on the medium, not the size of the gap.
D. Incorrect: Wavelength is unaffected by gap size.
Question 5
A bar vibrates with frequency to produce water waves in a ripple tank.
The waves pass through a gap of width in a barrier so that diffraction occurs.
Which combination of vibration frequency and gap width will produce the smallest angle of diffraction?
| vibration frequency | gap width | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `f/2` | `x/2` |
| B | `f/2` | `2x` |
| C | `2f` | `x/2` |
| D | `2f` | `2x` |
Answer: D
Explanation:
Diffraction angle becomes smaller when the gap is much larger than the wavelength.
Wavelength λ is related to frequency f by: `lambda = v/f`
Thus:
Higher frequency → smaller wavelength λ.
Smaller wavelength → less diffraction.
Wider gap → less diffraction.
To produce the smallest diffraction angle, we want:
Large gap width.
High frequency (small wavelength).
Question 6
Which of the following is the definition of diffraction?
A. Change of direction when waves cross the boundary between one medium and another.
B. Splitting of white light into colours.
C. Addition of two coherent waves to produce a stationary wave pattern.
D. Bending of waves around an obstacle.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Diffraction happens when a wave meets an object or slit.
It is defined as the bending of the waves around corners or through an aperture.
For very small aperture sizes the majority of the wave is blocked.
For large aperture sizes, the wave passes with very little diffraction, largely at the edges.
Question 7
For which types of wave does diffraction occur?
A. In all waves.
B. In soundwaves only.
C. In transverse waves only.
D. In light waves only.
Answer: A
Diffraction occurs in all types of wave including sound waves, light waves and all transverse waves.
Question 8
Wavefront diagrams can be used to indicate the frequency of waves.
Which wave has the lowest frequency?
Answer: A
The distance between two wavefronts is equal to one wavelength.
Lower frequency waves have longer wavelengths, and higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths.
Wave A has the longest wavelength. Therefore, wave A has the lowest frequency.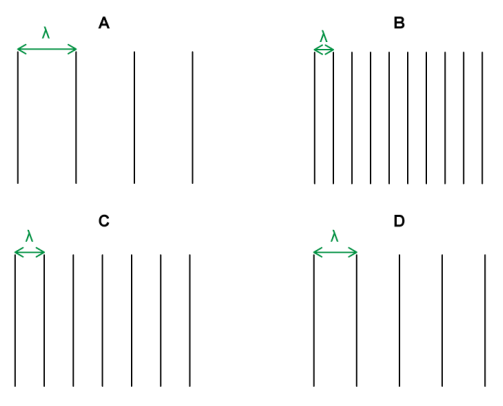
Question 9
An atomic lattice has a spacing of around 10-10 m, which electromagnetic wave would cause the most significant diffraction effect?
A. X-ray.
B. Infrared.
C. Microwave.
D. Ultraviolet.
Answer: A
Explanation:
For significant diffraction, the wavelength λ of the wave should be approximately the same size as the obstacle.
Thus, we need an electromagnetic wave with wavelength about 10−10 m.
X-ray is EM wave of wavelength about 10−10 m.
Question 10
Which property would be different at S compared to T? A. Frequency.
A. Frequency.
B. Amplitude.
C. Wavelength.
D. Velocity.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: The frequency is determined by the source and so remains constant.
B. Correct:
The diagram shows the wavefronts at S and T, the only difference between the two points is that the wave has travelled through a slit or gap.
Only the amplitude of the wave changes as some energy is dissipated as it passes through the gap.
C. Incorrect: The wavelength is constant as the wavefronts are constant in the diagram.
D. Incorrect: The velocity would remain constant as both wavelength and frequency are constant.
Question 1
Water waves in a ripple tank are made to pass through a small gap as shown.
Which diagram shows the waves after they have passed through the gap?

Question 2
Which wave behaviour is shown in the diagram? A. Diffraction.
A. Diffraction.
B. Doppler shift.
C. Interference.
D. Superposition.
Question 3
Which diagram best shows how water waves diffract when they pass through a gap in a barrier?
A. Gap causes straight lines to shift slightly.
B. Gap causes waves to spread in circular arcs.
C. Waves curve too soon before reaching the gap.
D. Gap does not affect the waves at all.
Question 4
Water waves of wavelength λ are incident normally on an obstacle with a narrow gap. The width of the gap is equal to λ. The waves from the gap emerge over an angle , as shown. Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
Which changes, if any, occur to θ and to the wavelength of the emerging waves?
| θ | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | decreases | remains the same |
| B | increases | remains the same |
| C | remains the same | decreases |
| D | remains the same | increases |
Question 5
A bar vibrates with frequency to produce water waves in a ripple tank.
The waves pass through a gap of width in a barrier so that diffraction occurs.
Which combination of vibration frequency and gap width will produce the smallest angle of diffraction?
| vibration frequency | gap width | |
|---|---|---|
| A | `f/2` | `x/2` |
| B | `f/2` | `2x` |
| C | `2f` | `x/2` |
| D | `2f` | `2x` |
Question 6
Which of the following is the definition of diffraction?
A. Change of direction when waves cross the boundary between one medium and another.
B. Splitting of white light into colours.
C. Addition of two coherent waves to produce a stationary wave pattern.
D. Bending of waves around an obstacle.
Question 7
For which types of wave does diffraction occur?
A. In all waves.
B. In soundwaves only.
C. In transverse waves only.
D. In light waves only.
Question 8
Wavefront diagrams can be used to indicate the frequency of waves.
Which wave has the lowest frequency?
Question 9
An atomic lattice has a spacing of around 10-10 m, which electromagnetic wave would cause the most significant diffraction effect?
A. X-ray.
B. Infrared.
C. Microwave.
D. Ultraviolet.
Question 10
Which property would be different at S compared to T? A. Frequency.
A. Frequency.
B. Amplitude.
C. Wavelength.
D. Velocity.