Question 1
For each of the following frequencies, state the type of electromagnetic wave to which it corresponds.
a. 200 kHz.
b. 100 MHz.
c. 5 × 1014 Hz.
d. 1018 Hz.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The table shows the wavelengths of five electromagnetic waves.
Which row correctly identifies the principal radiation for each of these wavelengths?
| 10⁻¹⁴ m | 10⁻¹⁰ m | 10⁻⁶ m | 10⁻² m | 10² m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | gamma-ray | X-ray | infrared | microwave | radio wave |
| B | radio wave | microwave | infrared | X-ray | gamma-ray |
| C | radio wave | microwave | ultraviolet | infrared | X-ray |
| D | X-ray | infrared | ultraviolet | microwave | radio wave |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The table lists possible wavelengths of four different electromagnetic waves.
Which row is correct?
| type of wave | approximate wavelength/m | |
|---|---|---|
| A | infrared | 10⁻⁵ |
| B | radio | 10⁻³ |
| C | ultraviolet | 10⁻¹² |
| D | X-rays | 10⁻⁷ |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Microwaves in a vacuum travel at speed and have wavelength of order of magnitude .
What are the speed and a possible order of magnitude of wavelength of X-rays in a vacuum?
| speed | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | X | 10⁻⁸ Y |
| B | X | 10⁻⁴ Y |
| C | 10⁴ X | Y |
| D | 10⁸ X | Y |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Two lasers emit light in a vacuum. One laser emits red light and the other emits green light.|
Which property of the light from the two lasers must be different?
A. Amplitude.
B. Frequency.
C. Intensity.
D. Speed.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which list shows electromagnetic waves in order of decreasing frequency?
A. Gamma-rays → infrared → ultraviolet → radio waves.
B. Gamma-rays → ultraviolet → infrared → radio waves.
C. Radio waves → infrared → ultraviolet → gamma-rays.
D. Radio waves → ultraviolet → infrared → gamma-rays.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which statement about electromagnetic waves is correct?
A. A wave of wavelength 5 × 10−6 is invisible to the human eye.
B. They can all travel at different speeds in free space.
C. They cannot be polarised.
D. They consist of vibrating atoms.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
An electromagnetic wave in free space has a frequency of 2.5 × 1014 Hz.
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum includes this frequency?
A. Infrared.
B. Microwave.
C. Ultraviolet.
D. X-ray.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
a. State one property of electromagnetic waves that is not common to other transverse waves.
b. The seven regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are represented by blocks labelled A to G in figure A typical wavelength for the visible region D is 500 nm.
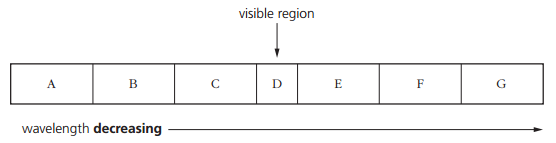 i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
ii. Calculate the frequency corresponding to a wavelength of 500 nm.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
For each of the following frequencies, state the type of electromagnetic wave to which it corresponds.
a. 200 kHz.
b. 100 MHz.
c. 5 × 1014 Hz.
d. 1018 Hz.
a. Radio waves.
b. Radio waves.
c. Visible light.
d. X-rays or γ-rays.
Question 2
Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
`v = fxx lambda`
`lambda = v / f`
`lambda = (3.00 xx 10^8) / (2 xx 10^18) = 1.5 xx 10^-10 " m" = "0.15 nm"`
Question 3
The table shows the wavelengths of five electromagnetic waves.
Which row correctly identifies the principal radiation for each of these wavelengths?
| 10⁻¹⁴ m | 10⁻¹⁰ m | 10⁻⁶ m | 10⁻² m | 10² m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | gamma-ray | X-ray | infrared | microwave | radio wave |
| B | radio wave | microwave | infrared | X-ray | gamma-ray |
| C | radio wave | microwave | ultraviolet | infrared | X-ray |
| D | X-ray | infrared | ultraviolet | microwave | radio wave |
Answer: A
Electromagnetic radiation types are categorized by their wavelengths (shorter = higher energy):
→ Gamma rays
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies.
10−10 m→ X-ray
Typical wavelength of X-rays ranges from 10−11 m to 10−8 m.
10−6 m → Infrared
Infrared radiation generally spans 10−6 m to 10−4 m.
10−2 m → Microwaves
Microwaves range from about 10−4 m to 10−1 m.
102 m → Radio waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the EM spectrum.
Question 4
The table lists possible wavelengths of four different electromagnetic waves.
Which row is correct?
| type of wave | approximate wavelength/m | |
|---|---|---|
| A | infrared | 10⁻⁵ |
| B | radio | 10⁻³ |
| C | ultraviolet | 10⁻¹² |
| D | X-rays | 10⁻⁷ |
Answer: A
Let’s review typical ranges of electromagnetic wave types: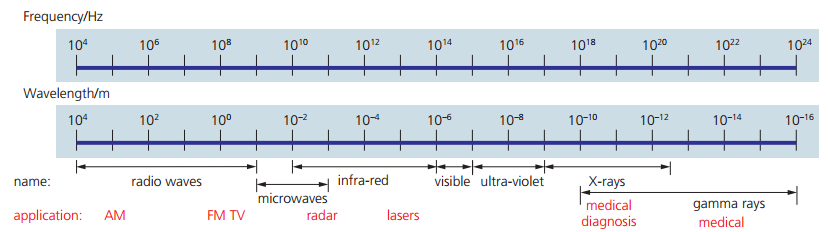
Question 5
Microwaves in a vacuum travel at speed and have wavelength of order of magnitude .
What are the speed and a possible order of magnitude of wavelength of X-rays in a vacuum?
| speed | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | X | 10⁻⁸ Y |
| B | X | 10⁻⁴ Y |
| C | 10⁴ X | Y |
| D | 10⁸ X | Y |
Answer: A
A. Correct:
All electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, including microwaves and X-rays, travel at the same speed, the speed of light c = 3 × 108 m.s-1. → So the speed of X-rays = X, the same as that of microwaves.
Microwaves typically have wavelengths around 10−2 , or roughly Y.
X-rays have wavelengths in the range of 10−8 to 10−12 m, much shorter than microwaves.
→ So a typical X-ray wavelength is about 10−8Y.
B. Incorrect: Speed is correct, but wavelength too long. 10−4Y = 10−6 m, which is more like ultraviolet, not X-rays.
C. Incorrect: Speed is too fast. X-rays don't travel faster than microwaves. All EM waves travel at
D. Incorrect: Speed is far too large, and not physically possible. EM waves can’t exceed c.
Question 6
Two lasers emit light in a vacuum. One laser emits red light and the other emits green light.|
Which property of the light from the two lasers must be different?
A. Amplitude.
B. Frequency.
C. Intensity.
D. Speed.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: The amplitude affects the intensity, not the color. Two lasers of different colors can have same or different amplitudes, but it's not required to differ.
B. Correct:
The color of light is determined by its frequency (or equivalently, its wavelength).
Red light has lower frequency and longer wavelength than green light.
Green light has higher frequency and shorter wavelength than red light.
Since one laser emits red and the other green, the frequency of the light must be different.
C. Incorrect: Intensity refers to the power per unit area. Two lasers can have the same or different intensities regardless of their color.
D. Incorrect: All electromagnetic waves, including red and green light, travel at the same speed in a vacuum:
c = 3 × 108
Question 7
Which list shows electromagnetic waves in order of decreasing frequency?
A. Gamma-rays → infrared → ultraviolet → radio waves.
B. Gamma-rays → ultraviolet → infrared → radio waves.
C. Radio waves → infrared → ultraviolet → gamma-rays.
D. Radio waves → ultraviolet → infrared → gamma-rays.
Answer: B
Base on the electromagnetic spectrum:
Question 8
Which statement about electromagnetic waves is correct?
A. A wave of wavelength 5 × 10−6 is invisible to the human eye.
B. They can all travel at different speeds in free space.
C. They cannot be polarised.
D. They consist of vibrating atoms.
Answer: A
A. Correct:
The wavelength 5 × 10−6 is 5 micrometers, which falls within the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The visible light range is approximately 400 nm to 700 nm (4 × 10−7 m to 7 × 10−7 m).
Therefore, 5 μm is outside the visible spectrum and cannot be seen by the human eye.
B. Incorrect: In a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed, c = 3 × 108 m, regardless of their frequency or wavelength. They only travel at different speeds in a medium, not in free space.
C. Incorrect: Electromagnetic waves can be polarised because they are transverse waves with oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Polarisation is a key property of transverse waves, and is not possible for longitudinal waves (like sound).
D. Incorrect: EM waves do not consist of vibrating atoms. They are composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
Question 9
An electromagnetic wave in free space has a frequency of 2.5 × 1014 Hz.
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum includes this frequency?
A. Infrared.
B. Microwave.
C. Ultraviolet.
D. X-ray.
Answer: A
Base on the electromagnetic spectrum:
Question 10
a. State one property of electromagnetic waves that is not common to other transverse waves.
b. The seven regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are represented by blocks labelled A to G in figure A typical wavelength for the visible region D is 500 nm.
 i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
ii. Calculate the frequency corresponding to a wavelength of 500 nm.
a. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or free space, unlike most other transverse waves which require a medium.
b.
i.
B: microwaves.
C: ultra-violet.
F: X-rays.
ii. `f = (3.00 xx 10^8)/(500 xx 10^-9) = 6.00 xx 10^14 " Hz"`
Question 1
For each of the following frequencies, state the type of electromagnetic wave to which it corresponds.
a. 200 kHz.
b. 100 MHz.
c. 5 × 1014 Hz.
d. 1018 Hz.
Question 2
Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
Question 3
The table shows the wavelengths of five electromagnetic waves.
Which row correctly identifies the principal radiation for each of these wavelengths?
| 10⁻¹⁴ m | 10⁻¹⁰ m | 10⁻⁶ m | 10⁻² m | 10² m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | gamma-ray | X-ray | infrared | microwave | radio wave |
| B | radio wave | microwave | infrared | X-ray | gamma-ray |
| C | radio wave | microwave | ultraviolet | infrared | X-ray |
| D | X-ray | infrared | ultraviolet | microwave | radio wave |
Question 4
The table lists possible wavelengths of four different electromagnetic waves.
Which row is correct?
| type of wave | approximate wavelength/m | |
|---|---|---|
| A | infrared | 10⁻⁵ |
| B | radio | 10⁻³ |
| C | ultraviolet | 10⁻¹² |
| D | X-rays | 10⁻⁷ |
Question 5
Microwaves in a vacuum travel at speed and have wavelength of order of magnitude .
What are the speed and a possible order of magnitude of wavelength of X-rays in a vacuum?
| speed | wavelength | |
|---|---|---|
| A | X | 10⁻⁸ Y |
| B | X | 10⁻⁴ Y |
| C | 10⁴ X | Y |
| D | 10⁸ X | Y |
Question 6
Two lasers emit light in a vacuum. One laser emits red light and the other emits green light.|
Which property of the light from the two lasers must be different?
A. Amplitude.
B. Frequency.
C. Intensity.
D. Speed.
Question 7
Which list shows electromagnetic waves in order of decreasing frequency?
A. Gamma-rays → infrared → ultraviolet → radio waves.
B. Gamma-rays → ultraviolet → infrared → radio waves.
C. Radio waves → infrared → ultraviolet → gamma-rays.
D. Radio waves → ultraviolet → infrared → gamma-rays.
Question 8
Which statement about electromagnetic waves is correct?
A. A wave of wavelength 5 × 10−6 is invisible to the human eye.
B. They can all travel at different speeds in free space.
C. They cannot be polarised.
D. They consist of vibrating atoms.
Question 9
An electromagnetic wave in free space has a frequency of 2.5 × 1014 Hz.
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum includes this frequency?
A. Infrared.
B. Microwave.
C. Ultraviolet.
D. X-ray.
Question 10
a. State one property of electromagnetic waves that is not common to other transverse waves.
b. The seven regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are represented by blocks labelled A to G in figure A typical wavelength for the visible region D is 500 nm.
 i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
i. Name the principle radiations and give a typical wavelength for each of the regions B, E and F.
ii. Calculate the frequency corresponding to a wavelength of 500 nm.