Question 1
A loudspeaker connected to a signal generator produces a steady note of frequency 256 Hz. An observer moves towards the loudspeaker at a speed of 25 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the sound that the observer hears (speed of sound = 330 m.s-1).
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A train with a whistle that emits a note of frequency 800 Hz is approaching a stationary observer at a speed of 60 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the note heard by the observer (speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency 420 Hz. The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of 25 m.s-1. The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
a. Explain why the pitch of the siren changes, as observed by the student.
b. Determine the maximum and minimum frequencies that the student will hear.
c. At which point in the boat’s motion will the student hear the most highpitched note?
(Speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A source emitting sound of a single frequency fs travels at constant speed directly towards an observer. The source then passes the observer and continues to move directly away from the observer. The velocity of the source remains constant.
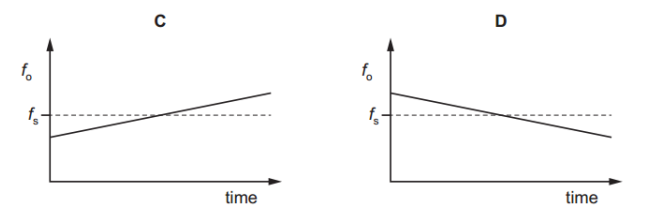
Which graph represents the variation with time of the frequency fo of the sound heard by the observer?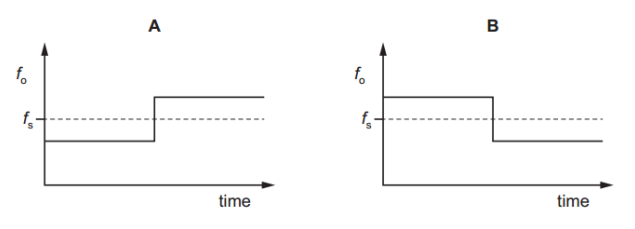
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A stationary person measures the speed and wavelength of the sound from a horn on a stationary vehicle. The person then repeats the measurements when the vehicle is approaching at a constant speed.
Which row describes the measured wavelength and the measured speed of the sound wave from the moving vehicle when compared with the sound wave from the stationary vehicle?
| wavelength of the sound wave | speed of the sound wave | |
|---|---|---|
| A | longer | greater |
| B | shorter | greater |
| C | longer | same |
| D | shorter | same |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A stationary source S emits a sound wave of frequency f.
The source now moves away from a stationary observer.
Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both higher than f.
B. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both lower than f.
C. The frequency of the source S is now lower than f.
D. The observed frequency is now lower than f.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
A person stands at the side of a straight railway track. A train moves towards the person and emits sound from its whistle. The person hears a sound of frequency 1690 Hz as the train approaches him. The person then hears a sound of frequency 1500 Hz as the train moves away from him. The speed of sound in air is 340 m.s-1. What is the speed of the train?
A. 20 m.s-1.
B. 38 m.s-1.
C. 41 m.s-1.
D. 43 m.s-1.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
A car is travelling at a constant velocity directly towards a man standing in the middle of the road. The driver sounds the car’s horn as a warning. The horn emits a sound wave of constant frequency. The frequency of the sound heard by the man is different from the frequency of the sound emitted by the horn. Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the sound emitted by the horn is greater than the frequency of the sound heard by the man.
B. The frequency of the sound heard by the man depends on the distance between the car and the man.
C. The sound waves continually accelerate as they move from the horn to the man.
D. The wavelength of the sound heard by the man is less than the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A source emits a sound wave of a single frequency. The Doppler effect causes a different frequency of sound to be heard by a stationary observer.
What is a requirement for the Doppler effect to occur?
A. A source that is moving as it produces the sound wave.
B. A source that produces a polarised sound wave.
C. A source that produces a sound wave of changing amplitude.
D. A source that produces a sound wave of changing frequency.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A police car travels towards a stationary observer at a speed of 15 m.s-1. The siren on the car emits a sound of frequency 250 Hz. Calculate the observed frequency. The speed of sound is 340 m.s-1.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
A loudspeaker connected to a signal generator produces a steady note of frequency 256 Hz. An observer moves towards the loudspeaker at a speed of 25 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the sound that the observer hears (speed of sound = 330 m.s-1).
When the observer is moving towards a stationary source (vo > 0), the apparent frequency increases.
We use the Doppler effect formula:
`f_o = f_s (v + v_o) / v== 256 xx ((330+25) / 330) = "275.4 Hz"`
Question 2
A train with a whistle that emits a note of frequency 800 Hz is approaching a stationary observer at a speed of 60 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the note heard by the observer (speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
The source is approaching the observer so we choose the minus sign for vo.
`f_o = (f_s × v) / (v - v_o)=f_o = (800 xx 330) / (330 - 60)="980 Hz"`
Question 3
A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency 420 Hz. The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of 25 m.s-1. The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
a. Explain why the pitch of the siren changes, as observed by the student.
b. Determine the maximum and minimum frequencies that the student will hear.
c. At which point in the boat’s motion will the student hear the most highpitched note?
(Speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
a. Doppler effect: source moving towards/away from observer leads to decreased/increased wavelength.
b. Maximum frequency when boat’s velocity is directed towards the observer.
`f_max = 420 xx (330 / (330 - 25)) = "454 Hz"`
Minimum frequency when boat’s velocity is directed away from observer.
`f_min = 420 *xx(330 / (330 + 25)) = "390 Hz"`
c. When boat’s velocity is directed at the student.
Question 4
A source emitting sound of a single frequency fs travels at constant speed directly towards an observer. The source then passes the observer and continues to move directly away from the observer. The velocity of the source remains constant.
Which graph represents the variation with time of the frequency fo of the sound heard by the observer?

Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Shows a step up in frequency after passing, which is incorrect. The frequency should drop, not rise.
B. Correct:
Before passing the observer: frequency > fsAfter passing the observer: frequency < fsAt the moment of passing: sudden drop in observed frequency.
C. Incorrect: Shows a gradual increase in frequency with time. This implies that either the speed of the source or the observer is changing - but the question states both velocities are constant.
D. Incorrect: Shows a gradual decrease in frequency - again implying changing velocity - which contradicts the given constant speed.
Question 5
A stationary person measures the speed and wavelength of the sound from a horn on a stationary vehicle. The person then repeats the measurements when the vehicle is approaching at a constant speed.
Which row describes the measured wavelength and the measured speed of the sound wave from the moving vehicle when compared with the sound wave from the stationary vehicle?
| wavelength of the sound wave | speed of the sound wave | |
|---|---|---|
| A | longer | greater |
| B | shorter | greater |
| C | longer | same |
| D | shorter | same |
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Approaching source shortens the wavelength. Speed of sound is constant.
B. Incorrect: Speed of sound is not affected by source motion.
C. Incorrect: Wavelength decreases when the source moves toward the observer.
D. Correct:
Wavelength: Shorter, because the wavefronts are compressed.
Speed of sound: Same, because the speed of sound in air doesn’t depend on whether the source is moving.
Question 6
A stationary source S emits a sound wave of frequency f.
The source now moves away from a stationary observer.
Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both higher than f.
B. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both lower than f.
C. The frequency of the source S is now lower than f.
D. The observed frequency is now lower than f.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: The observed frequency is not higher - it’s lower. The source frequency stays the same.
B. Incorrect: The source frequency does not change - only the observed frequency drops.
C. Incorrect: The source frequency stays at f; it's just the perception (observed frequency) that changes.
D. Correct:
The source is emitting a sound of constant true frequency f. That doesn’t change.
However, since the source is moving away, the observed frequency decreases.
Question 7
A person stands at the side of a straight railway track. A train moves towards the person and emits sound from its whistle. The person hears a sound of frequency 1690 Hz as the train approaches him. The person then hears a sound of frequency 1500 Hz as the train moves away from him. The speed of sound in air is 340 m.s-1. What is the speed of the train?
A. 20 m.s-1.
B. 38 m.s-1.
C. 41 m.s-1.
D. 43 m.s-1.
Answer: A
Let:
: Actual frequency of the train’s whistle.
: Speed of sound = 340 m.s-1
vs: speed of the train (what we need to find).
f1 = Hz (when train approaches).
f2 = Hz (when train moves away).
When approaching: `f_1 = (f_s xx v) / (v - v_s)`
When move away: `f_2 = (f_s xx v) / (v + v_s)`
`f_1 / (f_2) = (v + v_s)/(v - v_s)`
`1690 / 1500 = (340 + v_s) / (340 - v_s)`
`v_s=20.25" ""m.s"^-1`
Question 8
A car is travelling at a constant velocity directly towards a man standing in the middle of the road. The driver sounds the car’s horn as a warning. The horn emits a sound wave of constant frequency. The frequency of the sound heard by the man is different from the frequency of the sound emitted by the horn. Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the sound emitted by the horn is greater than the frequency of the sound heard by the man.
B. The frequency of the sound heard by the man depends on the distance between the car and the man.
C. The sound waves continually accelerate as they move from the horn to the man.
D. The wavelength of the sound heard by the man is less than the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: The frequency of the sound emitted by the horn is not greater than what the man hears. It is constant and lower than the observed frequency due to the Doppler effect.
B. Incorrect: The observed frequency does not depend on the distance between the car and the man, but on the relative velocity of the source and observer.
C. Incorrect: The sound waves do not accelerate. The speed of sound in air is constant (assuming constant medium conditions). The apparent change is in frequency/wavelength, not wave speed.
D. Correct:
When a source is moving towards a stationary observer, the observer hears a higher frequency than the actual frequency emitted.
The observed frequency is `f_o = (f_s xx v) / (v - v_s)`
Since v − vs < v, the denominator is smaller, so fo > fs
But the speed of sound remains constant. So, if the man hears a higher frequency but sound travels at the same speed, then: `lambda_o = v / f_o`
As fo > fs, that means λo < λsSo the wavelength of the sound heard by the man is shorter than the wavelength emitted by the horn.
Question 9
A source emits a sound wave of a single frequency. The Doppler effect causes a different frequency of sound to be heard by a stationary observer.
What is a requirement for the Doppler effect to occur?
A. A source that is moving as it produces the sound wave.
B. A source that produces a polarised sound wave.
C. A source that produces a sound wave of changing amplitude.
D. A source that produces a sound wave of changing frequency.
Answer: A
A. Correct:
If the source moves while producing sound waves, each successive wavefront is either compressed (if approaching) or stretched (if receding).
This change in wavelength results in a different observed frequency than the original emitted frequency.
B. Incorrect: sound waves cannot be polarised. Polarisation only applies to transverse waves, such as light. Sound waves are longitudinal, and thus cannot exhibit polarisation.
C. Incorrect: changing amplitude affects loudness, not frequency. The Doppler effect is purely about frequency shifts, not volume.
D. Incorrect: this would result in a genuine change in frequency, not a perceived one. The Doppler effect assumes that the source emits a constant frequency, and the shift is observed due to motion, not because the frequency itself is changing.
Question 10
A police car travels towards a stationary observer at a speed of 15 m.s-1. The siren on the car emits a sound of frequency 250 Hz. Calculate the observed frequency. The speed of sound is 340 m.s-1.
`f_o = (f_s xx v) / (v - v_s)= (250 xx 340) / (340 - 15)="260 Hz"`
Question 1
A loudspeaker connected to a signal generator produces a steady note of frequency 256 Hz. An observer moves towards the loudspeaker at a speed of 25 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the sound that the observer hears (speed of sound = 330 m.s-1).
Question 2
A train with a whistle that emits a note of frequency 800 Hz is approaching a stationary observer at a speed of 60 m.s-1. Calculate the frequency of the note heard by the observer (speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
Question 3
A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency 420 Hz. The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of 25 m.s-1. The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
a. Explain why the pitch of the siren changes, as observed by the student.
b. Determine the maximum and minimum frequencies that the student will hear.
c. At which point in the boat’s motion will the student hear the most highpitched note?
(Speed of sound in air = 330 m.s-1).
Question 4
A source emitting sound of a single frequency fs travels at constant speed directly towards an observer. The source then passes the observer and continues to move directly away from the observer. The velocity of the source remains constant.
Which graph represents the variation with time of the frequency fo of the sound heard by the observer?

Question 5
A stationary person measures the speed and wavelength of the sound from a horn on a stationary vehicle. The person then repeats the measurements when the vehicle is approaching at a constant speed.
Which row describes the measured wavelength and the measured speed of the sound wave from the moving vehicle when compared with the sound wave from the stationary vehicle?
| wavelength of the sound wave | speed of the sound wave | |
|---|---|---|
| A | longer | greater |
| B | shorter | greater |
| C | longer | same |
| D | shorter | same |
Question 6
A stationary source S emits a sound wave of frequency f.
The source now moves away from a stationary observer.
Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both higher than f.
B. The frequency of the source S and the observed frequency are now both lower than f.
C. The frequency of the source S is now lower than f.
D. The observed frequency is now lower than f.
Question 7
A person stands at the side of a straight railway track. A train moves towards the person and emits sound from its whistle. The person hears a sound of frequency 1690 Hz as the train approaches him. The person then hears a sound of frequency 1500 Hz as the train moves away from him. The speed of sound in air is 340 m.s-1. What is the speed of the train?
A. 20 m.s-1.
B. 38 m.s-1.
C. 41 m.s-1.
D. 43 m.s-1.
Question 8
A car is travelling at a constant velocity directly towards a man standing in the middle of the road. The driver sounds the car’s horn as a warning. The horn emits a sound wave of constant frequency. The frequency of the sound heard by the man is different from the frequency of the sound emitted by the horn. Which statement is correct?
A. The frequency of the sound emitted by the horn is greater than the frequency of the sound heard by the man.
B. The frequency of the sound heard by the man depends on the distance between the car and the man.
C. The sound waves continually accelerate as they move from the horn to the man.
D. The wavelength of the sound heard by the man is less than the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn.
Question 9
A source emits a sound wave of a single frequency. The Doppler effect causes a different frequency of sound to be heard by a stationary observer.
What is a requirement for the Doppler effect to occur?
A. A source that is moving as it produces the sound wave.
B. A source that produces a polarised sound wave.
C. A source that produces a sound wave of changing amplitude.
D. A source that produces a sound wave of changing frequency.
Question 10
A police car travels towards a stationary observer at a speed of 15 m.s-1. The siren on the car emits a sound of frequency 250 Hz. Calculate the observed frequency. The speed of sound is 340 m.s-1.