Question 1
Beryllium and radium are both in Group 2.
a. Write the electronic configuration of beryllium.
b. Give the equations for the reactions of beryllium and radium with oxygen.
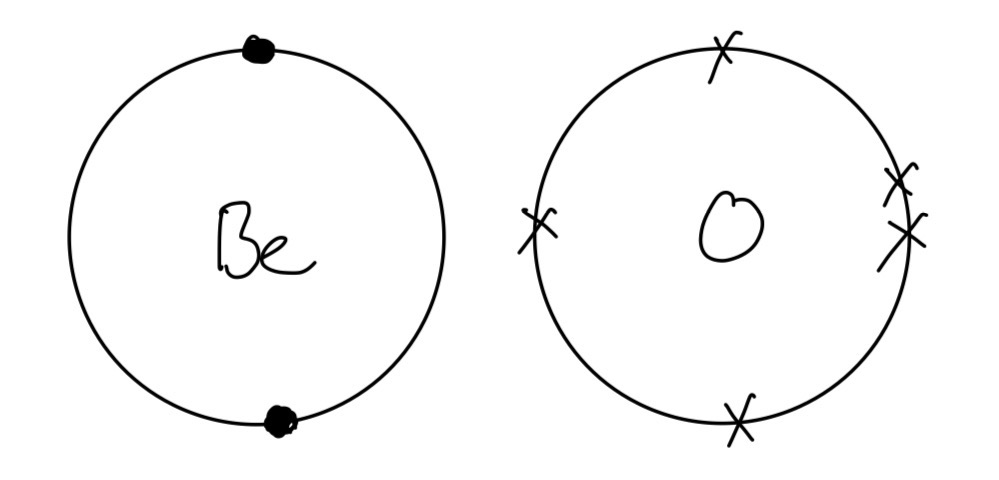
c. Using dot-and-cross diagrams, and showing the outer electrons only, draw the electronic configurations of beryllium and oxygen before and after bonding.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A. Draw a diagram to show the metallic bonding in both beryllium and radium.
B. Using your diagram, explain why beryllium has a higher melting point than radium.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Exactly 0.1 moles of calcium hydroxide and barium hydroxide are added to separate beakers containing 100 cm3 of water and stirred to form saturated solutions. Explain which solution has the higher pH value.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Strontium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form strontium chloride, water and carbon dioxide.
A. Describe how you could prove that the gas produced is carbon dioxide.
B. Carbon dioxide is also produced when strontium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid. The effervescence observed in this reaction stops after a short period of time.
Suggest why the reaction stops even though the reactants have not been used up.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Which substance will not be a product of the thermal decomposition of hydrated magnesium nitrate?
A. dinitrogen monoxide
B. magnesium oxide
C. oxygen
D. steam
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Thermal decomposition of compound S releases carbon dioxide gas and forms a white solid, T. S and T are not soluble in water. Compound T is used as a refractory kiln lining.
What is compound S?
A. CaCO3
B. MgCO3
C. CaO
D. MgO
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Group II nitrates undergo thermal decomposition according to the following equation.
`X(NO_3)_2 → XO + 2NO_2 + 1/2 O_2`
Which Group II nitrate requires the highest temperature to bring about its thermal decomposition?
A. Barium nitrate
B. Calcium nitrate
C. Magnesium nitrate
D. Strontium nitrate
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which statements about calcium oxide are correct?
| 1 | It is produced when calcium nitrate is heated. |
| 2 | It can be reduced by heating with magnesium. |
| 3 | It reacts with cold water. |
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Rat poison needs to be insoluble in rainwater but soluble at the low pH of stomach contents.
What is a suitable barium compound to use for rat poison?
A. Barium carbonate
B. Barium chloride
C. Barium hydroxide
D. Barium sulfate
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
The sketch graph shows the variation of one physical or chemical property with another for the Group II elements.
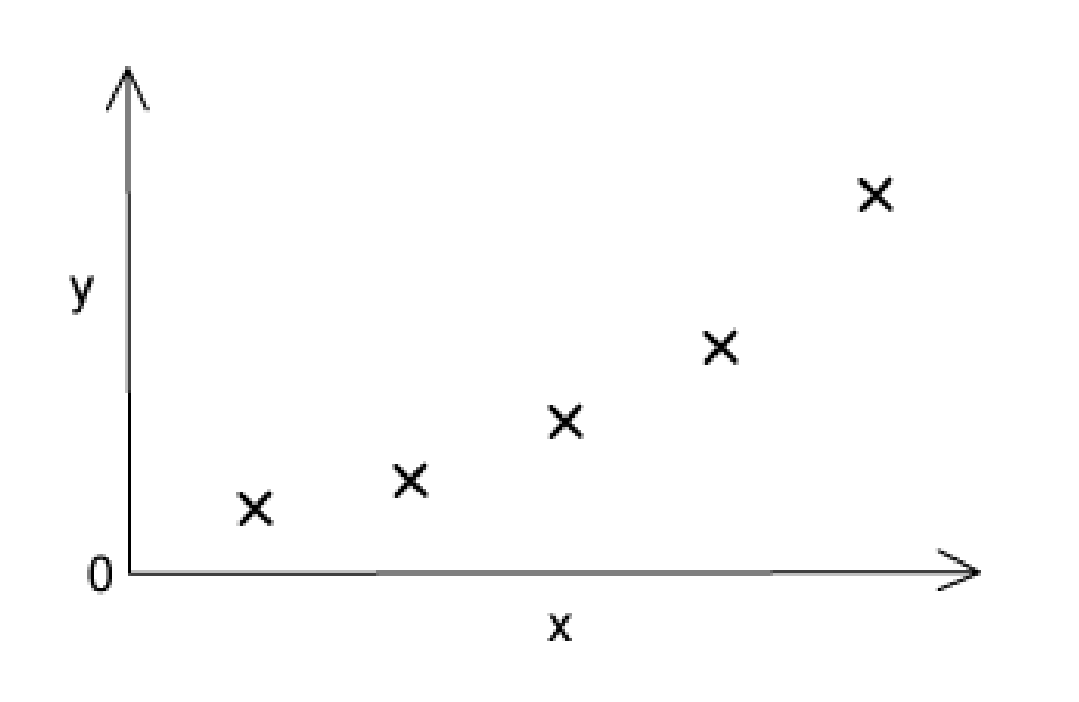
What are the correct labels for the axes with x-axis and y-axis, respectively?
A. First ionisation energy - Atomic number
B. First ionisation energy - Atomic radius
C. Atomic number - Melting point
D. Atomic number - Mass number
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Beryllium and radium are both in Group 2.
a. Write the electronic configuration of beryllium.
b. Give the equations for the reactions of beryllium and radium with oxygen.
c. Using dot-and-cross diagrams, and showing the outer electrons only, draw the electronic configurations of beryllium and oxygen before and after bonding.
a. The electronic configuration of beryllium is `1s^2 2s^2`
b. The equations for the reactions of beryllium and radium with oxygen
`2Be + O_2 -> 2BeO`
`2Ra + O_2 -> 2RaO`
c.
Before bonding
After bonding
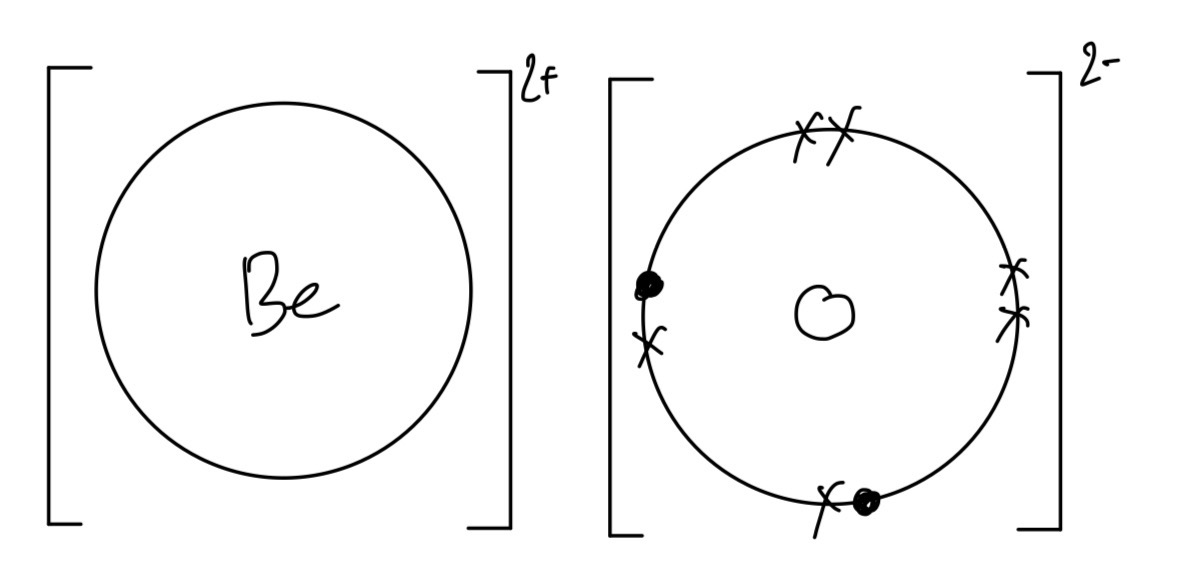
Question 2
A. Draw a diagram to show the metallic bonding in both beryllium and radium.
B. Using your diagram, explain why beryllium has a higher melting point than radium.
A.
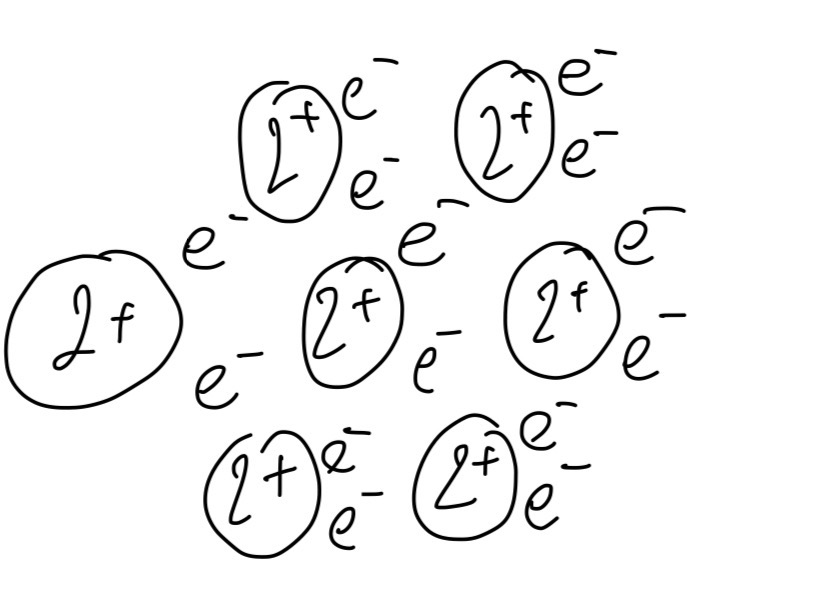
B.
The electrons are less attracted to the positively charged ions in radium because the charge density on the positive ions is lower than in beryllium. Because beryllium's metallic bond is stronger than radium's, melting it requires a greater temperature.
Question 3
Exactly 0.1 moles of calcium hydroxide and barium hydroxide are added to separate beakers containing 100 cm3 of water and stirred to form saturated solutions. Explain which solution has the higher pH value.
The trend in solubility in Group 2 hydroxides and sulfates: going down Group 2, the solubility of the hydroxides decreases, whereas that of the sulfates increases. Thus, Ba(OH)2 is more soluble (in water) than Ca(OH)2, leading to producing more OH⁻ (aq) to has higher pH value.
Question 4
Strontium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form strontium chloride, water and carbon dioxide.
A. Describe how you could prove that the gas produced is carbon dioxide.
B. Carbon dioxide is also produced when strontium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid. The effervescence observed in this reaction stops after a short period of time.
Suggest why the reaction stops even though the reactants have not been used up.
A. The gas produced is CO2 by looking at the phenomenon in the reaction with bubbling the gas through limewater, which turns cloudy or forms a white precipitate.
B. Because strontium sulfate is formed, which is insoluble and coated the strontium carbonate.
Question 5
Which substance will not be a product of the thermal decomposition of hydrated magnesium nitrate?
A. dinitrogen monoxide
B. magnesium oxide
C. oxygen
D. steam
The answer is A
Steam, magnesium oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen are the products of the thermal breakdown of hydrated magnesium nitrate. Dinitrogen monoxide, which is not a byproduct of the thermal breakdown of hydrated magnesium nitrate, is the correct response.
Question 6
Thermal decomposition of compound S releases carbon dioxide gas and forms a white solid, T. S and T are not soluble in water. Compound T is used as a refractory kiln lining.
What is compound S?
A. CaCO3
B. MgCO3
C. CaO
D. MgO
The answer is B
To be used as a refractory kiln lining, it will not be decomposed at very high temperatures. Not only that, but this compound also is not soluble in water. Therefore, T must be MgO
A is incorrect because CaO which is product of CaCO3 thermal decomposition is soluble in water
C and D are incorrect because metal oxides are the product of thermal decomposition of metal carbonate
Question 7
Group II nitrates undergo thermal decomposition according to the following equation.
`X(NO_3)_2 → XO + 2NO_2 + 1/2 O_2`
Which Group II nitrate requires the highest temperature to bring about its thermal decomposition?
A. Barium nitrate
B. Calcium nitrate
C. Magnesium nitrate
D. Strontium nitrate
The answer is A
When we go down the group, Group II nitrates will be required higher temperature for thermal decomposition, as such, the more polarised they are, the more possible they will be able to decompose thermally.
Question 8
Which statements about calcium oxide are correct?
| 1 | It is produced when calcium nitrate is heated. |
| 2 | It can be reduced by heating with magnesium. |
| 3 | It reacts with cold water. |
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
The answer is C
When calcium nitrate is heated, the thermal decomposition will occur
`2Ca(NO_3)_2 -> 2CaO + 4NO_2 + O_2`
Calcium oxide reacts with cold water to generate Ca(OH)2
`CaO (s) + H_2O (l) -> Ca(OH)_2 (s)`
Statement 2 is incorrect because elements in Group 2 are really reactive, and Ca is more reactive than Mg, as such, it could not be reduced
Question 9
Rat poison needs to be insoluble in rainwater but soluble at the low pH of stomach contents.
What is a suitable barium compound to use for rat poison?
A. Barium carbonate
B. Barium chloride
C. Barium hydroxide
D. Barium sulfate
The answer is A
| Compound | Soluble in water | Soluble in stomach acid |
| Barium carbonate | No | Yes |
| Barium chloride | Yes | No |
| Barium hydroxide | Yes | Yes |
| Barium sulfate | No | No |
Question 10
The sketch graph shows the variation of one physical or chemical property with another for the Group II elements.

What are the correct labels for the axes with x-axis and y-axis, respectively?
A. First ionisation energy - Atomic number
B. First ionisation energy - Atomic radius
C. Atomic number - Melting point
D. Atomic number - Mass number
The answer is D
Because the atomic number increases when we go down Group II, so does mass.
A and B are incorrect because the first ionisation energy would be on the y-axis.
C is incorrect because the melting point of Be is the highest. More specifically, the interaction between atoms in a group decreases with increasing atom size, resulting in rather free packing. A metallic connection holds the atoms together. As you move down a group, the bonding gets weaker. The strongest metallic connection is found in beryllium, which is the smallest member of the group.
Question 1
Beryllium and radium are both in Group 2.
a. Write the electronic configuration of beryllium.
b. Give the equations for the reactions of beryllium and radium with oxygen.
c. Using dot-and-cross diagrams, and showing the outer electrons only, draw the electronic configurations of beryllium and oxygen before and after bonding.
Question 2
A. Draw a diagram to show the metallic bonding in both beryllium and radium.
B. Using your diagram, explain why beryllium has a higher melting point than radium.
Question 3
Exactly 0.1 moles of calcium hydroxide and barium hydroxide are added to separate beakers containing 100 cm3 of water and stirred to form saturated solutions. Explain which solution has the higher pH value.
Question 4
Strontium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form strontium chloride, water and carbon dioxide.
A. Describe how you could prove that the gas produced is carbon dioxide.
B. Carbon dioxide is also produced when strontium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid. The effervescence observed in this reaction stops after a short period of time.
Suggest why the reaction stops even though the reactants have not been used up.
Question 5
Which substance will not be a product of the thermal decomposition of hydrated magnesium nitrate?
A. dinitrogen monoxide
B. magnesium oxide
C. oxygen
D. steam
Question 6
Thermal decomposition of compound S releases carbon dioxide gas and forms a white solid, T. S and T are not soluble in water. Compound T is used as a refractory kiln lining.
What is compound S?
A. CaCO3
B. MgCO3
C. CaO
D. MgO
Question 7
Group II nitrates undergo thermal decomposition according to the following equation.
`X(NO_3)_2 → XO + 2NO_2 + 1/2 O_2`
Which Group II nitrate requires the highest temperature to bring about its thermal decomposition?
A. Barium nitrate
B. Calcium nitrate
C. Magnesium nitrate
D. Strontium nitrate
Question 8
Which statements about calcium oxide are correct?
| 1 | It is produced when calcium nitrate is heated. |
| 2 | It can be reduced by heating with magnesium. |
| 3 | It reacts with cold water. |
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
Question 9
Rat poison needs to be insoluble in rainwater but soluble at the low pH of stomach contents.
What is a suitable barium compound to use for rat poison?
A. Barium carbonate
B. Barium chloride
C. Barium hydroxide
D. Barium sulfate
Question 10
The sketch graph shows the variation of one physical or chemical property with another for the Group II elements.

What are the correct labels for the axes with x-axis and y-axis, respectively?
A. First ionisation energy - Atomic number
B. First ionisation energy - Atomic radius
C. Atomic number - Melting point
D. Atomic number - Mass number