Question 1
The properties of elements and their compounds show similarities, differences and trends depending on the positions of the elements in the Periodic Table.
The positions of some elements are shown.
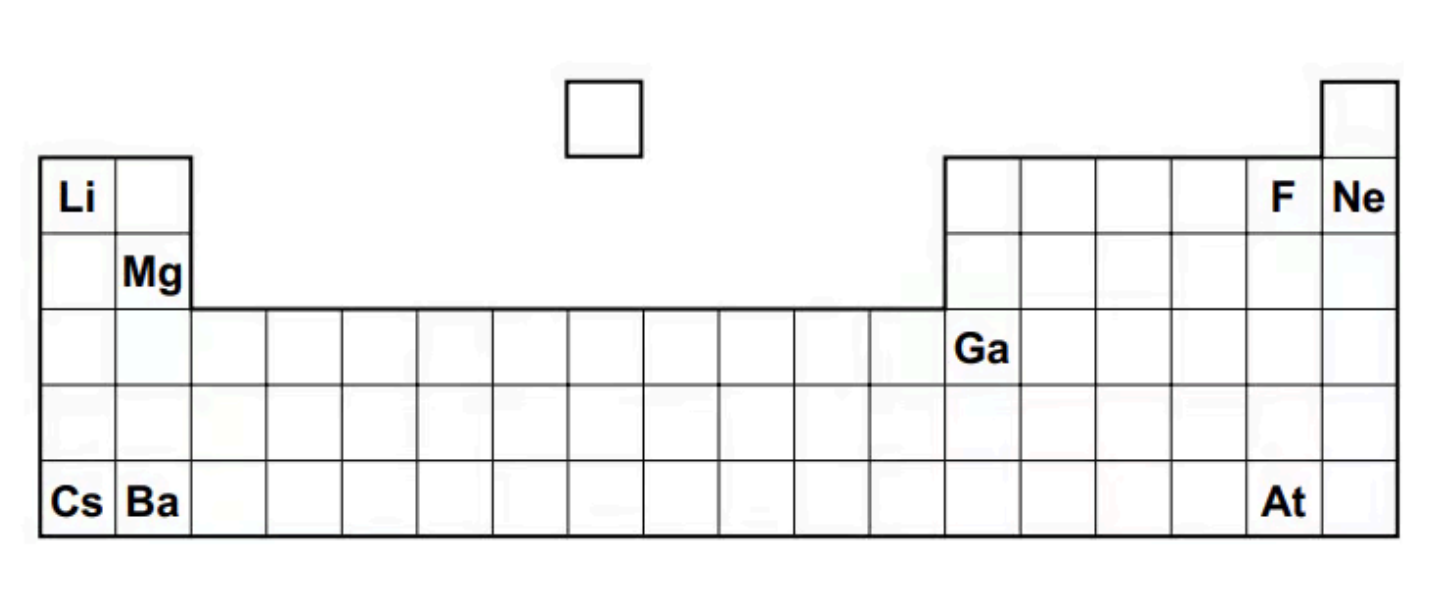
A. Using the table above, identify the element that forms a soluble hydroxide and an insoluble sulfate
B. Using the table above, identify the most volatile element in a group that contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature and pressure
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The figure shows the relative first ionisation energies of six successive elements in the Periodic Table.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
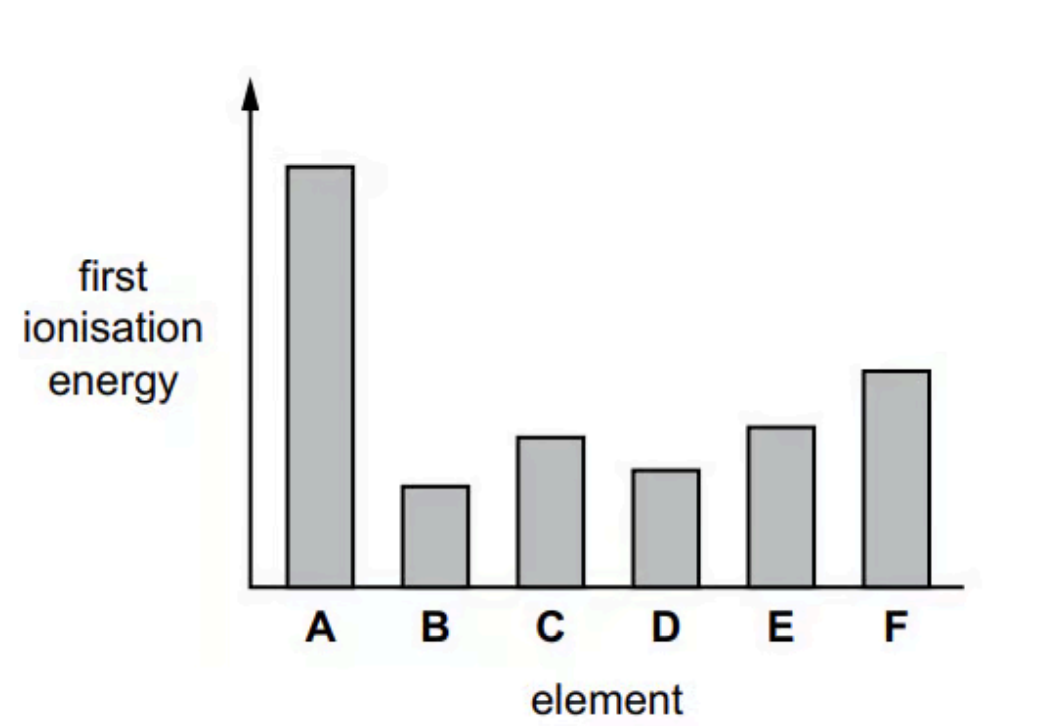
Suggest why the first ionisation energy of B is much less than that of A
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Sketch a graph to show the trend in the atomic radius of successive elements in Period 3.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The table below shows successive ionisation energies of an element A, found in Period 3 of the Periodic Table
| Number of electrons | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Ionisation Energy (kJ mol-1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21268 | 25431 | 29872 |
Identify element A.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The successive ionisation energies of an element, X, are shown in the figure below. The vertical axis plots log (ionisation energy) instead of ionisation energy to represent the data without an unreasonably long vertical axis.
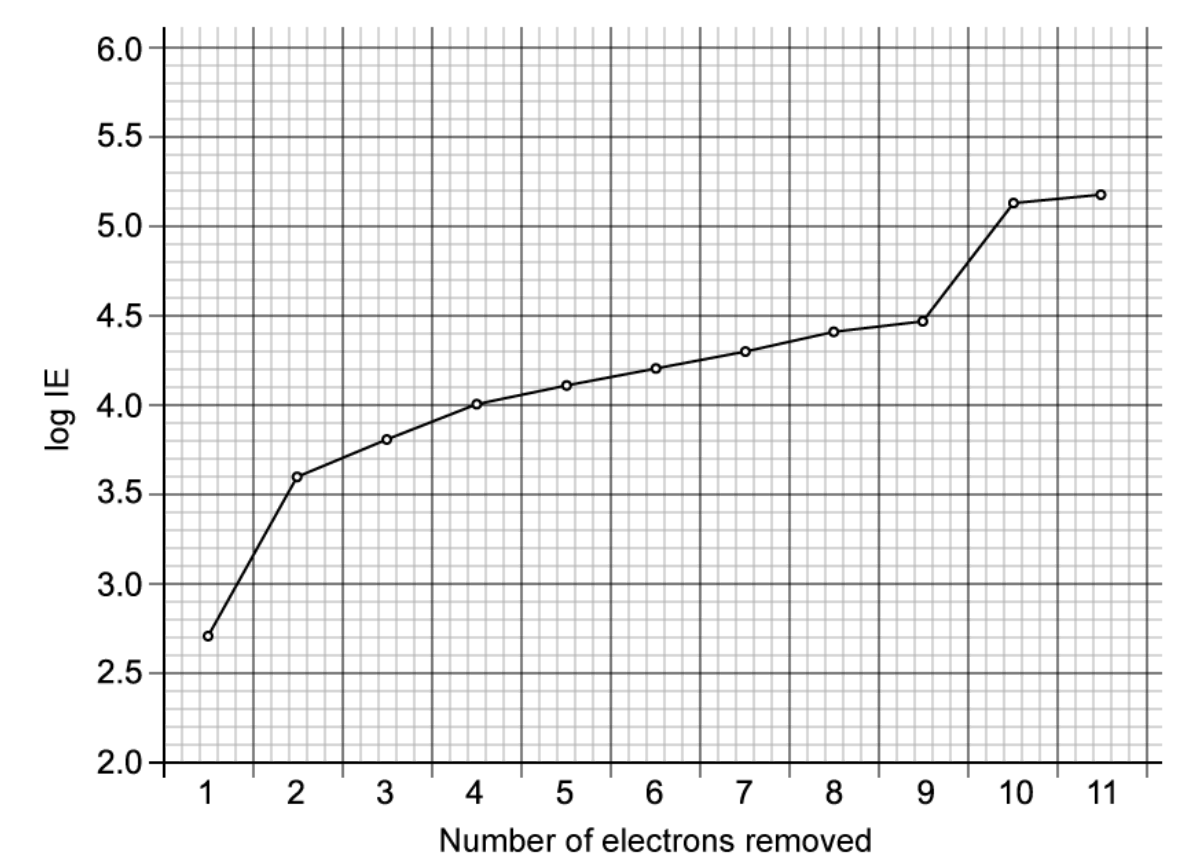
Identify element X and give its full electron configuration.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Element Y is in the same period as Sodium. When Y is reacted with chlorine to form a chloride which has a pH of 2. When this chloride is reacted with water a rapid reaction occurs producing white vapour and white precipitate.
A. Identify element Y
B. Write the equation for when the chloride formed from element Y reacts with water. Include state symbols in your answer.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Element Z reacts with oxygen to form an oxide that is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The oxide formed can react with both acids and bases.
What could be the identity of Z?
A. Si
B. Mg
C. Cl
D. Al
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Element X forms an oxide with a high melting point of 1710 °C. The oxide reacts with NaOH (aq).
What is the identity of X?
A. Si
B. Na
C. Cl
D. S
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
The period 4 elements gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As) and selenium (Se) are the elements directly below aluminium, silicon, phosphorus and sulfur in the Periodic Table.
The properties of each period 4 element resemble those of the period 3 element directly above it.
Which period 4 elements form oxides that dissolve in water to give an acid solution?
A. Ga and Ge
B. Ge and Se
C. As and Se
D. Se only
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
The successive ionisation energies of elements X and Y are shown below.
| Element X | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 590 | 1145 | 4912 | 6491 | 8153 | 10496 | 12270 | 14206 |
| Element Y | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21267 | 25431 | 29872 |
X and Y form ions with the same electron configuration as argon.
What are the identities of elements X and Y respectively?
A. Calcium and phosphorus
B. Sodium and oxygen
C. Magnesium and nitrogen
D. Phosphorus and potassium
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The properties of elements and their compounds show similarities, differences and trends depending on the positions of the elements in the Periodic Table.
The positions of some elements are shown.

A. Using the table above, identify the element that forms a soluble hydroxide and an insoluble sulfate
B. Using the table above, identify the most volatile element in a group that contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature and pressure
A. The element that forms a soluble hydroxide and an insoluble sulfate is Ba.
Remark: The trend in solubility in Group 2 hydroxides and sulfates: going down Group 2, the solubility of the hydroxides decreases, whereas that of the sulfates increases.
B. The most volatile element in a group that contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature and pressure is F.
Remark: Group 17 is the only group which contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature and pressure.
Question 2
The figure shows the relative first ionisation energies of six successive elements in the Periodic Table.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.

Suggest why the first ionisation energy of B is much less than that of A
Because the element B has the outer electron which is removed from a higher energy level. In addition, there is more shielding by inner electrons, which results in less attraction to the nucleus.
Question 3
Sketch a graph to show the trend in the atomic radius of successive elements in Period 3.

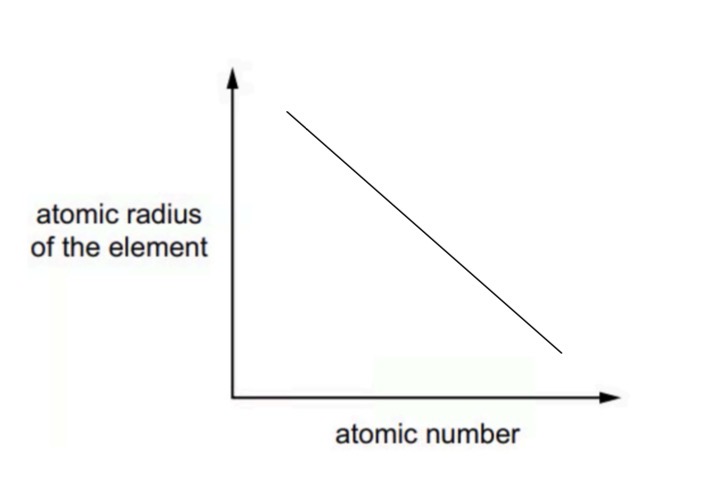
The line will decrease from left to right according to the increasing atomic number.
When we increase the nuclear charge and there are electrons in the same shell, leading to a greater attraction between the nucleus and electrons
Question 4
The table below shows successive ionisation energies of an element A, found in Period 3 of the Periodic Table
| Number of electrons | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Ionisation Energy (kJ mol-1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21268 | 25431 | 29872 |
Identify element A.
Element A is phosphorus because there is a large jump between ionisation energies 5 and 6.
Remark: The big jump happens after the 5th ionisation energy, that means that the 6th ionisation energy is large, as such, the element is in group 5.
Question 5
The successive ionisation energies of an element, X, are shown in the figure below. The vertical axis plots log (ionisation energy) instead of ionisation energy to represent the data without an unreasonably long vertical axis.

Identify element X and give its full electron configuration.
The element X is Sodium and its electron configuration is `1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^1`.
The graph shows that the element has a total of 11 electrons. As we know, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. In addition, from this graph, how many shells the elements have by looking at large jump in the energy required to remove successive electrons are elucidated.
Question 6
Element Y is in the same period as Sodium. When Y is reacted with chlorine to form a chloride which has a pH of 2. When this chloride is reacted with water a rapid reaction occurs producing white vapour and white precipitate.
A. Identify element Y
B. Write the equation for when the chloride formed from element Y reacts with water. Include state symbols in your answer.
A. The element Y is Silicon
B. The equation for when the chloride formed from element Y reacts with water
`SiCl_4 (l) + 2H_2O (l) -> SiO_2 (g) + 4HCl (g)`
Question 7
Element Z reacts with oxygen to form an oxide that is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The oxide formed can react with both acids and bases.
What could be the identity of Z?
A. Si
B. Mg
C. Cl
D. Al
The answer is D
The oxide formed can react with both acids and bases, which means that the oxide is amphoteric.
an oxide is solid at room temperature that means that this is a metal oxide.
A is incorrect because it is not a metal
B and C are incorrect because oxides of these metal are not amphoteric
Question 8
Element X forms an oxide with a high melting point of 1710 °C. The oxide reacts with NaOH (aq).
What is the identity of X?
A. Si
B. Na
C. Cl
D. S
The answer is A.
`Si (s) + O_2 (g) -> SiO_2(s)`
`SiO_2 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) -> Na_2SiO_3 (aq) + H_2O (l)`
B is incorrect because this oxide formed would not react with NaOH (aq)
C is incorrect because oxide of Cl has low melting point because it is a simple covalent structure
D is incorrect because oxide of S has low melting point because it is a simple covalent structure
Question 9
The period 4 elements gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As) and selenium (Se) are the elements directly below aluminium, silicon, phosphorus and sulfur in the Periodic Table.
The properties of each period 4 element resemble those of the period 3 element directly above it.
Which period 4 elements form oxides that dissolve in water to give an acid solution?
A. Ga and Ge
B. Ge and Se
C. As and Se
D. Se only
The answer is C
In period 3, the oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water, for example
`SO_3 + H_2O -> H_2SO_4`
A is incorrect because gallium oxide does not react with water because, in this solid lattice, they are held too tightly. As for Ge, it has a giant covalent structure.
B is incorrect because Ge has a giant covalent structure
D is incorrect because it lacks As.
Question 10
The successive ionisation energies of elements X and Y are shown below.
| Element X | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 590 | 1145 | 4912 | 6491 | 8153 | 10496 | 12270 | 14206 |
| Element Y | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21267 | 25431 | 29872 |
X and Y form ions with the same electron configuration as argon.
What are the identities of elements X and Y respectively?
A. Calcium and phosphorus
B. Sodium and oxygen
C. Magnesium and nitrogen
D. Phosphorus and potassium
The answer is A
As for element X, there is a large jump in ionisation energy between the second and the third electron, meaning that X must be in group 2 with two outer electrons
As for element Y, there is a large jump in ionisation energy between the fifth and sixth electron, meaning that Y must be in group 5 with five outer electrons.
As we know, Argon has 18 electrons.
B is incorrect because the sodium ion has 10 electrons and the oxygen ion has 10 electrons
C is incorrect because the magnesium ion has 10 electrons and a nitrogen has 10 electrons
D is incorrect because potassium is not a Group 2 element.
Question 1
The properties of elements and their compounds show similarities, differences and trends depending on the positions of the elements in the Periodic Table.
The positions of some elements are shown.

A. Using the table above, identify the element that forms a soluble hydroxide and an insoluble sulfate
B. Using the table above, identify the most volatile element in a group that contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature and pressure
Question 2
The figure shows the relative first ionisation energies of six successive elements in the Periodic Table.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.

Suggest why the first ionisation energy of B is much less than that of A
Question 3
Sketch a graph to show the trend in the atomic radius of successive elements in Period 3.

Question 4
The table below shows successive ionisation energies of an element A, found in Period 3 of the Periodic Table
| Number of electrons | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Ionisation Energy (kJ mol-1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21268 | 25431 | 29872 |
Identify element A.
Question 5
The successive ionisation energies of an element, X, are shown in the figure below. The vertical axis plots log (ionisation energy) instead of ionisation energy to represent the data without an unreasonably long vertical axis.

Identify element X and give its full electron configuration.
Question 6
Element Y is in the same period as Sodium. When Y is reacted with chlorine to form a chloride which has a pH of 2. When this chloride is reacted with water a rapid reaction occurs producing white vapour and white precipitate.
A. Identify element Y
B. Write the equation for when the chloride formed from element Y reacts with water. Include state symbols in your answer.
Question 7
Element Z reacts with oxygen to form an oxide that is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The oxide formed can react with both acids and bases.
What could be the identity of Z?
A. Si
B. Mg
C. Cl
D. Al
Question 8
Element X forms an oxide with a high melting point of 1710 °C. The oxide reacts with NaOH (aq).
What is the identity of X?
A. Si
B. Na
C. Cl
D. S
Question 9
The period 4 elements gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As) and selenium (Se) are the elements directly below aluminium, silicon, phosphorus and sulfur in the Periodic Table.
The properties of each period 4 element resemble those of the period 3 element directly above it.
Which period 4 elements form oxides that dissolve in water to give an acid solution?
A. Ga and Ge
B. Ge and Se
C. As and Se
D. Se only
Question 10
The successive ionisation energies of elements X and Y are shown below.
| Element X | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 590 | 1145 | 4912 | 6491 | 8153 | 10496 | 12270 | 14206 |
| Element Y | ||||||||
| IE | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th |
| IE (kJ mol -1) | 1012 | 1907 | 2914 | 4964 | 6274 | 21267 | 25431 | 29872 |
X and Y form ions with the same electron configuration as argon.
What are the identities of elements X and Y respectively?
A. Calcium and phosphorus
B. Sodium and oxygen
C. Magnesium and nitrogen
D. Phosphorus and potassium