Question 1
a. Explain what is meant by the term ‘periodic property’.
b. The graph shows how a periodic property varies when plotted against atomic number for Period 3 (sodium to argon).
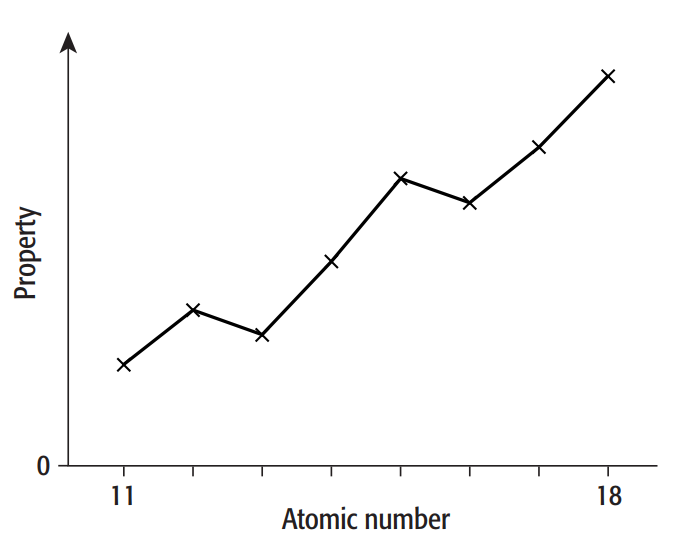
i. Identify the property.
ii.Explain the overall trend across the period.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The variation of melting point with atomic number for Periods 2 and 3 is shown in the graph below
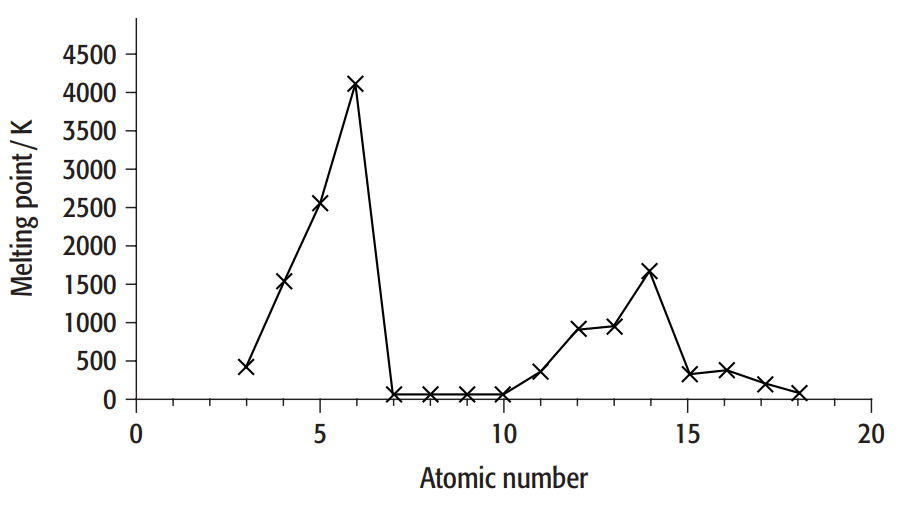
a. Explain what we mean when we say melting point is a periodic property.
b. Explain the following.
i. The melting point of silicon is much greater than that of phosphorus.
ii. The melting point of aluminum is greater than that of sodium.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies across Periods 2 and 3.
B. Explain this trend.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies down each group of the Periodic Table.
B. Explain this trend.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The electrical conductivity of the elements in Period 3 varies across the period as shown in
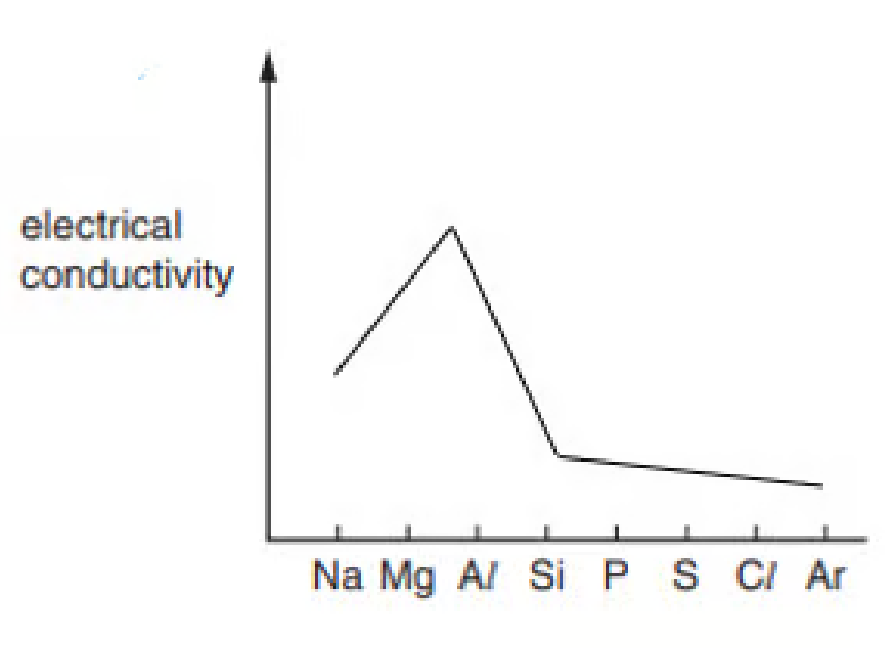
Explain why aluminum has a much higher electrical conductivity than sulfur. You should refer to the structure of both elements
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table show variations in their behaviour across the period. The figure below shows the variation of melting points of the elements across Period 3
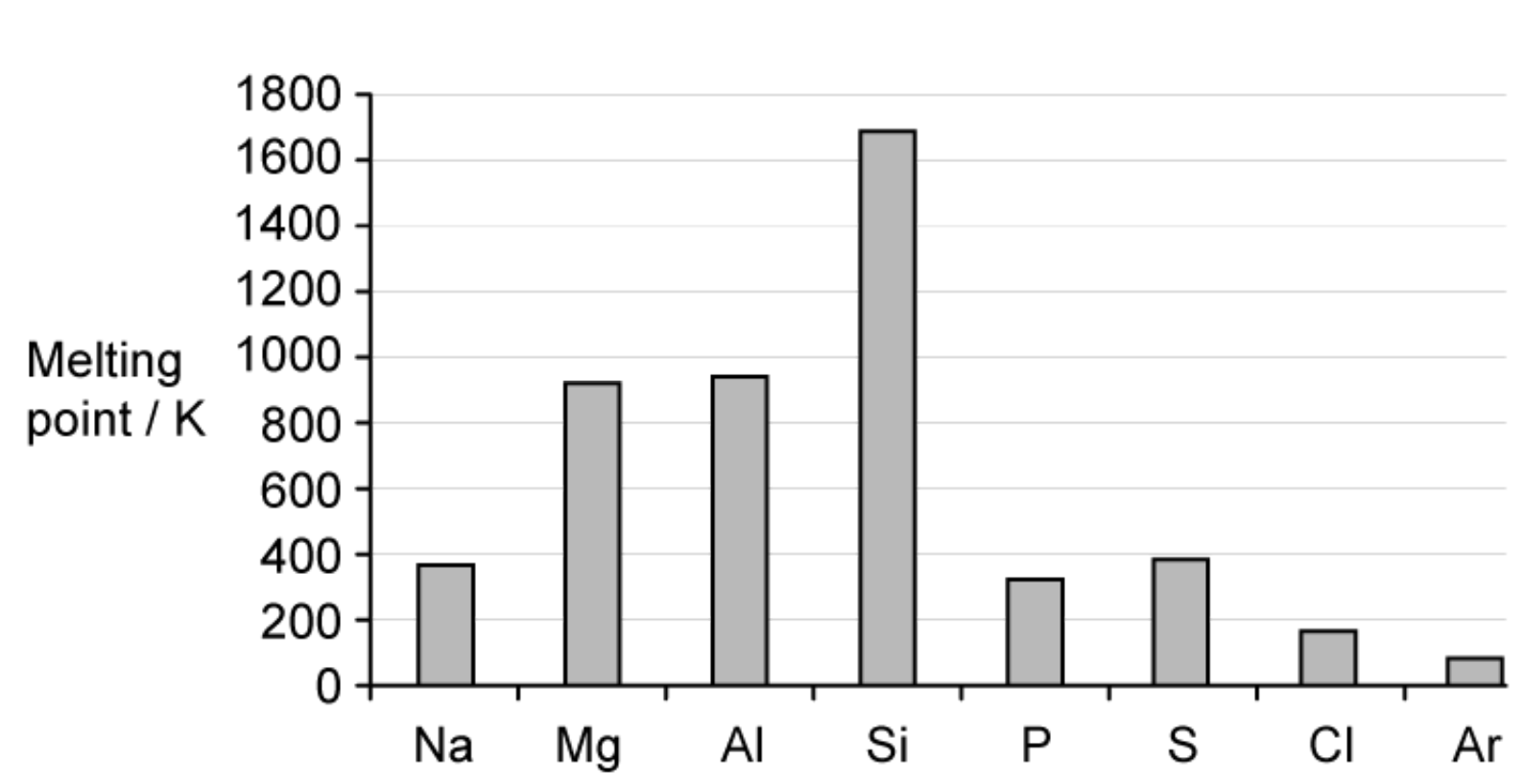
A. Explain the variation of melting points from P to Ar.
B. Explain why Si has a much higher melting point than any of the other elements in the period.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Going across Period 3, a trend in electronegativity can also be observed.
A. Define the term electronegativity.
B. Complete the figure below to show how electronegativity changes along Period 3.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Sodium sulfide, Na2S, is a reactive yellow solid, produced when sodium and sulfur react together.
Use of the periodic table is relevant to this question.
How do the ionic radius and atomic radius of sodium compare with those of sulfur?
A. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
B. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
C. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
D. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
The trends in three physical properties of the elements of period 3 are shown in the graphs.
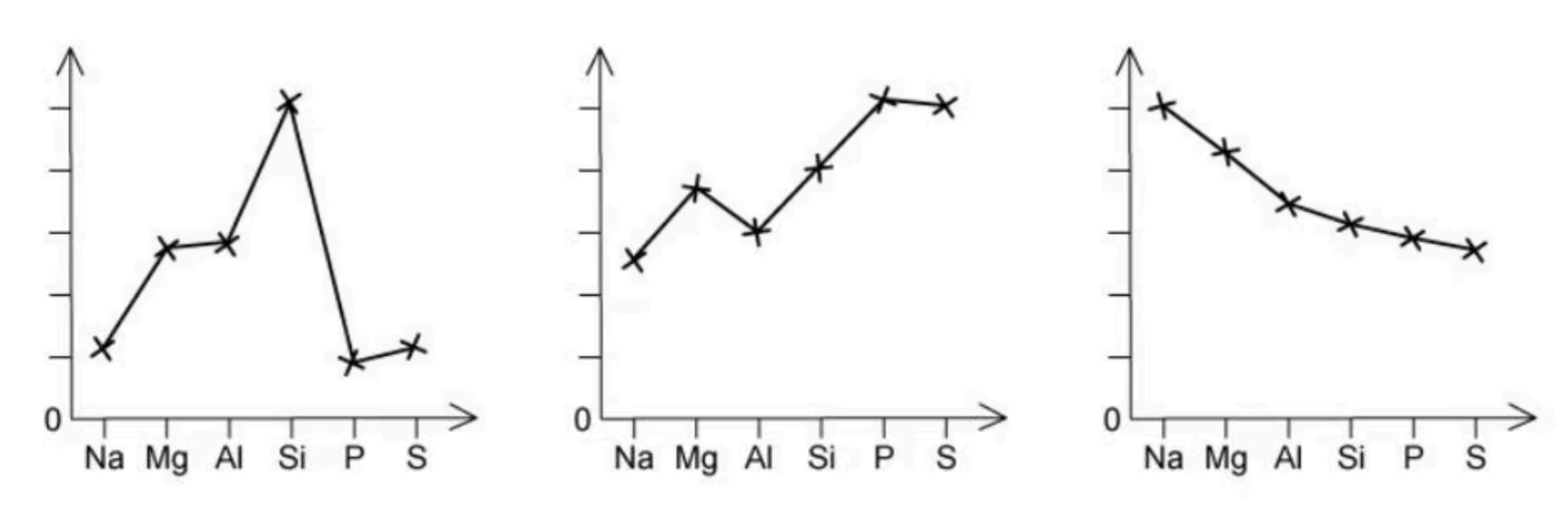
Which physical property is not illustrated?
A. Electrical conductivity
B. Atomic radius
C. Melting point
D. Melting point
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Consecutive elements X, Y and Z, are in the third period of the Periodic Table. Element Y has the highest first ionisation energy and the lowest melting point of these three elements.
What could be the identities of X, Y and Z?
A. Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulfur
B. Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium
C. Aluminium, Silicon, Phosphorus
D. Magnesium, Aluminium, Silicon
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
a. Explain what is meant by the term ‘periodic property’.
b. The graph shows how a periodic property varies when plotted against atomic number for Period 3 (sodium to argon).

i. Identify the property.
ii.Explain the overall trend across the period.
a. The elements are arranged in the periodic table according to periodic properties, which are recurrent patterns in their physical and chemical makeup. These tendencies can be described and comprehended by examining the electron configurations of the elements, and they can be predicted simply by looking at the periodic table.
b.
i. This is about ionisation energies because it is easily noticed that there are differences in nuclear charge, making the distances of electrons in the shell and subshell distinct and due to different amounts of shielding.
ii. As time passes, the outermost electron shell fills up without any new shells being added, and the nuclear charge rises concurrently. It becomes more difficult to remove an electron as a result of the increased attractive force acting on each electron in the outer shell.
Question 2
The variation of melting point with atomic number for Periods 2 and 3 is shown in the graph below

a. Explain what we mean when we say melting point is a periodic property.
b. Explain the following.
i. The melting point of silicon is much greater than that of phosphorus.
ii. The melting point of aluminum is greater than that of sodium.
a. It displays a recurring pattern throughout every time frame.
b.
i. While phosphorus is a simple molecular material, meaning that molecules are bound together by weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces), silicon has a giant covalent structure, meaning that all of the bonds are strong covalent bonds.
ii. Although sodium and aluminum have a similar metallic structure and connection, aluminum's metal ions have a higher charge than sodium's. While each sodium atom contributes only one electron to the "sea" of delocalized electrons, each aluminum atom contributes three. Consequently, more energy is required to separate the ions and melt aluminum because of the stronger attraction between the positive ions and delocalized electrons in aluminum.
Question 3
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies across Periods 2 and 3.
B. Explain this trend.
A. It decreases across the period.
B. The outermost electron shell fills up as the period passes, but no additional shells are occupied, and the nuclear charge rises concurrently. Consequently, each outer-shell electron experiences an increase in the attractive attraction, which pulls the electrons in and reduces the atomic radius.
Question 4
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies down each group of the Periodic Table.
B. Explain this trend.
A. It increases down the group.
B. The structure gains electron shells as the group descends.
Question 5
The electrical conductivity of the elements in Period 3 varies across the period as shown in

Explain why aluminum has a much higher electrical conductivity than sulfur. You should refer to the structure of both elements
Because Aluminium has a giant metallic lattice, meaning that it has free or delocalised electron to carry the charge, whereas sulfur is a simple molecule without delocalised electron.
Question 6
The elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table show variations in their behaviour across the period. The figure below shows the variation of melting points of the elements across Period 3

A. Explain the variation of melting points from P to Ar.
B. Explain why Si has a much higher melting point than any of the other elements in the period.
A. Because all contain instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces between molecules. The relative magnitude of these forces is S>P>Cl>Ar and sulfur has the greatest number of electrons and the number of electrons in the molecules decreases.
B. Because Si has a giant covalent structure.
Question 7
Going across Period 3, a trend in electronegativity can also be observed.
A. Define the term electronegativity.
B. Complete the figure below to show how electronegativity changes along Period 3.

A. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons or a pair of electrons to itself in a covalent bond.
B. Line increase over across Period 3 because nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases but they are in similar shielding.
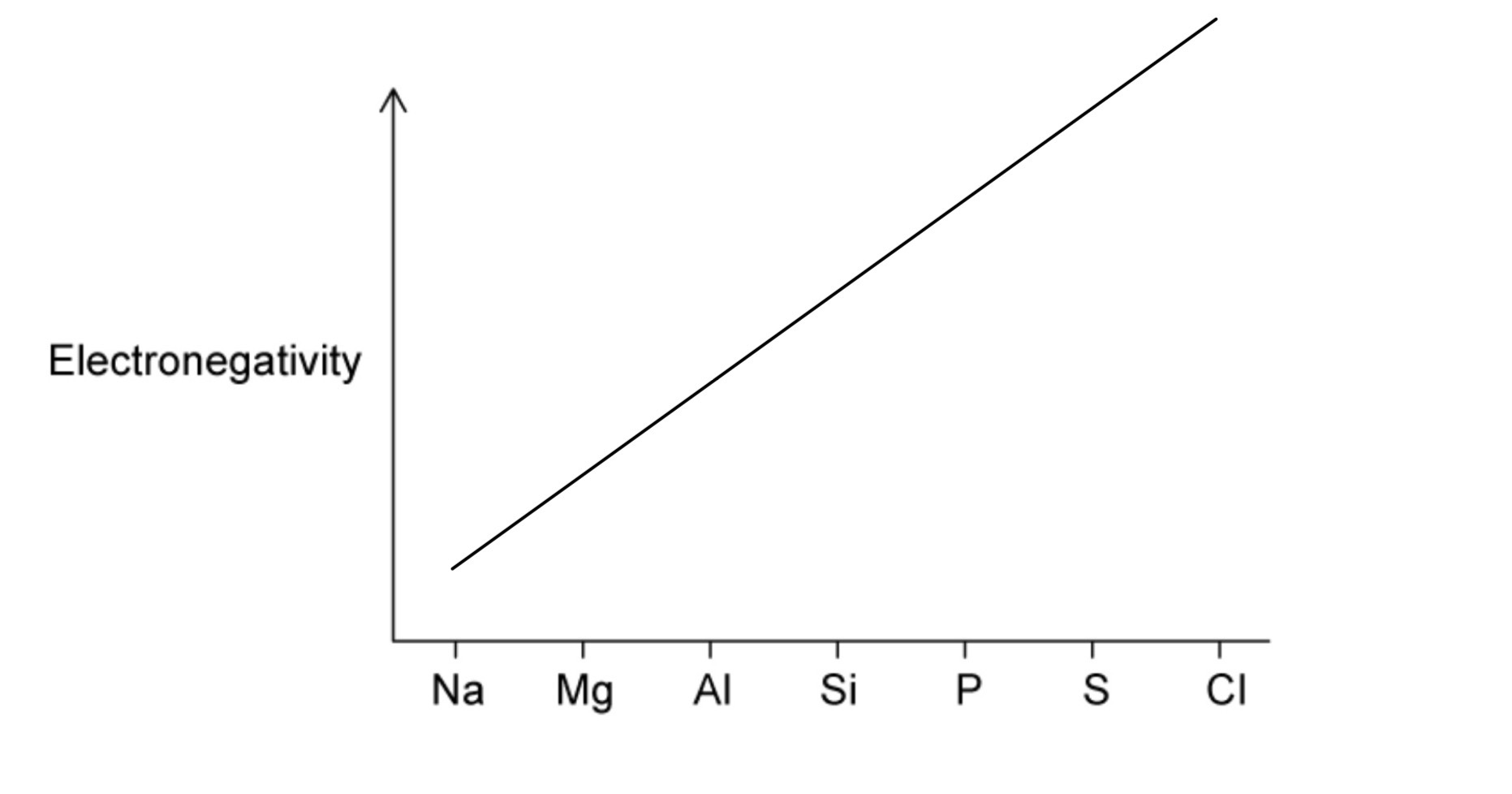
Question 8
Sodium sulfide, Na2S, is a reactive yellow solid, produced when sodium and sulfur react together.
Use of the periodic table is relevant to this question.
How do the ionic radius and atomic radius of sodium compare with those of sulfur?
A. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
B. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
C. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
D. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
The answer is B
Both are in Period 3. The atomic radius decreases from the left to the right across a period. The ionic radius increases from the left to the right across a period.
Question 9
The trends in three physical properties of the elements of period 3 are shown in the graphs.

Which physical property is not illustrated?
A. Electrical conductivity
B. Atomic radius
C. Melting point
D. Melting point
The answer is A
The melting point increases across the period from Na to Si and then drops significantly.
First ionisation energy varies, however, the trend is to increase across the period in general.
Atomic radius decreases from the left to the right across the period because the number of electron shells stays the same but the nuclear charge increases.
Question 10
Consecutive elements X, Y and Z, are in the third period of the Periodic Table. Element Y has the highest first ionisation energy and the lowest melting point of these three elements.
What could be the identities of X, Y and Z?
A. Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulfur
B. Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium
C. Aluminium, Silicon, Phosphorus
D. Magnesium, Aluminium, Silicon
The answer is A
First ionisation energies: Silicon (X) < Sulfur (Z) < Phosphorus (Y)
Melting points: Phosphorus (Y) < Sulfur (Z) < Silicon Silicon (X)
There is a general increase in first ionisation energy across the period because of increasing nuclear charge. However, there is a decrease in first ionisation energies between groups 2 and 3 and between groups 5 and 6. That leads to sulfur (Z) having lower first ionisation energy than Phosphorus (Y) because the electron being removed is paired.
Silicon (X) has the highest melting point because it has a giant covalent structure, as such, strong covalent bonds. Sulfur (Z) has a higher melting point than Phosphorus (Y) because it contains more electrons, although both are simple covalent molecules.
B is incorrect because first ionisation energy: Na < Al < Mg and melting point: Na < Mg < Al
C is incorrect because first ionisation energy: Al < Si < P and melting point: P < Al < Si
D is incorrect because first ionisation energy: Al < Mg < Si and melting point: Mg < Al < Si
Question 1
a. Explain what is meant by the term ‘periodic property’.
b. The graph shows how a periodic property varies when plotted against atomic number for Period 3 (sodium to argon).

i. Identify the property.
ii.Explain the overall trend across the period.
Question 2
The variation of melting point with atomic number for Periods 2 and 3 is shown in the graph below

a. Explain what we mean when we say melting point is a periodic property.
b. Explain the following.
i. The melting point of silicon is much greater than that of phosphorus.
ii. The melting point of aluminum is greater than that of sodium.
Question 3
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies across Periods 2 and 3.
B. Explain this trend.
Question 4
A. Describe how the atomic radius varies down each group of the Periodic Table.
B. Explain this trend.
Question 5
The electrical conductivity of the elements in Period 3 varies across the period as shown in

Explain why aluminum has a much higher electrical conductivity than sulfur. You should refer to the structure of both elements
Question 6
The elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table show variations in their behaviour across the period. The figure below shows the variation of melting points of the elements across Period 3

A. Explain the variation of melting points from P to Ar.
B. Explain why Si has a much higher melting point than any of the other elements in the period.
Question 7
Going across Period 3, a trend in electronegativity can also be observed.
A. Define the term electronegativity.
B. Complete the figure below to show how electronegativity changes along Period 3.

Question 8
Sodium sulfide, Na2S, is a reactive yellow solid, produced when sodium and sulfur react together.
Use of the periodic table is relevant to this question.
How do the ionic radius and atomic radius of sodium compare with those of sulfur?
A. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
B. Sodium < Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
C. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium > Sulfur
D. Sodium > Sulfur and Sodium < Sulfur
Question 9
The trends in three physical properties of the elements of period 3 are shown in the graphs.

Which physical property is not illustrated?
A. Electrical conductivity
B. Atomic radius
C. Melting point
D. Melting point
Question 10
Consecutive elements X, Y and Z, are in the third period of the Periodic Table. Element Y has the highest first ionisation energy and the lowest melting point of these three elements.
What could be the identities of X, Y and Z?
A. Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulfur
B. Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium
C. Aluminium, Silicon, Phosphorus
D. Magnesium, Aluminium, Silicon