Question 1
There are three possible isomers, A, B and C, with the molecular formula C3H8O.
Isomers A and B are positional isomers of each other.
Isomer C is a functional group isomer of A and B.
A student uses the following equation to calculate that the percentage by mass of carbon in all three isomers is 60.0 %
`"Percentage by mass" = "total mass of element"/ "overall mass of compound" ×100`
Calculate the percentage by mass of hydrogen and oxygen in all three isomers
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The infrared spectrum of C3H8O shown in the figure does not have a peak in the region of 3200 - 3600 cm-1
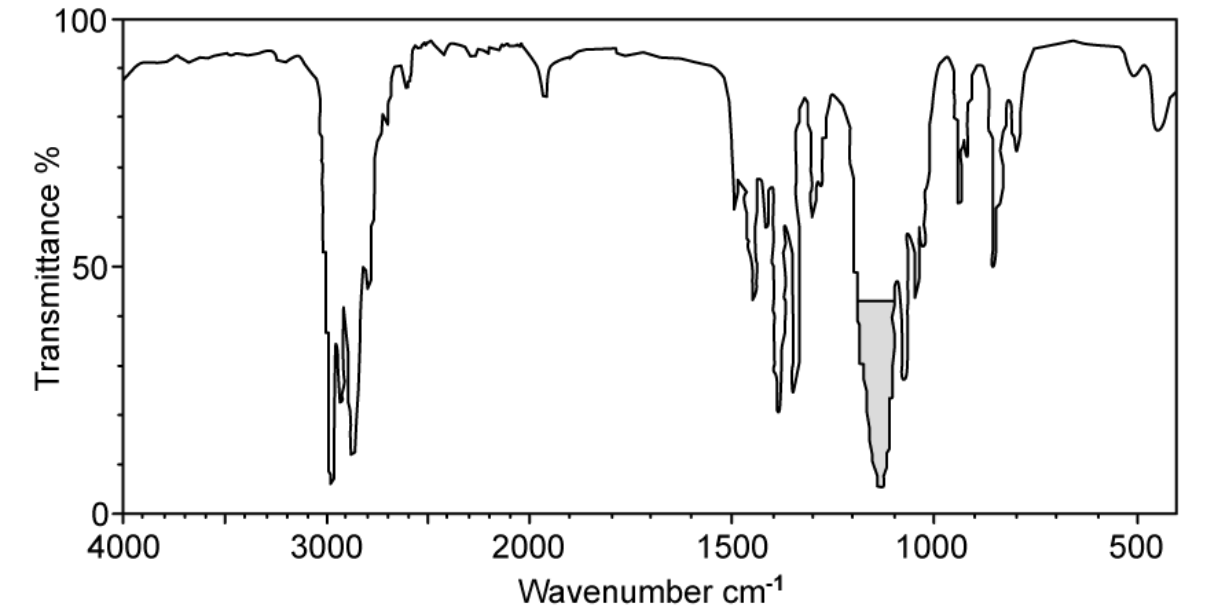
A. Suggest a structure of this compound
B. Suggest which bonds the highlighted peak at around 1130 cm-1 could represent.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
This question is about some isomeric alcohols with the molecular formula C5H12O.
Some alcohols were heated with potassium dichromate(VI) and sulfuric acid. The organic compounds were separated from the reaction mixtures and purified.
The infrared spectra of two of these organic compounds are shown in the figure below
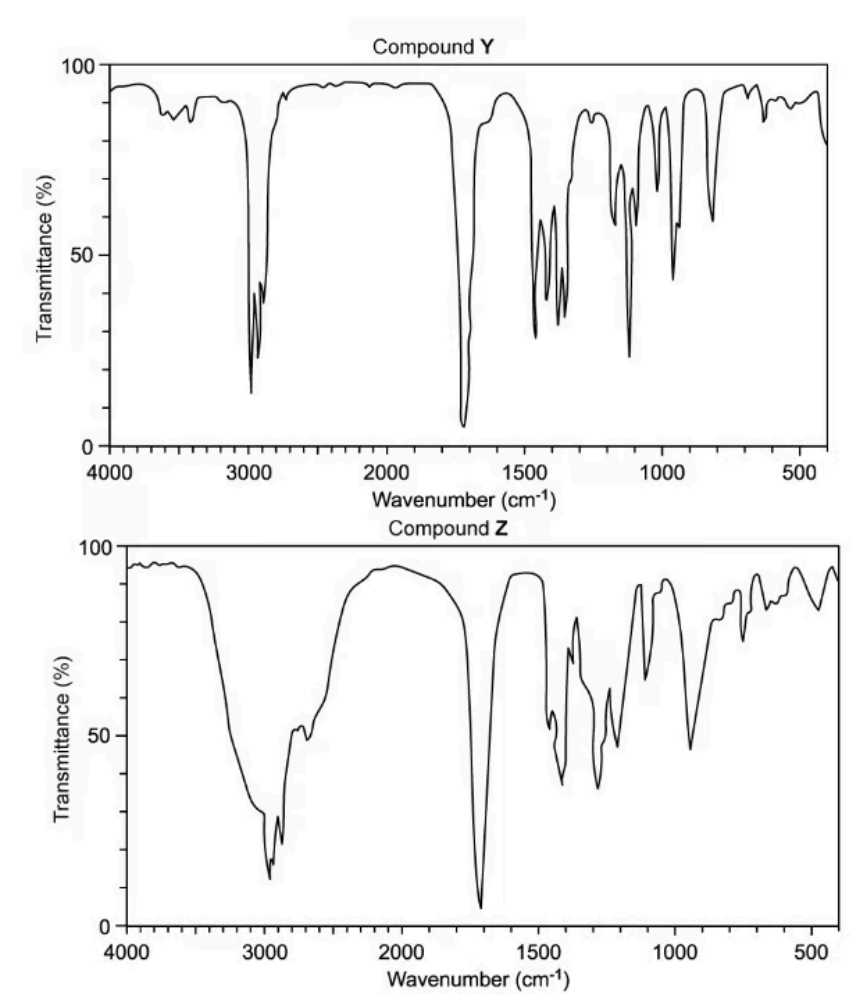
Deduce the type of compound responsible for each spectrum
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Scientists use analytical techniques such as infrared spectroscopy to determine if a desired reaction has taken place.
Explain how infrared spectroscopy generates useful information about an organic molecule
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
In an experiment to prepare a sample of ethanal, CH3CHO, ethanol, C2H5OH, is reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) and the reaction mixture is distilled. The infrared spectra for ethanol and ethanal are shown
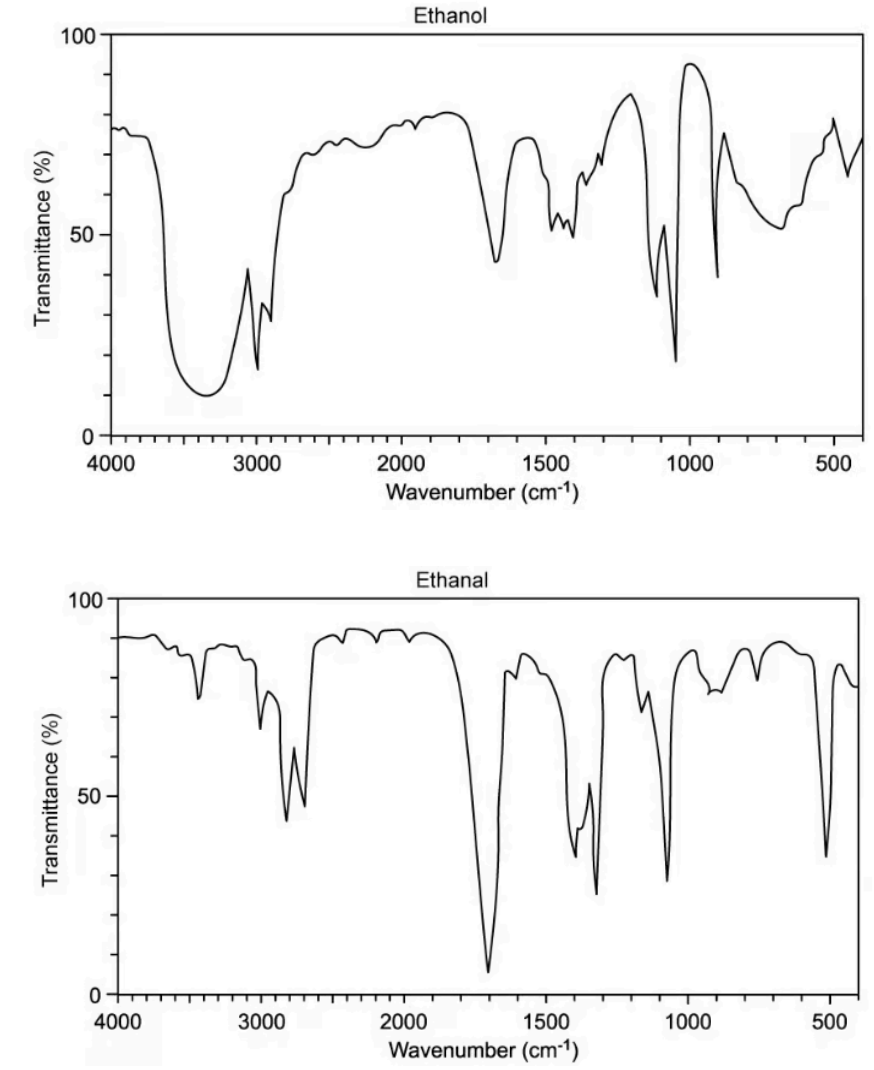
A. State the bonds that give rise to the absorption in the ethanol spectrum at 3400 cm-1 and the absorption in the ethanal spectrum at 1720 cm-1
B. Explain why the absorption at 3400 cm-1 in the ethanol spectrum does not appear in the spectrum for ethanal
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Compounds X, Y and Z were analysed using IR spectroscopy. The spectrum of one of the compounds is shown in
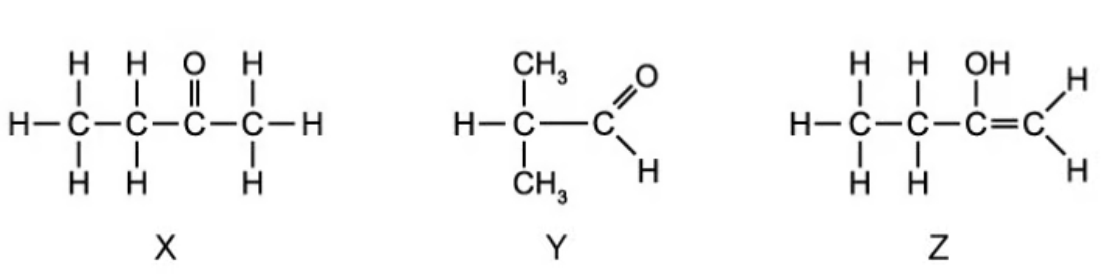
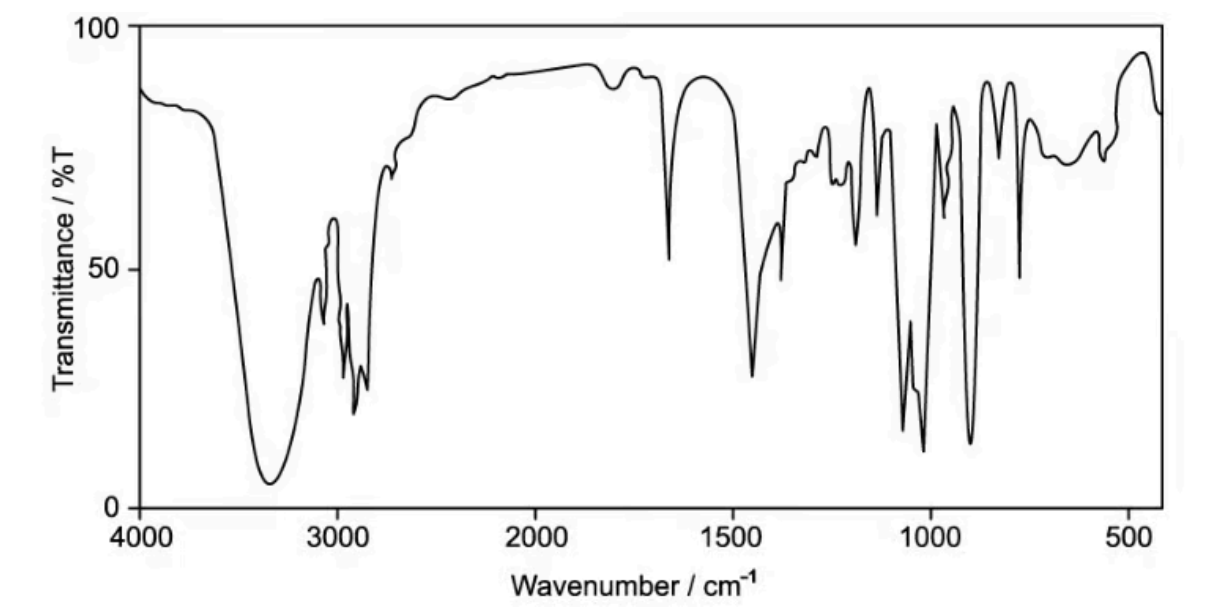
A. Identify which of the three compounds X, Y or Z this spectrum belongs to. Explain your reasoning
B. Explain why infrared spectroscopy alone could not be used to distinguish between compounds X and Y
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
C and D are isomers with the molecular formula C3H6O2 . The infra-red spectra of isomers C and D are shown
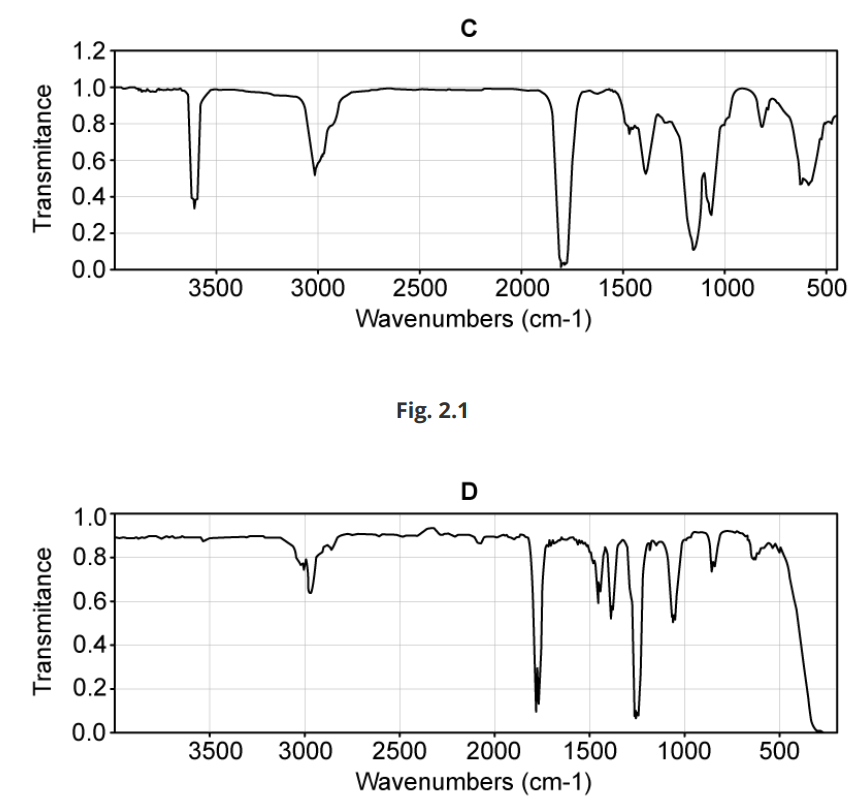
Draw possible structures of isomers C and D
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which of the following statements about propanal, CH3CH2CHO, and propanone, CH3COCH3 is not correct?
The compounds have:
A. Molecular ion peaks at different mass to charge ratios.
B. Different fragmentation patterns in the mass spectrum.
C. Absorption in the infrared spectrum due to the carbonyl group.
D. A different fingerprint region in the infrared spectrum.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which of the following cannot be obtained from an infrared spectrum?
A. The molecular mass
B. The presence of C=O bonds
C. The presence of O-H bonds
D. The identity of a compound through comparison with other spectra
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
The infrared spectrum of a compound is shown below
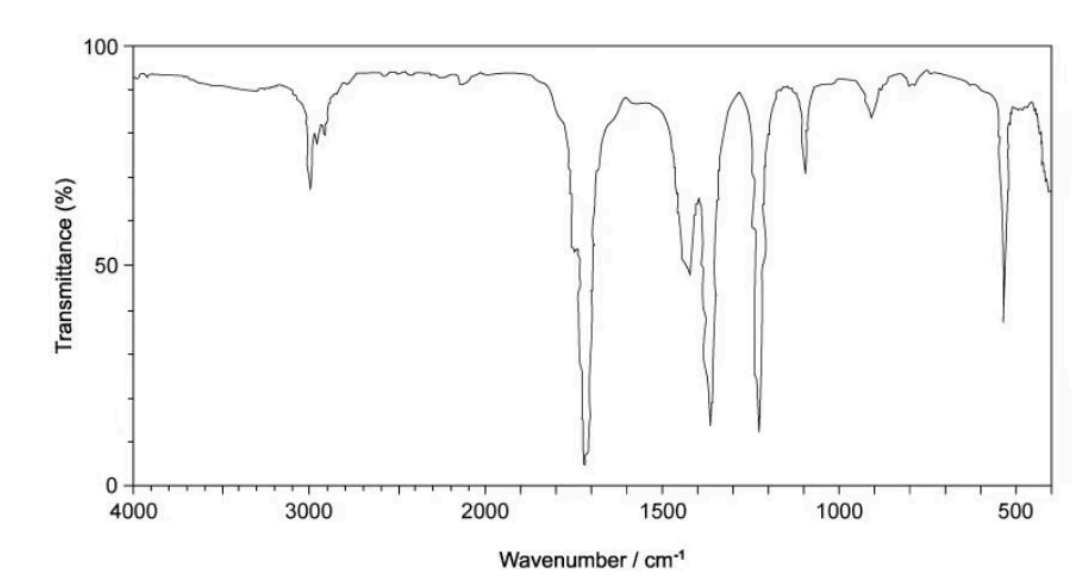
Which compound is shown by the infrared spectrum?
A. Propan-1-ol
B. Propan-2-ol
C. Propanal
D. Propanone
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
There are three possible isomers, A, B and C, with the molecular formula C3H8O.
Isomers A and B are positional isomers of each other.
Isomer C is a functional group isomer of A and B.
A student uses the following equation to calculate that the percentage by mass of carbon in all three isomers is 60.0 %
`"Percentage by mass" = "total mass of element"/ "overall mass of compound" ×100`
Calculate the percentage by mass of hydrogen and oxygen in all three isomers
The percentage by mass of hydrogen and oxygen in all three isomers
Mr of C3H8O = `(3xx12.0)xx(8xx1.0)+16.0 = 60.0`
Percentage by mass of hydrogen = `8.0 / 60.0 xx 100% = 13.3%`
Percentage by mass of oxygen = `16.0 / 60.0 xx 100% = 26.7%`
Question 2
The infrared spectrum of C3H8O shown in the figure does not have a peak in the region of 3200 - 3600 cm-1

A. Suggest a structure of this compound
B. Suggest which bonds the highlighted peak at around 1130 cm-1 could represent.
A. A structure of this compound
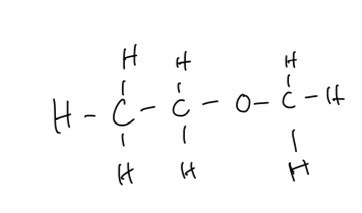
B. The highlighted peak at around 1130 cm-1 could represent C-O bonds
Question 3
This question is about some isomeric alcohols with the molecular formula C5H12O.
Some alcohols were heated with potassium dichromate(VI) and sulfuric acid. The organic compounds were separated from the reaction mixtures and purified.
The infrared spectra of two of these organic compounds are shown in the figure below

Deduce the type of compound responsible for each spectrum
The type of compound responsible for spectrum Y is ketone because this spectrum contains 1700 - 1750 cm-1 range for the C=O bond
The type of compound responsible for spectrum Z is carboxylic acid because this spectrum contains both ranges of 1700 - 1750 cm-1 for the C=O bond and 2500 - 3000 cm-1 for the O-H bond.
Question 4
Scientists use analytical techniques such as infrared spectroscopy to determine if a desired reaction has taken place.
Explain how infrared spectroscopy generates useful information about an organic molecule
Infrared spectroscopy generates useful information about an organic molecule by causing certain bonds via vibrational mode. From that, it characterizes the type of functional group present within a molecule
Question 5
In an experiment to prepare a sample of ethanal, CH3CHO, ethanol, C2H5OH, is reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) and the reaction mixture is distilled. The infrared spectra for ethanol and ethanal are shown

A. State the bonds that give rise to the absorption in the ethanol spectrum at 3400 cm-1 and the absorption in the ethanal spectrum at 1720 cm-1
B. Explain why the absorption at 3400 cm-1 in the ethanol spectrum does not appear in the spectrum for ethanal
A. The bonds that give rise to the absorption in the ethanol spectrum at 3400 cm-1 for O-H bond and the absorption in the ethanal spectrum at 1720 cm-1 for C=O bond
B. The absorption at 3400 cm-1 in the ethanol spectrum does not appear in the spectrum for ethanal because in ethanal molecule, there is no O-H bond while this band belongs to O-H bond.
Question 6
Compounds X, Y and Z were analysed using IR spectroscopy. The spectrum of one of the compounds is shown in


A. Identify which of the three compounds X, Y or Z this spectrum belongs to. Explain your reasoning
B. Explain why infrared spectroscopy alone could not be used to distinguish between compounds X and Y
A. There is a peak at around 3300 - 3600 cm-1 for O-H bond and a peak at around 1600 - 1700 cm-1 for C=C bond. Thus, compound Z is a suitable choice.
B. Because both have the same key functional group which is the carbonyl group and nothing else. This group will appear at 1650 - 1750 cm-1 for C=O bond.
Question 7
C and D are isomers with the molecular formula C3H6O2 . The infra-red spectra of isomers C and D are shown

Draw possible structures of isomers C and D
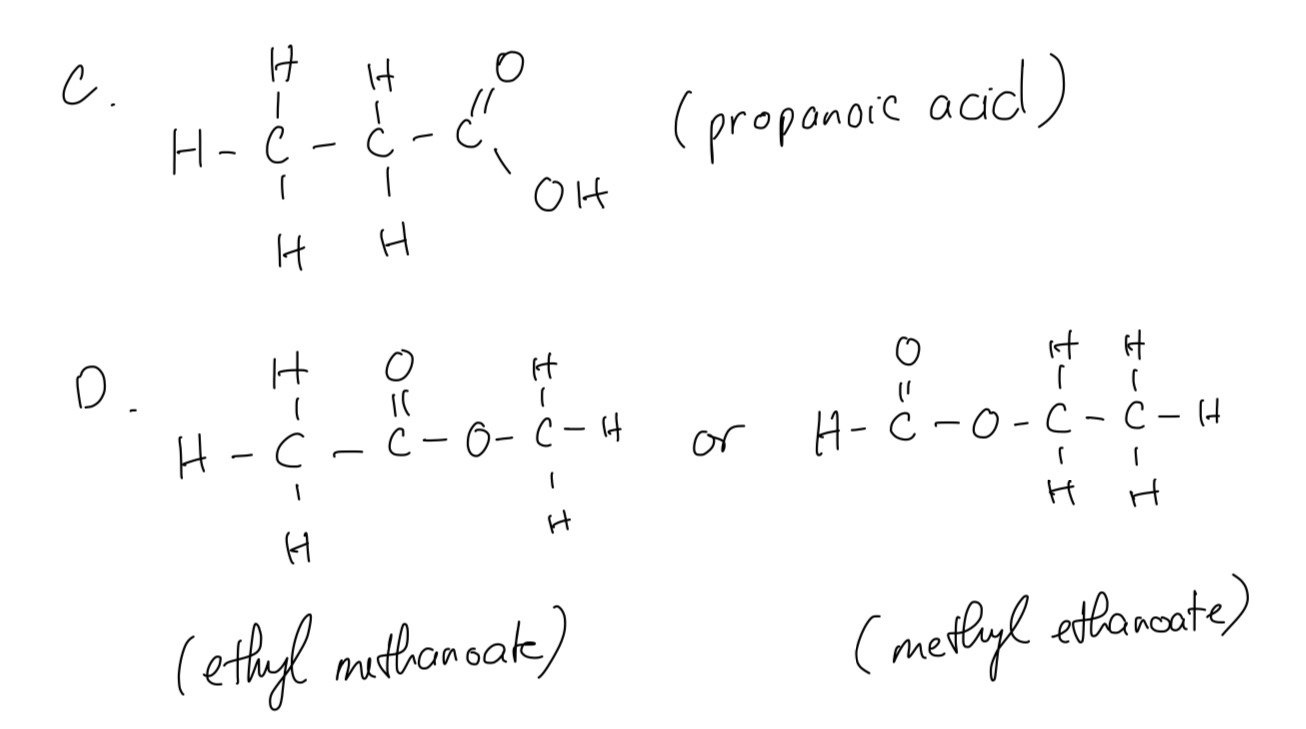
Question 8
Which of the following statements about propanal, CH3CH2CHO, and propanone, CH3COCH3 is not correct?
The compounds have:
A. Molecular ion peaks at different mass to charge ratios.
B. Different fragmentation patterns in the mass spectrum.
C. Absorption in the infrared spectrum due to the carbonyl group.
D. A different fingerprint region in the infrared spectrum.
The answer is A
Both have a molecular ion peak at m/e = 58 with `CH_3CH_2CHO^+` ion and `CH_3COCH""_3^+` ion for each compound, respectively.
B is incorrect because they will present different patterns in the MS
C is incorrect because both have C=O bond
D is incorrect because they will have a different fingerprint region in the infrared spectrum
Question 9
Which of the following cannot be obtained from an infrared spectrum?
A. The molecular mass
B. The presence of C=O bonds
C. The presence of O-H bonds
D. The identity of a compound through comparison with other spectra
The answer is A
IR spectrum is used to identify functional groups within a molecule based on vibrational frequencies
B, C, and D are incorrect because the infrared spectrum can give us these information
Question 10
The infrared spectrum of a compound is shown below

Which compound is shown by the infrared spectrum?
A. Propan-1-ol
B. Propan-2-ol
C. Propanal
D. Propanone
The answer is D
There is a peak at around 1700 cm-1. This represents for C=O bond.
A and B are incorrect because they are alcohols
C is incorrect because it will have 2 another peaks appearing at 2900-2800 cm-1 and 2770-2700 cm-1
Question 1
There are three possible isomers, A, B and C, with the molecular formula C3H8O.
Isomers A and B are positional isomers of each other.
Isomer C is a functional group isomer of A and B.
A student uses the following equation to calculate that the percentage by mass of carbon in all three isomers is 60.0 %
`"Percentage by mass" = "total mass of element"/ "overall mass of compound" ×100`
Calculate the percentage by mass of hydrogen and oxygen in all three isomers
Question 2
The infrared spectrum of C3H8O shown in the figure does not have a peak in the region of 3200 - 3600 cm-1

A. Suggest a structure of this compound
B. Suggest which bonds the highlighted peak at around 1130 cm-1 could represent.
Question 3
This question is about some isomeric alcohols with the molecular formula C5H12O.
Some alcohols were heated with potassium dichromate(VI) and sulfuric acid. The organic compounds were separated from the reaction mixtures and purified.
The infrared spectra of two of these organic compounds are shown in the figure below

Deduce the type of compound responsible for each spectrum
Question 4
Scientists use analytical techniques such as infrared spectroscopy to determine if a desired reaction has taken place.
Explain how infrared spectroscopy generates useful information about an organic molecule
Question 5
In an experiment to prepare a sample of ethanal, CH3CHO, ethanol, C2H5OH, is reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) and the reaction mixture is distilled. The infrared spectra for ethanol and ethanal are shown

A. State the bonds that give rise to the absorption in the ethanol spectrum at 3400 cm-1 and the absorption in the ethanal spectrum at 1720 cm-1
B. Explain why the absorption at 3400 cm-1 in the ethanol spectrum does not appear in the spectrum for ethanal
Question 6
Compounds X, Y and Z were analysed using IR spectroscopy. The spectrum of one of the compounds is shown in


A. Identify which of the three compounds X, Y or Z this spectrum belongs to. Explain your reasoning
B. Explain why infrared spectroscopy alone could not be used to distinguish between compounds X and Y
Question 7
C and D are isomers with the molecular formula C3H6O2 . The infra-red spectra of isomers C and D are shown

Draw possible structures of isomers C and D
Question 8
Which of the following statements about propanal, CH3CH2CHO, and propanone, CH3COCH3 is not correct?
The compounds have:
A. Molecular ion peaks at different mass to charge ratios.
B. Different fragmentation patterns in the mass spectrum.
C. Absorption in the infrared spectrum due to the carbonyl group.
D. A different fingerprint region in the infrared spectrum.
Question 9
Which of the following cannot be obtained from an infrared spectrum?
A. The molecular mass
B. The presence of C=O bonds
C. The presence of O-H bonds
D. The identity of a compound through comparison with other spectra
Question 10
The infrared spectrum of a compound is shown below

Which compound is shown by the infrared spectrum?
A. Propan-1-ol
B. Propan-2-ol
C. Propanal
D. Propanone