Question 1
a. Alcohols and alkenes are versatile chemicals that are often involved in many organic synthetic reaction schemes.
Butan-1-ol can be converted directly into 1-bromobutane.
State the reagents and conditions required for this conversion.
b. Heating butan-1-ol with concentrated sulfuric acid causes the loss of a small molecule.
State the type of reaction involved and name the resulting alkene.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
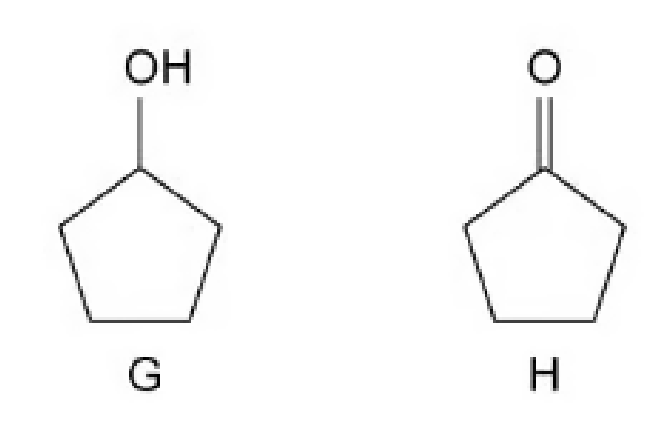
Describe one simple test-tube reaction that allows you to distinguish between compounds G and H shown in
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
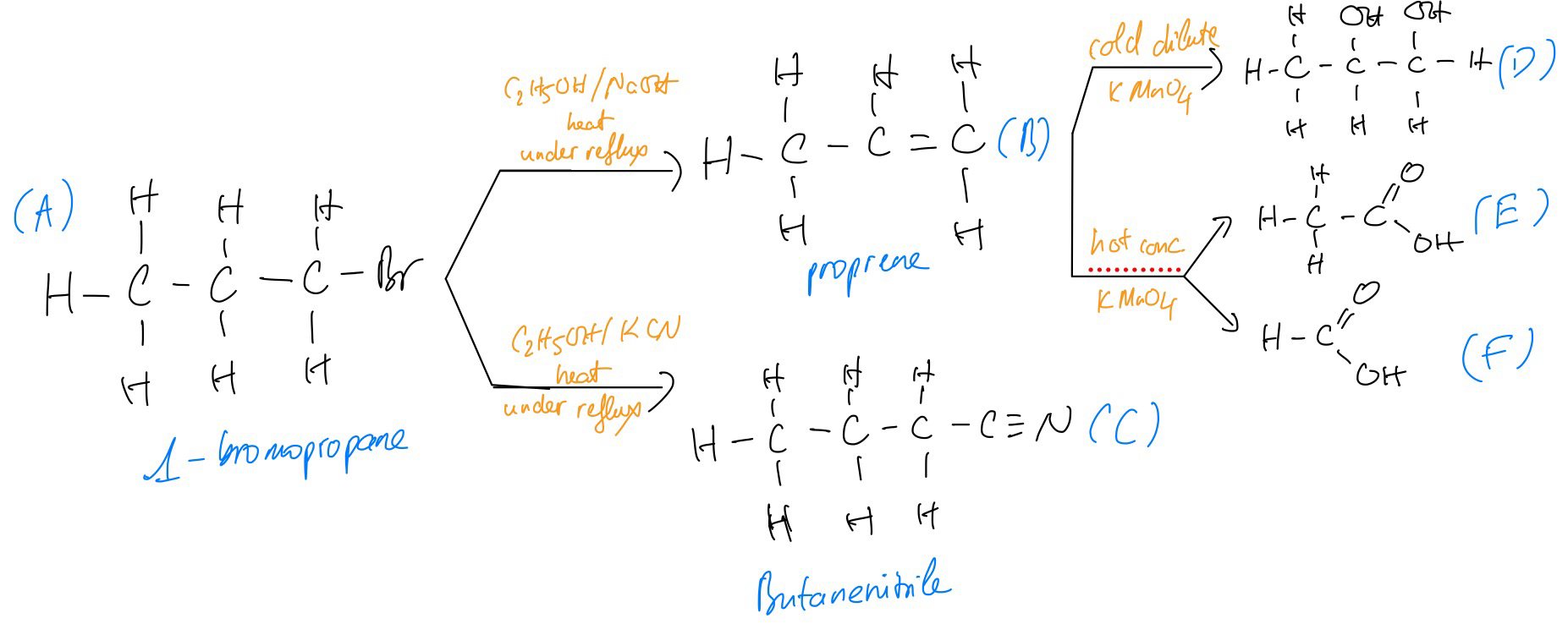
a. A reaction pathway is shown in
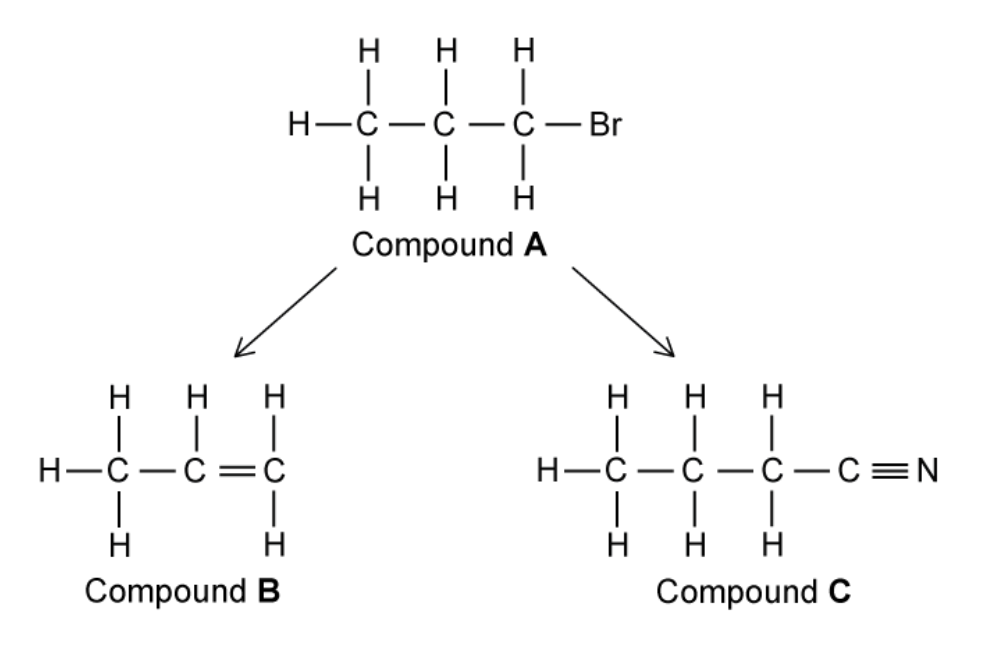
State the reagents and conditions required for the conversion of compounds
b. Name compound C shown in figure above in part (a)
c.
i. Compound B reacts with cold dilute potassium manganate(VII) to form compound D. Draw the structure of compound D
ii. Compound B also reacts with hot concentrated potassium manganate(VII) to form compounds E and F. Draw the structure of compounds E and F
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
a. But-2-ene can be converted into butan-2-ol by two different synthetic routes. One route can be carried out as a one-step process whilst the other requires two steps.
State reagents and provide an equation, using structural formulae, for the one-step process
b. Draw a reaction scheme, including reagents and conditions for the two step process
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
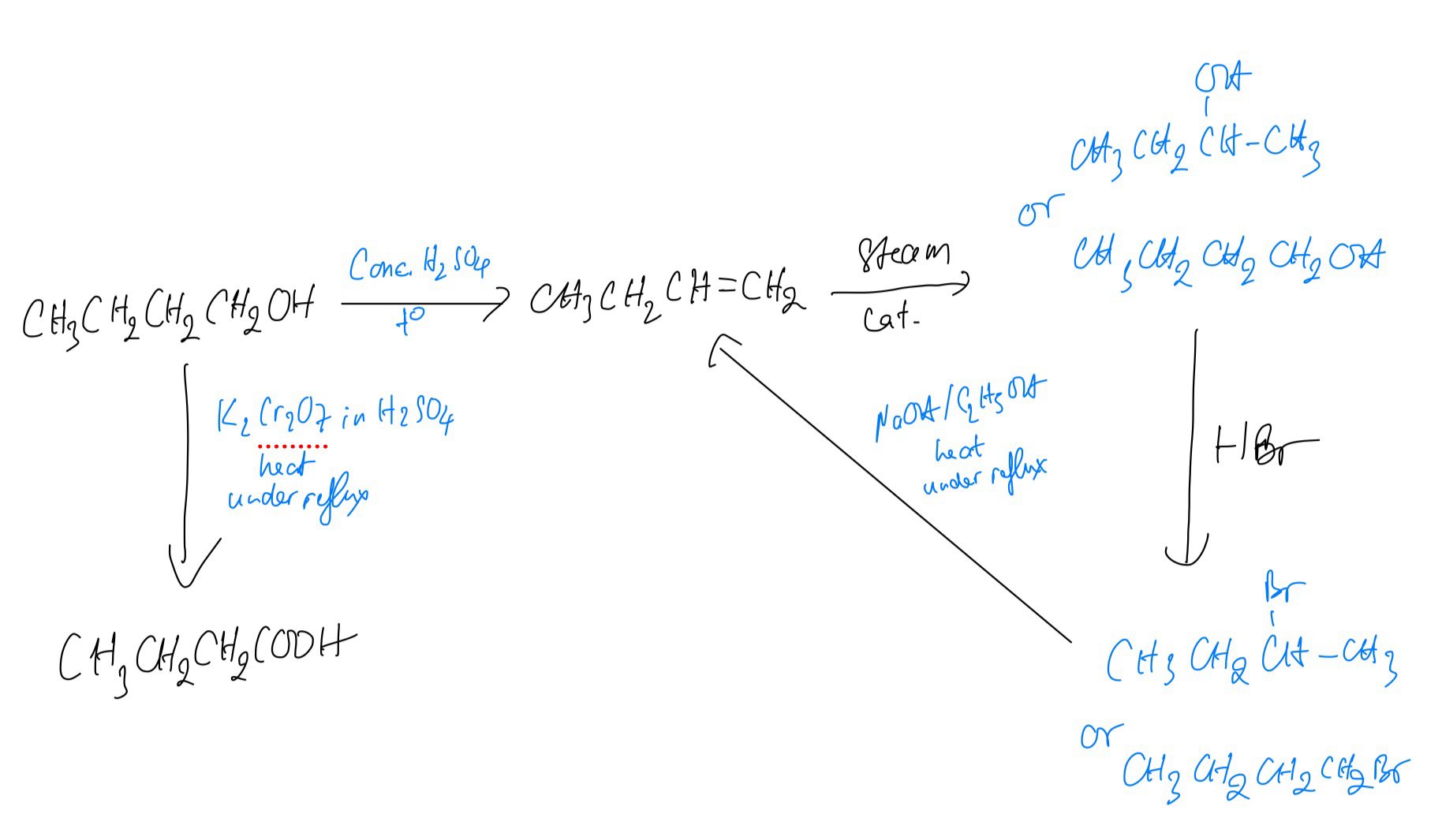
A series of reactions based on butan-1-ol is shown
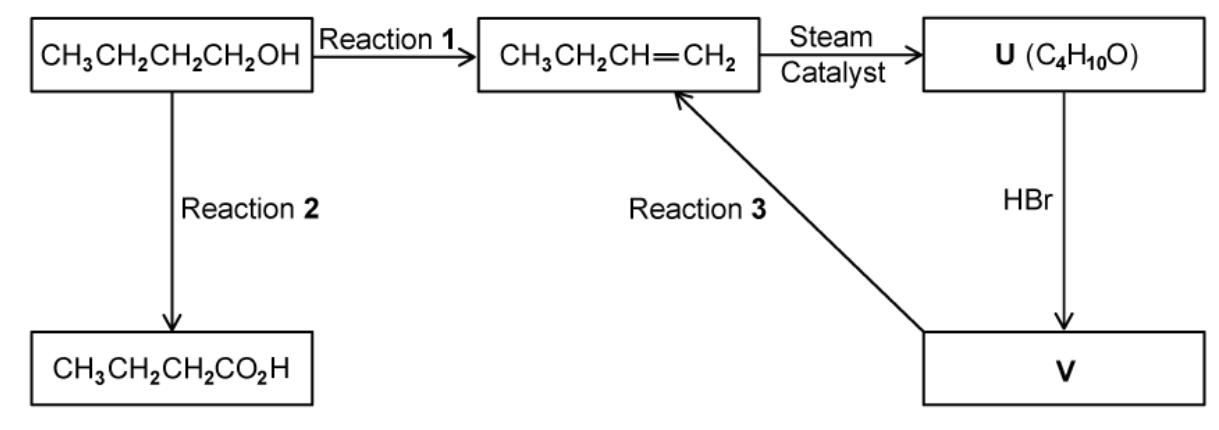
Identify every suitable reagent and conditions as well as structure in figure above
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
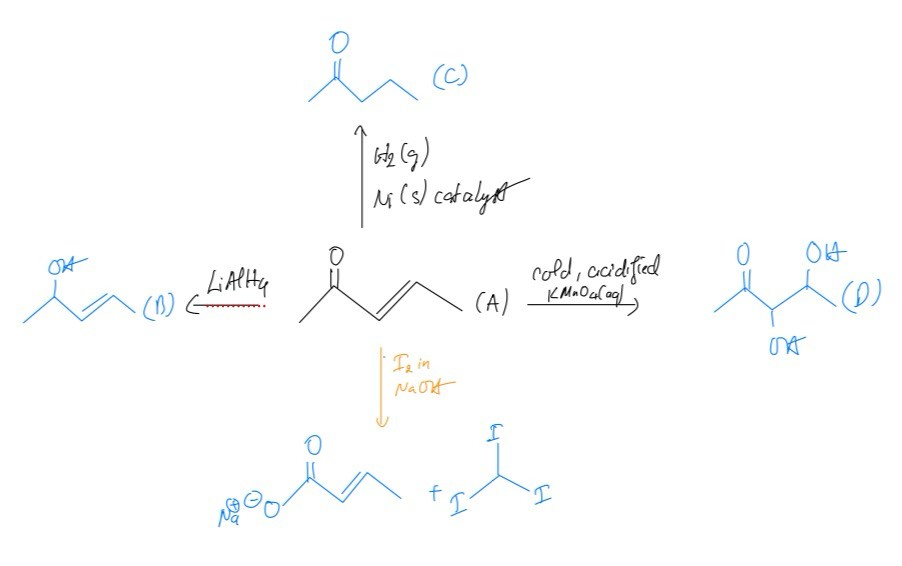
Some reactions of compound A are shown in
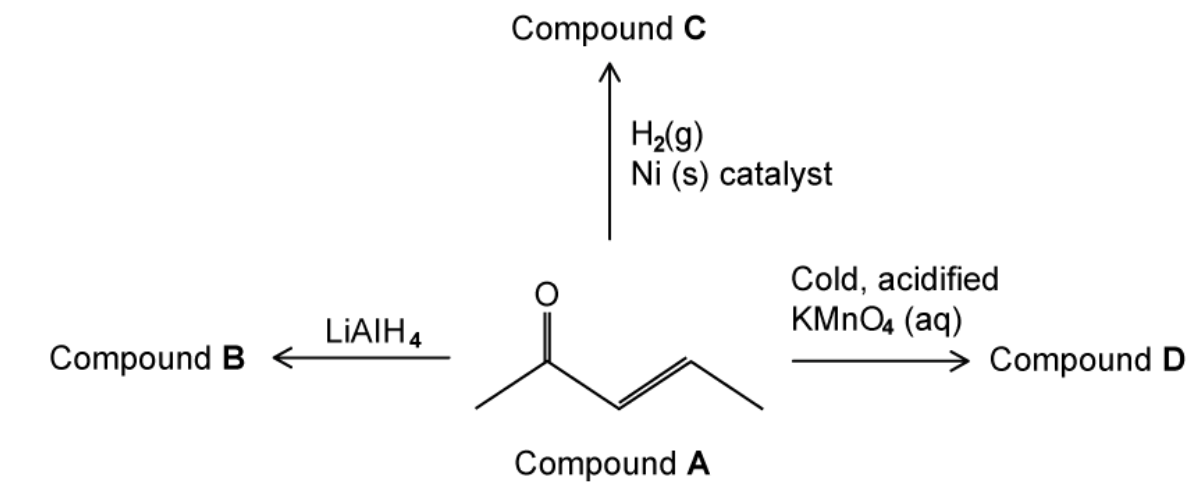
a. Draw the skeletal structures of compounds B, C and D
b. Compound A reacts with iodine and sodium hydroxide ions to give two products. Draw the skeletal structures of these two products
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The reaction scheme shows three steps to synthesise 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile from propene.
Suggest the reagents and conditions required for theses reactions including compounds
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Lactic acid occurs naturally, for example in sour milk
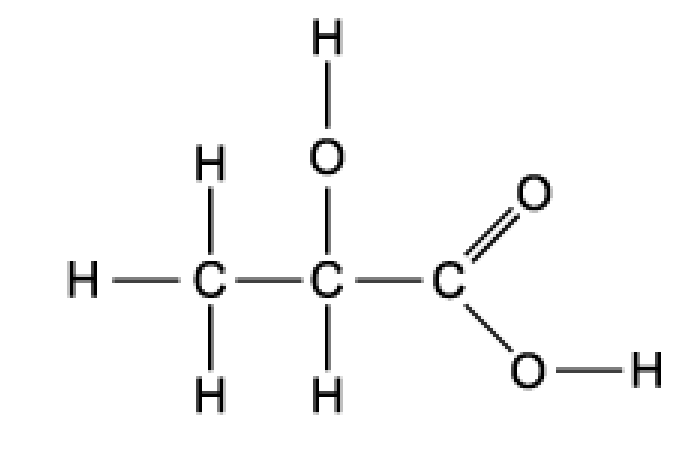
What is a property of lactic acid?
A. It decolourises aqueous bromine rapidly
B. It is insoluble in water
C. It reduces Fehling’s reagent
D. It reacts with sodium carbonate
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which reagent can be used to convert `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_3`into `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_2Cl`?
A. Chlorine in bright sunlight at 100 °C
B. Concentrated hydrochloric acid at 100 °C
C. Phosphorus pentachloride at room temperature
D. Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride, SOCl2) at 50 °C
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A compound C has the following properties:
What could C be?
A. Propene
B. Propanol
C. Propanoic acid
D. Propyl propanoate
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
a. Alcohols and alkenes are versatile chemicals that are often involved in many organic synthetic reaction schemes.
Butan-1-ol can be converted directly into 1-bromobutane.
State the reagents and conditions required for this conversion.
b. Heating butan-1-ol with concentrated sulfuric acid causes the loss of a small molecule.
State the type of reaction involved and name the resulting alkene.
a. The reagents and conditions required for this conversion are NaBr in H2SO4 solution under heat with reflux.
Remarks: There are various synthetic routes for preparing organic molecules. The answer will be acceptable as long as it’s suitable, for example, slowly adding PBr3
b. The type of this reaction is called elimination or dehydration
The resulting alkene is but-1-ene
Question 2
Describe one simple test-tube reaction that allows you to distinguish between compounds G and H shown in

One simple test-tube reaction that allows you to distinguish between compounds G and H is using acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution because compound G with secondary alcohol can be oxidised to a ketone along with colour change from orange to green, while there is no change in compound H because ketone will not reaction with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution
Question 3
a. A reaction pathway is shown in

State the reagents and conditions required for the conversion of compounds
b. Name compound C shown in figure above in part (a)
c.
i. Compound B reacts with cold dilute potassium manganate(VII) to form compound D. Draw the structure of compound D
ii. Compound B also reacts with hot concentrated potassium manganate(VII) to form compounds E and F. Draw the structure of compounds E and F
Question 4
a. But-2-ene can be converted into butan-2-ol by two different synthetic routes. One route can be carried out as a one-step process whilst the other requires two steps.
State reagents and provide an equation, using structural formulae, for the one-step process
b. Draw a reaction scheme, including reagents and conditions for the two step process
a. The reagents and an equation, using structural formulae, for the one-step process
Reagents: steam in acid catalyst
Equation:
`CH_3CHCHCH_3 + H_2O -> CH_3CHOHCH_2CH_3`
b. A reaction scheme, including reagents and conditions for the two step process
But-2-ene -> 2-bromobutane -> butan-2-ol
Step 1: HBr solution
Step 2: aqueous alkaline hydroxide
Question 5
A series of reactions based on butan-1-ol is shown

Identify every suitable reagent and conditions as well as structure in figure above
Question 6
Some reactions of compound A are shown in

a. Draw the skeletal structures of compounds B, C and D
b. Compound A reacts with iodine and sodium hydroxide ions to give two products. Draw the skeletal structures of these two products
Question 7
The reaction scheme shows three steps to synthesise 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile from propene.
Suggest the reagents and conditions required for theses reactions including compounds
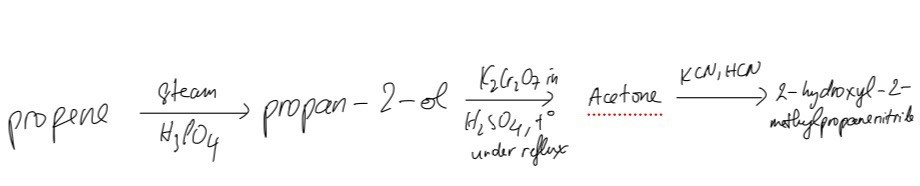
Question 8
Lactic acid occurs naturally, for example in sour milk

What is a property of lactic acid?
A. It decolourises aqueous bromine rapidly
B. It is insoluble in water
C. It reduces Fehling’s reagent
D. It reacts with sodium carbonate
The answer is D
It will create a salt with CO2 and H2O
A is incorrect because bromine water is decolorised when we have alkene compound
B is incorrect because because it has carboxylic acid group and alcohol which both have polar properties
C is incorrect because only aldehyde reacts with Fehling’s reagent to form carboxylic acid
Question 9
Which reagent can be used to convert `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_3`into `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_2Cl`?
A. Chlorine in bright sunlight at 100 °C
B. Concentrated hydrochloric acid at 100 °C
C. Phosphorus pentachloride at room temperature
D. Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride, SOCl2) at 50 °C
The answer is A
This reaction will be occurred via free-radical substitution in which a halogen atom will replace one H atom to create a new molecule.
B, C and D are incorrect because these compounds are used in the nucleophilic substitution for the conversion of alcohols.
Question 10
A compound C has the following properties:
What could C be?
A. Propene
B. Propanol
C. Propanoic acid
D. Propyl propanoate
The answer is C
A is incorrect because it is a gas and insoluble in water as well as not reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide
B is incorrect because it is a liquid and soluble in water but not react with aqueous sodium hydroxide due to a weak base
D is incorrect because it is not soluble in water
Question 1
a. Alcohols and alkenes are versatile chemicals that are often involved in many organic synthetic reaction schemes.
Butan-1-ol can be converted directly into 1-bromobutane.
State the reagents and conditions required for this conversion.
b. Heating butan-1-ol with concentrated sulfuric acid causes the loss of a small molecule.
State the type of reaction involved and name the resulting alkene.
Question 2
Describe one simple test-tube reaction that allows you to distinguish between compounds G and H shown in

Question 3
a. A reaction pathway is shown in

State the reagents and conditions required for the conversion of compounds
b. Name compound C shown in figure above in part (a)
c.
i. Compound B reacts with cold dilute potassium manganate(VII) to form compound D. Draw the structure of compound D
ii. Compound B also reacts with hot concentrated potassium manganate(VII) to form compounds E and F. Draw the structure of compounds E and F
Question 4
a. But-2-ene can be converted into butan-2-ol by two different synthetic routes. One route can be carried out as a one-step process whilst the other requires two steps.
State reagents and provide an equation, using structural formulae, for the one-step process
b. Draw a reaction scheme, including reagents and conditions for the two step process
Question 5
A series of reactions based on butan-1-ol is shown

Identify every suitable reagent and conditions as well as structure in figure above
Question 6
Some reactions of compound A are shown in

a. Draw the skeletal structures of compounds B, C and D
b. Compound A reacts with iodine and sodium hydroxide ions to give two products. Draw the skeletal structures of these two products
Question 7
The reaction scheme shows three steps to synthesise 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile from propene.
Suggest the reagents and conditions required for theses reactions including compounds
Question 8
Lactic acid occurs naturally, for example in sour milk

What is a property of lactic acid?
A. It decolourises aqueous bromine rapidly
B. It is insoluble in water
C. It reduces Fehling’s reagent
D. It reacts with sodium carbonate
Question 9
Which reagent can be used to convert `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_3`into `CH_3CH_2CO_2CH_2Cl`?
A. Chlorine in bright sunlight at 100 °C
B. Concentrated hydrochloric acid at 100 °C
C. Phosphorus pentachloride at room temperature
D. Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride, SOCl2) at 50 °C
Question 10
A compound C has the following properties:
What could C be?
A. Propene
B. Propanol
C. Propanoic acid
D. Propyl propanoate