Question 1
When 1-chloropropane is heated under reflux with ethanolic potassium cyanide, KCN, the following reaction occurs.
`CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + KCN → CH_3CH_2CH_2CN + KCl`
A. Draw the displayed formula of the organic product formed in this reaction
B. State the IUPAC name of this organic product
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The CH3CH2CH2CN can undergo hydrolysis
A. Write the equation for the acid hydrolysis of CH3CH2CH2CN
B. Draw the displayed formula of the intermediate formed when CH3CH2CH2CN is hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
This question is about hydroxynitriles.
The hydroxynitrile shown in the figure below can be prepared from the reaction between propanal and hydrogen cyanide.
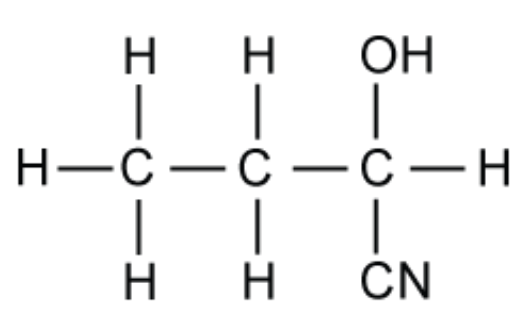
A. Give the IUPAC name of this hydroxynitrile
B. Write and name the type of the reaction mechanism of this hydroxynitrile formation from reaction between propanal and the cyanide ion
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Halogenoalkanes are often used as intermediates in organic reactions
Three reactions of bromoethane, CH3CH2Br, are shown in
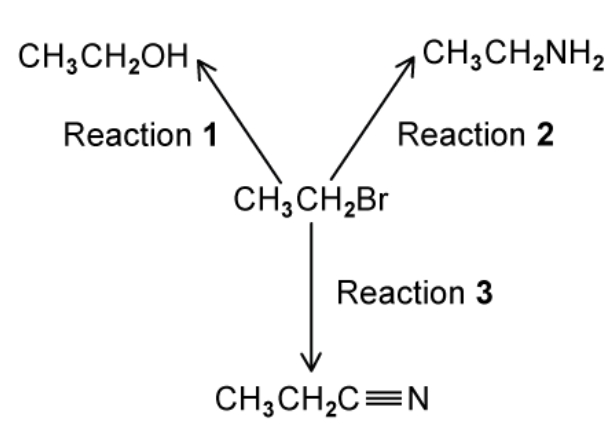
a. For each reaction, state the reagent and solvent used
b. The product of reaction 2 can be converted into CH3CN
i. Name the compound CH3CN
ii. Name the type of reaction used to form CH3CN
c. The product of reaction 3 can be used to produce propanoic acid by two different hydrolysis reactions. Compare the two types of hydrolysis reaction in the production of propanoic acid from the product of reaction 3
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile contains sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms.
A. Draw the displayed formula of this molecule
B. State the number of sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms in a molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile.
C. 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile can be produced from compound X, a secondary alcohol, in a two-step synthesis.
State the reagents and conditions required for step 1 and step 2
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile is useful in the synthesis of a variety of medicines and pharmaceuticals.
A. Draw the skeletal formula of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
B. 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile undergoes hydrolysis when heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Write an equation for the hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Hydrolysis of CH3CH2CN with dilute HCl produces which compound?
A. CH3COOH
B. CH3CH2CH2NH3
C. CH3CH2COOH
D. CH3CH2COH
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
The equation shows a chemical reaction
`CH_3CH_2CHClCH_3 + CN^- → CH_3CH_2CH(CH_3)CN + Cl^-`
What is the name for this type of reaction?
A. Nucleophilic substitution
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic addition
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and hydrochloric acid?
A. Propanoic acid and ammonia
B. Propanoic acid and ammonium chloride
C. Ethanoic acid and ammonia
D. Ethanoic acid and ammonium chloride
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and sodium hydroxide?
A. Sodium propanoate and ammonia
B. Sodium propanoate ammonium chloride
C. Sodium ethanoate and ammonia
D. Sodium ethanoate and ammonium chloride
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
When 1-chloropropane is heated under reflux with ethanolic potassium cyanide, KCN, the following reaction occurs.
`CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + KCN → CH_3CH_2CH_2CN + KCl`
A. Draw the displayed formula of the organic product formed in this reaction
B. State the IUPAC name of this organic product
A. The displayed formula of the organic product formed in this reaction
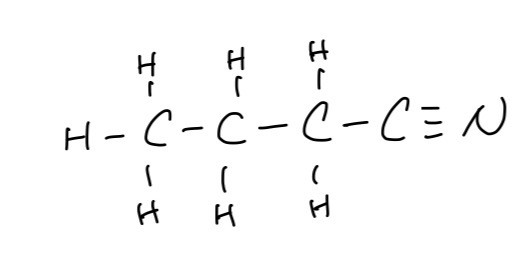
B. The IUPAC name of this organic product is butanenitrile
Question 2
The CH3CH2CH2CN can undergo hydrolysis
A. Write the equation for the acid hydrolysis of CH3CH2CH2CN
B. Draw the displayed formula of the intermediate formed when CH3CH2CH2CN is hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide
A. The equation for the acid hydrolysis of CH3CH2CH2CN
`CH_3CH_2CH_2CN + HCl + 2H_2O -> CH_3CH_2CH_2COOH + NH_4Cl`
B. The displayed formula of the intermediate formed when CH3CH2CH2CN is hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide
`CH_3CH_2CH_2CN + NaOH + 2H_2O -> CH_3CH_2CH_2COO^-) Na^+ +NH_3`
Question 3
This question is about hydroxynitriles.
The hydroxynitrile shown in the figure below can be prepared from the reaction between propanal and hydrogen cyanide.

A. Give the IUPAC name of this hydroxynitrile
B. Write and name the type of the reaction mechanism of this hydroxynitrile formation from reaction between propanal and the cyanide ion
A. This is 2-hydroxybutanenitrile.
Remark: the longest carbon chain is four carbons and there is a nitrile group which is in the first position. This must be called butanenitrile.
B. The type of this reaction mechanism is nucleophilic addition in which C=O carbonyl group is broken down to add another species which is cyanide ion.
Question 4
Halogenoalkanes are often used as intermediates in organic reactions
Three reactions of bromoethane, CH3CH2Br, are shown in

a. For each reaction, state the reagent and solvent used
b. The product of reaction 2 can be converted into CH3CN
i. Name the compound CH3CN
ii. Name the type of reaction used to form CH3CN
c. The product of reaction 3 can be used to produce propanoic acid by two different hydrolysis reactions. Compare the two types of hydrolysis reaction in the production of propanoic acid from the product of reaction 3
a. The reagen and solvent are used for each reaction
Reaction 1: Alkaline hydroxide in water
Reaction 2: Ammonia in alcohol
Reaction 3: Alkaline cyanide in alcohol
b.
i. The compound CH3CN is called ethanenitrile
ii. The type of reaction used to form CH3CN is oxidation or dehydrogenation
c.
There are some differences between both types of hydrolysis reactions. The two types of hydrolysis are acid hydrolysis and alkaline hydrolysis.
Acid hydrolysis forms propanoic acid in one step while alkaline hydrolysis forms propanoic acid in two steps. Acid hydrolysis forms an ammonium salt, whereas alkaline hydrolysis forms ammonia
For similarity, both types of hydrolysis require water and acid which is used to acidify the metal carboxylate salt.
Question 5
A molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile contains sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms.
A. Draw the displayed formula of this molecule
B. State the number of sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms in a molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile.
C. 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile can be produced from compound X, a secondary alcohol, in a two-step synthesis.
State the reagents and conditions required for step 1 and step 2
A. The displayed formula of this molecule
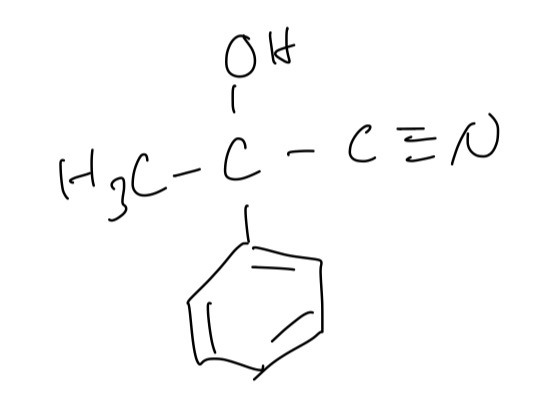
B. The number of sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms in a molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile are 1, 6 and 2 respectively
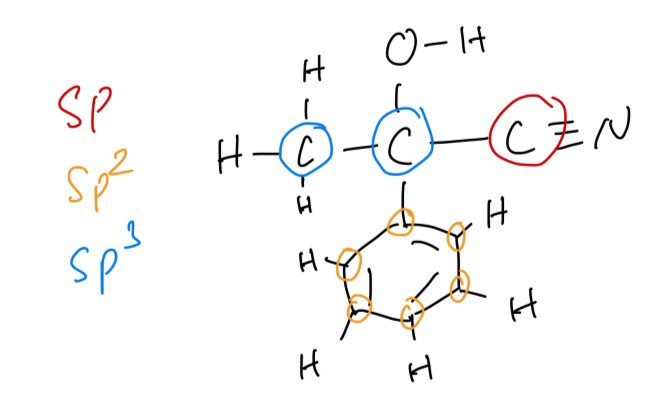
C. The reagents and conditions required for
step 1: K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4 in H2SO4 under heat
step 2: HCN and KCN under heat
Question 6
2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile is useful in the synthesis of a variety of medicines and pharmaceuticals.
A. Draw the skeletal formula of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
B. 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile undergoes hydrolysis when heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Write an equation for the hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
A. The skeletal formula of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
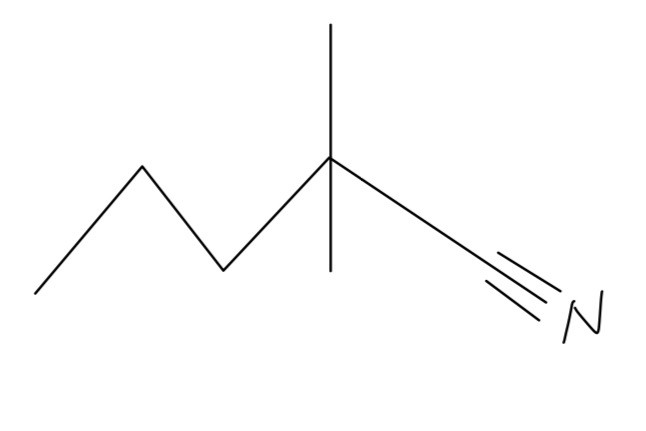
B. An equation for the hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile is
`CH_3(CH_2)_2C(CH_3)_2CN + HCl + 2H_2O -> CH_3(CH_2)_2C(CH_3)_2COOH + NH_4Cl`
Question 7
Hydrolysis of CH3CH2CN with dilute HCl produces which compound?
A. CH3COOH
B. CH3CH2CH2NH3
C. CH3CH2COOH
D. CH3CH2COH
The answer is C
A is incorrect because the carbon chain is wrong
B is incorrect because this is a primary amine which is generated by reduction of nitrile
D is incorrect because this molecule cannot be formed by hydrolysis of CH3CH2CN
Question 8
The equation shows a chemical reaction
`CH_3CH_2CHClCH_3 + CN^- → CH_3CH_2CH(CH_3)CN + Cl^-`
What is the name for this type of reaction?
A. Nucleophilic substitution
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic addition
The answer is A
B is incorrect because CN- is not electrophile
C is incorrect because it could not be a free radical substitution in which halogen atom will replace hydrogen atom in alkanes
D is incorrect because it is a substitution instead
Question 9
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and hydrochloric acid?
A. Propanoic acid and ammonia
B. Propanoic acid and ammonium chloride
C. Ethanoic acid and ammonia
D. Ethanoic acid and ammonium chloride
The answer is D
A & B are incorrect because the number of carbons in the carbon chain should remain unchanged.
C is incorrect because the ammonia in solution will serve as a base to form an ammonium salt
Question 10
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and sodium hydroxide?
A. Sodium propanoate and ammonia
B. Sodium propanoate ammonium chloride
C. Sodium ethanoate and ammonia
D. Sodium ethanoate and ammonium chloride
The answer is C
A & B are incorrect because the number of carbons in the carbon chain should remain unchanged
D is incorrect because an ammonium salt could be created when ethanenitrile reacts with hydrochloric acid
Question 1
When 1-chloropropane is heated under reflux with ethanolic potassium cyanide, KCN, the following reaction occurs.
`CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + KCN → CH_3CH_2CH_2CN + KCl`
A. Draw the displayed formula of the organic product formed in this reaction
B. State the IUPAC name of this organic product
Question 2
The CH3CH2CH2CN can undergo hydrolysis
A. Write the equation for the acid hydrolysis of CH3CH2CH2CN
B. Draw the displayed formula of the intermediate formed when CH3CH2CH2CN is hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide
Question 3
This question is about hydroxynitriles.
The hydroxynitrile shown in the figure below can be prepared from the reaction between propanal and hydrogen cyanide.

A. Give the IUPAC name of this hydroxynitrile
B. Write and name the type of the reaction mechanism of this hydroxynitrile formation from reaction between propanal and the cyanide ion
Question 4
Halogenoalkanes are often used as intermediates in organic reactions
Three reactions of bromoethane, CH3CH2Br, are shown in

a. For each reaction, state the reagent and solvent used
b. The product of reaction 2 can be converted into CH3CN
i. Name the compound CH3CN
ii. Name the type of reaction used to form CH3CN
c. The product of reaction 3 can be used to produce propanoic acid by two different hydrolysis reactions. Compare the two types of hydrolysis reaction in the production of propanoic acid from the product of reaction 3
Question 5
A molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile contains sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms.
A. Draw the displayed formula of this molecule
B. State the number of sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon atoms in a molecule of 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile.
C. 2-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanenitrile can be produced from compound X, a secondary alcohol, in a two-step synthesis.
State the reagents and conditions required for step 1 and step 2
Question 6
2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile is useful in the synthesis of a variety of medicines and pharmaceuticals.
A. Draw the skeletal formula of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
B. 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile undergoes hydrolysis when heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Write an equation for the hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethylpentanenitrile
Question 7
Hydrolysis of CH3CH2CN with dilute HCl produces which compound?
A. CH3COOH
B. CH3CH2CH2NH3
C. CH3CH2COOH
D. CH3CH2COH
Question 8
The equation shows a chemical reaction
`CH_3CH_2CHClCH_3 + CN^- → CH_3CH_2CH(CH_3)CN + Cl^-`
What is the name for this type of reaction?
A. Nucleophilic substitution
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic addition
Question 9
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and hydrochloric acid?
A. Propanoic acid and ammonia
B. Propanoic acid and ammonium chloride
C. Ethanoic acid and ammonia
D. Ethanoic acid and ammonium chloride
Question 10
What are the products in the reaction of ethanenitrile and sodium hydroxide?
A. Sodium propanoate and ammonia
B. Sodium propanoate ammonium chloride
C. Sodium ethanoate and ammonia
D. Sodium ethanoate and ammonium chloride