Question 1
a. Propylamine can be produced from 1-bromopropane.
Complete the equation for the formation of propylamine.
b. State the necessary reagents and conditions to produce propylamine from 1- bromopropane.
c. Name the reaction mechanism that takes place when propylamine is produced from 1- bromopropane.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Propylamine is a colourless liquid that is used to manufacture a variety of chemicals including textile resins, drugs and pesticides. It can be produced by the reaction of 1- chloropropane with ammonia.
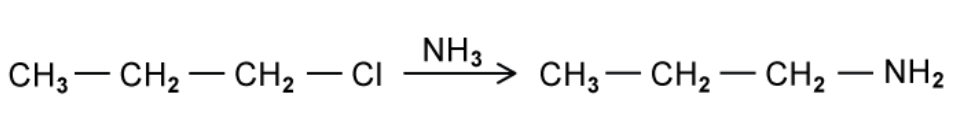
A. State the role of the ammonia in this reaction
B. Name the type of reaction that occurs in this synthesis of propylamine
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The reaction between 1-chloropropane and ammonia proceeds in two steps.
Step 1 involves the formation of an intermediate.
Step 2 forms the final propylamine product.
As the reaction proceeds, the bond angles around the nitrogen atom change. Explain these changes in the bond angles around the nitrogen atom.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Figure below shows a reaction sequence to form an amine
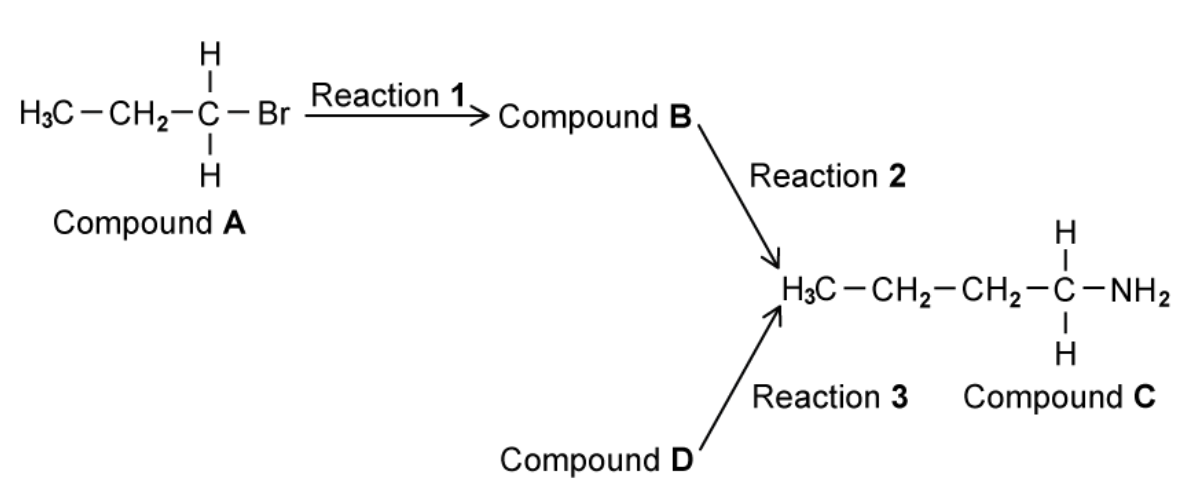
A. Identify every compounds and name reactions 2 and 3
B. Reaction 1 heats compound A under reflux with an ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of compound A with the ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide to form compound B.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Butylamine is an organic compound used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides. One possible method of making butylamine from 1-chlorobutane is shown
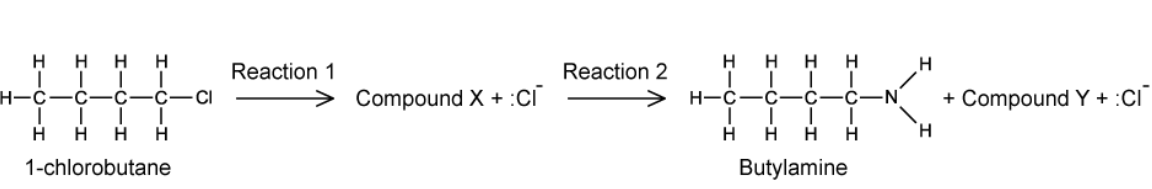
A. Deduce the type of reaction that occurs in reaction 1
B. State suitable reagents and conditions for reaction 1
C. Draw the mechanism for reaction 1 and label compound X in your answer
D. The by-products Cl- and compound Y can combine together to form compound Z.
State the name of compound Z
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Compound X is produced from cyclohexene. An amine which is a relatively weak base containing one nitrogen atom can be produced from compound X in one step.
A. Outline a mechanism for the formation of compound X from cyclohexene. You will need to give suitable reagents in your answer.
B. One condition that is needed to convert compound X into the amine molecule is that the reagent needs to be in excess. State the reagent and any other required conditions for the reaction and why the reagent needs to be in excess
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which of the following is the displayed formula for ethylamine?
A. 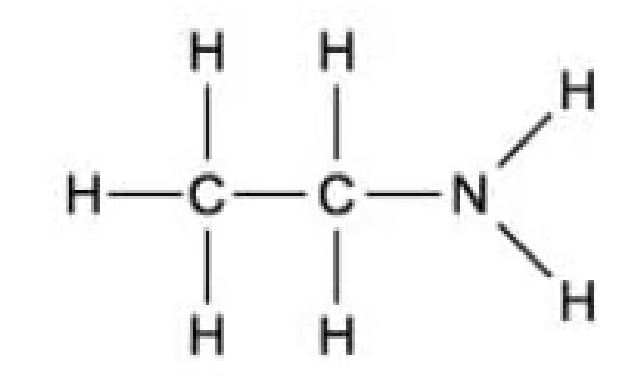
B. 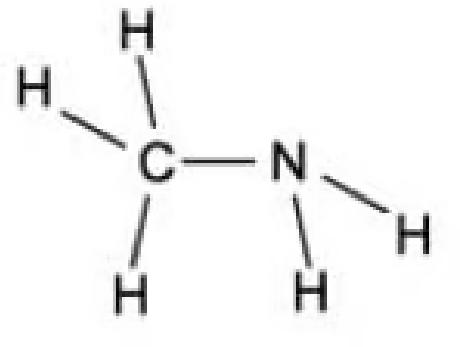
C. 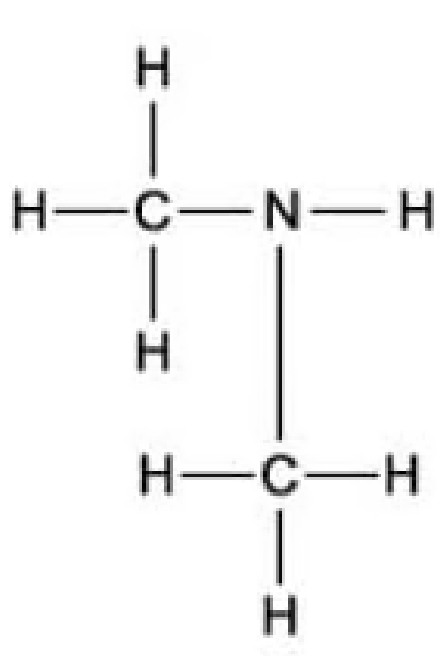
D. 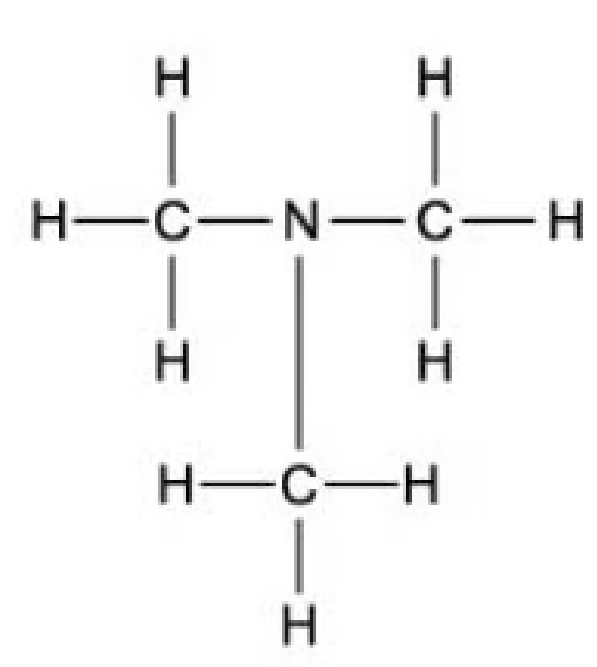
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What type of reaction makes ethylamine from bromoethane?
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
C. Nucleophilic substitution
D. Electrophilic substitution
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
When 1-bromoethane reacts with an equal amount of X. What would X be and what is the product of this reaction?
A. Ammonia - Amine
B. Methylamine - Amide
C. Water - Weak acid
D. Methanol - Ethyl methaoate
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Methyl iodide can be heated with ammonia. Which of the options describes the products of this reaction?
A. Methylamine
B. Dimethylamine
C. Trimethylamine
D. All of the above
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
a. Propylamine can be produced from 1-bromopropane.
Complete the equation for the formation of propylamine.
b. State the necessary reagents and conditions to produce propylamine from 1- bromopropane.
c. Name the reaction mechanism that takes place when propylamine is produced from 1- bromopropane.
a. The equation for the formation of propylamine
`CH_3CH_2CH_2Br + NH_3 -> CH_3CH_2CH_2NH_2 + HBr`
b. The necessary reagents and conditions to produce propylamine from 1- bromopropane involve excess ammonia with ethanol under pressure
c. This reaction mechanism belongs to nucleophilic substitution. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in NH3 serves as a nucleophile to attack the partial charge of the C atom then break the C-Br bond down and substitute Br.
Question 2
Propylamine is a colourless liquid that is used to manufacture a variety of chemicals including textile resins, drugs and pesticides. It can be produced by the reaction of 1- chloropropane with ammonia.

A. State the role of the ammonia in this reaction
B. Name the type of reaction that occurs in this synthesis of propylamine
A. The ammonia in this reaction is a nucleophile
B. This is nucleophilic substitution. The Cl group is replaced by an NH2 group
Question 3
The reaction between 1-chloropropane and ammonia proceeds in two steps.
Step 1 involves the formation of an intermediate.
Step 2 forms the final propylamine product.
As the reaction proceeds, the bond angles around the nitrogen atom change. Explain these changes in the bond angles around the nitrogen atom.
To explain these changes in the bond angles around the nitrogen atom, ammonia and propylamine have bond angles of 107° around the nitrogen atom, while the intermediate has a bond angle of 109.5°. Ammonia and propylamine have a pyramidal form because of the increased repulsion caused by the lone pair of nitrogen electrons. The intermediate has a tetrahedral structure because of the four bonding pairs that surround the nitrogen atom.
Question 4
Figure below shows a reaction sequence to form an amine

A. Identify every compounds and name reactions 2 and 3
B. Reaction 1 heats compound A under reflux with an ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of compound A with the ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide to form compound B.
A. The type of reaction 2 is the reduction and reaction 3 is nucleophilic substitution
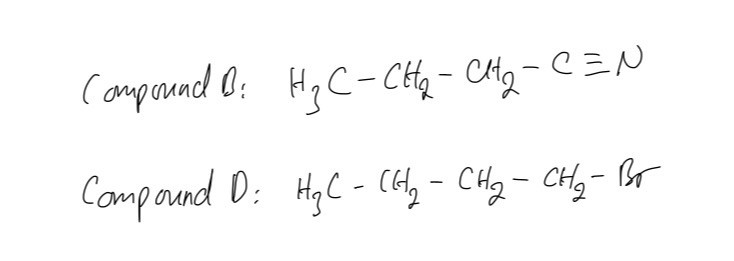
B. The mechanism for the reaction of compound A with the ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide to form compound B
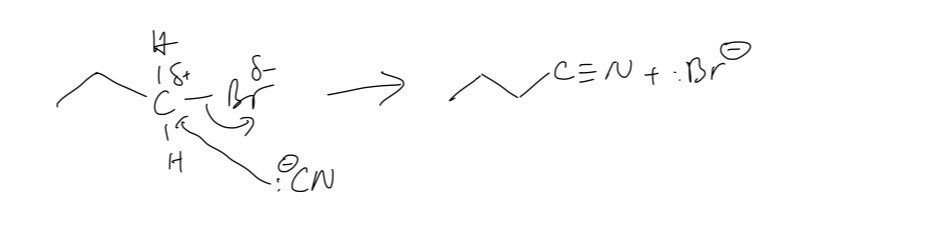
Question 5
Butylamine is an organic compound used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides. One possible method of making butylamine from 1-chlorobutane is shown

A. Deduce the type of reaction that occurs in reaction 1
B. State suitable reagents and conditions for reaction 1
C. Draw the mechanism for reaction 1 and label compound X in your answer
D. The by-products Cl- and compound Y can combine together to form compound Z.
State the name of compound Z
A. The type of reaction that occurs in reaction 1 is nucleophilic substitution
B. Suitable reagents and conditions for reaction 1 are excess ammonia in ethanol under pressure
C. The mechanism for reaction 1
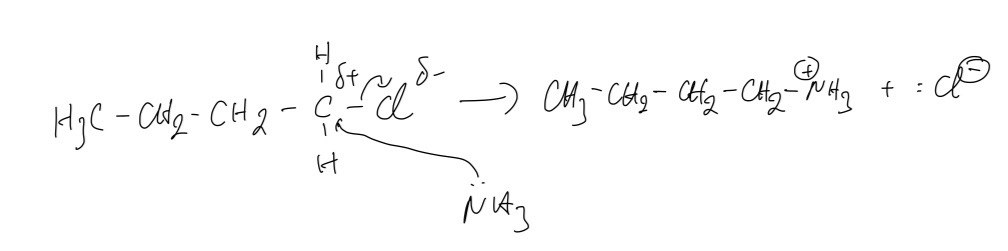
D. Here we can easily predict compound Y is `NH""_4^+`. Therefore, the compound Z is ammonium chloride.
Question 6
Compound X is produced from cyclohexene. An amine which is a relatively weak base containing one nitrogen atom can be produced from compound X in one step.
A. Outline a mechanism for the formation of compound X from cyclohexene. You will need to give suitable reagents in your answer.
B. One condition that is needed to convert compound X into the amine molecule is that the reagent needs to be in excess. State the reagent and any other required conditions for the reaction and why the reagent needs to be in excess
A. Here we use HBr solution and this is the mechanism of reaction
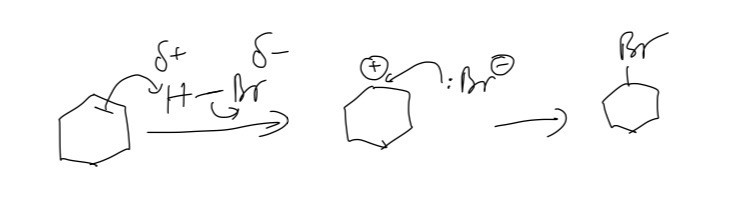
B. The conversion of compound X into amine product will involve excess ammonia in ethanol under pressure. We need to use excess reagents to prevent amine from attacking that compound again to form the secondary amine.
Question 7
Which of the following is the displayed formula for ethylamine?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
The answer is A.
B is incorrect because this is methylamine
C is incorrect because this is dimethylamine
D is incorrect because this is trimethylamine
Question 8
What type of reaction makes ethylamine from bromoethane?
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
C. Nucleophilic substitution
D. Electrophilic substitution
The answer is C
A nucleophilic substitution includes a nucleophile which can donate a pair of electrons
A is incorrect because oxidation of bromoethane will generate ethanol
C is incorrect because it will create double bond
D is incorrect because ammonia is nucleophile
Question 9
When 1-bromoethane reacts with an equal amount of X. What would X be and what is the product of this reaction?
A. Ammonia - Amine
B. Methylamine - Amide
C. Water - Weak acid
D. Methanol - Ethyl methaoate
The answer is A
B is incorrect because it will create secondary amine instead of amide
C is incorrect because halogenoalkane react with water via hydrolysis reaction then generating alcohol which is a weak base
D is incorrect because it will create methoxyethane via nucleophilic substitution instead of ester
Question 10
Methyl iodide can be heated with ammonia. Which of the options describes the products of this reaction?
A. Methylamine
B. Dimethylamine
C. Trimethylamine
D. All of the above
The answer is D
As we learned, the reaction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia produces primary amines. However, the nitrogen in the compound will continue to react with another methyl iodine to form a mixture of amines with different orders of amines because of lone pairs of electron presence via nucleophilic reaction. Therefore, that’s why we use excess ammonia in ethanol to prevent the formation of a mixture.
Question 1
a. Propylamine can be produced from 1-bromopropane.
Complete the equation for the formation of propylamine.
b. State the necessary reagents and conditions to produce propylamine from 1- bromopropane.
c. Name the reaction mechanism that takes place when propylamine is produced from 1- bromopropane.
Question 2
Propylamine is a colourless liquid that is used to manufacture a variety of chemicals including textile resins, drugs and pesticides. It can be produced by the reaction of 1- chloropropane with ammonia.

A. State the role of the ammonia in this reaction
B. Name the type of reaction that occurs in this synthesis of propylamine
Question 3
The reaction between 1-chloropropane and ammonia proceeds in two steps.
Step 1 involves the formation of an intermediate.
Step 2 forms the final propylamine product.
As the reaction proceeds, the bond angles around the nitrogen atom change. Explain these changes in the bond angles around the nitrogen atom.
Question 4
Figure below shows a reaction sequence to form an amine

A. Identify every compounds and name reactions 2 and 3
B. Reaction 1 heats compound A under reflux with an ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of compound A with the ethanolic solution of potassium cyanide to form compound B.
Question 5
Butylamine is an organic compound used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides. One possible method of making butylamine from 1-chlorobutane is shown

A. Deduce the type of reaction that occurs in reaction 1
B. State suitable reagents and conditions for reaction 1
C. Draw the mechanism for reaction 1 and label compound X in your answer
D. The by-products Cl- and compound Y can combine together to form compound Z.
State the name of compound Z
Question 6
Compound X is produced from cyclohexene. An amine which is a relatively weak base containing one nitrogen atom can be produced from compound X in one step.
A. Outline a mechanism for the formation of compound X from cyclohexene. You will need to give suitable reagents in your answer.
B. One condition that is needed to convert compound X into the amine molecule is that the reagent needs to be in excess. State the reagent and any other required conditions for the reaction and why the reagent needs to be in excess
Question 7
Which of the following is the displayed formula for ethylamine?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
Question 8
What type of reaction makes ethylamine from bromoethane?
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
C. Nucleophilic substitution
D. Electrophilic substitution
Question 9
When 1-bromoethane reacts with an equal amount of X. What would X be and what is the product of this reaction?
A. Ammonia - Amine
B. Methylamine - Amide
C. Water - Weak acid
D. Methanol - Ethyl methaoate
Question 10
Methyl iodide can be heated with ammonia. Which of the options describes the products of this reaction?
A. Methylamine
B. Dimethylamine
C. Trimethylamine
D. All of the above