Question 1
a. This question is about carboxylic acids.
State the general formula of a carboxylic acid.
b. Name the carboxylic acid shown
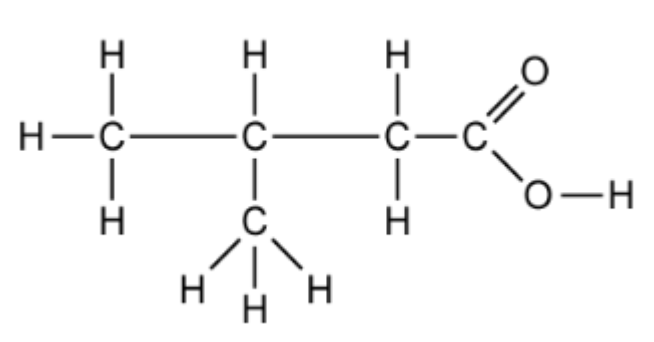
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Write a balanced symbol equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of propanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate powder to form the soluble sodium propanoate salt and two other products.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
There is a conversion of propanoic acid into propan-1-ol and vice versa
a. Write an equation for propan-1-ol formation, using [H] to represent the reducing agent.
b.
i What type of reaction is propanic acid formation?
ii. Suggest a suitable reagent and conditions for this reaction
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Two students try to prepare 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid in the laboratory as shown figure below
Both students oxidise butane‑1,2‑diol to form P in reaction 1. One student then reduces P using LiAlH4 . Q is formed. The other student reduces P using NaBH4. R is formed.
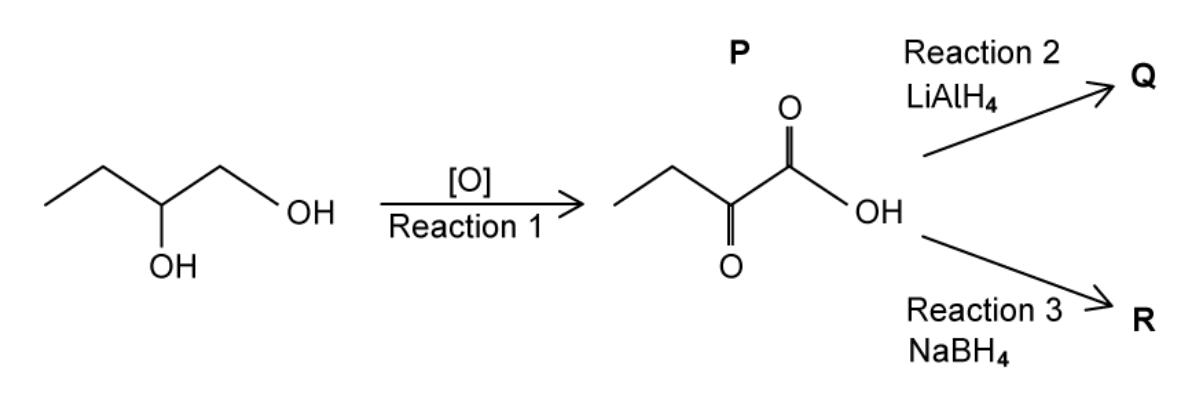
A. State the reagents and conditions required for reaction 1.
B. Identify which of Q or R is 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid and explain the difference between reactions 2 and 3
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A third student prepares 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid using propanal as the starting material as shown in the figure below. In step 1 the student reacts propanal with a mixture of NaCN and HCN.
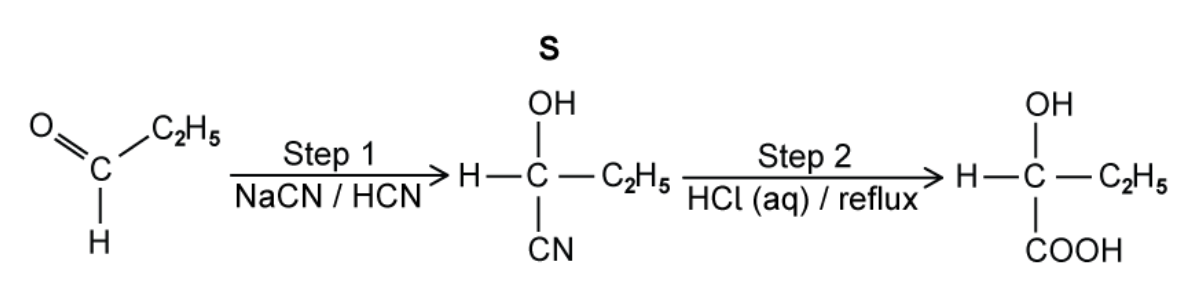
A. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of propanal with the mixture of NaCN and HCN to form S.
B. Complete the equation for the reaction in step 2, when S is heated under reflux with HCl (aq).
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Two reaction sequences to produce glycolic acid are shown
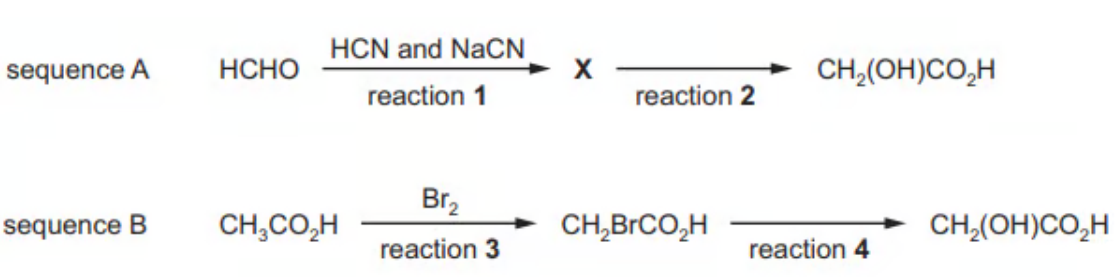
A. Draw the structure of X
B. Name the reagent used for reaction 2
C. Name the mechanism for reaction 3
D. Suggest the essential condition for reaction 3
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Identify the types of reaction and the reagents for each step in the following synthesis of the ethyl ester X.
`CH_2=CH_2 → CH_3CH_2Br → CH_3CH_2OH → RCO_2CH_2CH_3 (X)`
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which reaction does not produce propanoic acid?
A. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sodium hydroxide
B. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sulfuric acid
C. Heating propanal under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
D. Heating propanol under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Propionitrile, CH3CH2C ≡ N, is used to produce propanoic acid.
What are the conditions for this reaction?
A. NaOH
B. H+ / Na2Cr2O7
C. NaBH4
D. H+ / H2O
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Apples contain a compound called malic acid
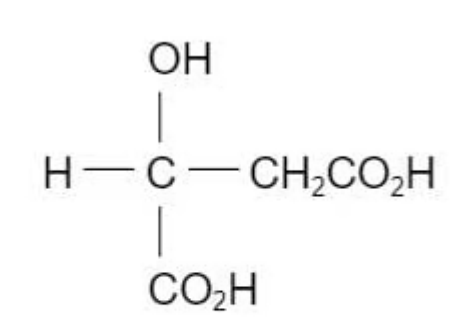
Which substance will react with only one hydroxyl groups in malic acid under suitable conditions?
A. Na (s)
B. PCl5
C. NaOH (aq)
D. `Cr_2O""_7^(2-)"/"H^+ (aq)`
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
a. This question is about carboxylic acids.
State the general formula of a carboxylic acid.
b. Name the carboxylic acid shown

a. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is CnH2n+1COOH
b. This is 3-methylbutanoic acid
Question 2
Write a balanced symbol equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of propanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate powder to form the soluble sodium propanoate salt and two other products.
A balanced symbol equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of propanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate powder to form the soluble sodium propanoate salt and two other products
`CH_3CH_2COOH (aq) + NaHCO_3 (s) -> CH_3CH_2COONa (aq) + H_2O (l) + CO_2 (g)`
Question 3
There is a conversion of propanoic acid into propan-1-ol and vice versa
a. Write an equation for propan-1-ol formation, using [H] to represent the reducing agent.
b.
i What type of reaction is propanic acid formation?
ii. Suggest a suitable reagent and conditions for this reaction
a. An equation for propan-1-ol formation
`CH_3CH_2COOH + 4[H] -> CH_3CH_2CH_2OH + H_2O`
The reduction of this alcohol will produce propan-1-ol and water under LiAlH4
b.
i. This is an oxidation of primary alcohols or aldehydes
ii. A suitable reagent and conditions for this reaction include acidified K2Cr2O7 or acidified KMnO4 and refluxing.
Question 4
Two students try to prepare 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid in the laboratory as shown figure below
Both students oxidise butane‑1,2‑diol to form P in reaction 1. One student then reduces P using LiAlH4 . Q is formed. The other student reduces P using NaBH4. R is formed.

A. State the reagents and conditions required for reaction 1.
B. Identify which of Q or R is 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid and explain the difference between reactions 2 and 3
A. A suitable reagent and conditions for this reaction include acidified K2Cr2O7 or acidified KMnO4 and refluxing.
B. NaBH4 cannot reduce carboxylic acid bcause it’s weaker reducing agent than LiAlH4 which is only used for reducing carboxylic acid. Thus, R is 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid
Question 5
A third student prepares 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid using propanal as the starting material as shown in the figure below. In step 1 the student reacts propanal with a mixture of NaCN and HCN.

A. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of propanal with the mixture of NaCN and HCN to form S.
B. Complete the equation for the reaction in step 2, when S is heated under reflux with HCl (aq).
A. The mechanism for the reaction of propanal with the mixture of NaCN and HCN to form S
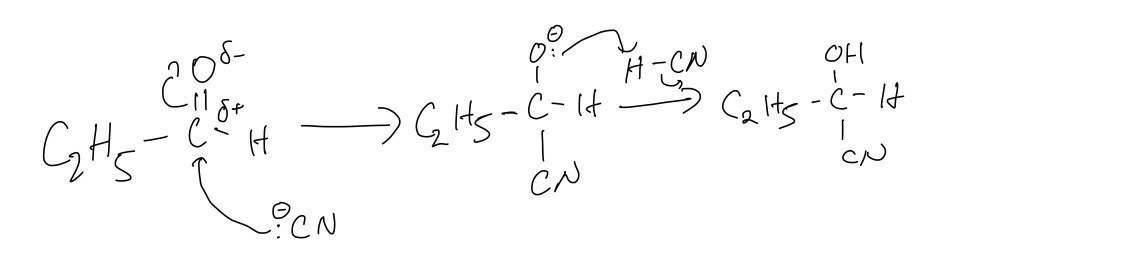
B. The equation for the reaction in step 2, when S is heated under reflux with HCl (aq)
`C_2H_5CH(OH)CN + HCl + 2H_2O → C_2H_5CH(OH)COOH + NH_4Cl`
Question 6
Two reaction sequences to produce glycolic acid are shown

A. Draw the structure of X
B. Name the reagent used for reaction 2
C. Name the mechanism for reaction 3
D. Suggest the essential condition for reaction 3
A. The structure of X is CH2(OH)CN
B. The reagent used for reaction 2 is phosphoric acid or sulfuric acid
C. The mechanism for reaction 3 is free-radical substitution
D. The essential condition for reaction 3 is UV/light
Question 7
Identify the types of reaction and the reagents for each step in the following synthesis of the ethyl ester X.
`CH_2=CH_2 → CH_3CH_2Br → CH_3CH_2OH → RCO_2CH_2CH_3 (X)`
Step 1: The conversion of an alkene into a bromoalkane by using HBr(g) as the reagent at room temperature via an electrophilic addition reaction
Step 2: The conversion from bromoalkane to alcohol by using the reagent NaOH(aq) + heat via a nucleophilic substitution reaction
Step 3: The conversion of an alcohol into an ester by heating with RCOOH and concentrated H2SO4 via an esterification reaction
Question 8
Which reaction does not produce propanoic acid?
A. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sodium hydroxide
B. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sulfuric acid
C. Heating propanal under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
D. Heating propanol under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
The answer is A
Because it will create sodium propanoate and ammonia instead
B, C and D are incorrect because they will generate propanoic acid
Question 9
Propionitrile, CH3CH2C ≡ N, is used to produce propanoic acid.
What are the conditions for this reaction?
A. NaOH
B. H+ / Na2Cr2O7
C. NaBH4
D. H+ / H2O
The answer is D
A is incorrect because the nitriles will be hydrolyzed with OH- under reflux, leading not to the production of carboxylic acid
B is incorrect because Na2Cr2O7 will be used to oxdise propanol and propanal instead
C is incorrect because NaBH4 is a weak reducing agent
Question 10
Apples contain a compound called malic acid

Which substance will react with only one hydroxyl groups in malic acid under suitable conditions?
A. Na (s)
B. PCl5
C. NaOH (aq)
D. `Cr_2O""_7^(2-)"/"H^+ (aq)`
The answer is D
Carboxylic acid groups are not oxidised with acidified dichromate ions anymore. Therefore, alcohols could be oxidised without affecting carboxylic acid groups.
A is incorrect because sodium metals will react with three of these functional groups to create salt and hydrogen
B is incorrect because PCl will react with carboxylic acid groups to create acid chloride
`RCOOH + PCl_5 -> RCH_2Cl + POCl_3 + HCl`
C is incorrect because it is similar to sodium metals, thus, resulting in the production of salt and water
Question 1
a. This question is about carboxylic acids.
State the general formula of a carboxylic acid.
b. Name the carboxylic acid shown

Question 2
Write a balanced symbol equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of propanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate powder to form the soluble sodium propanoate salt and two other products.
Question 3
There is a conversion of propanoic acid into propan-1-ol and vice versa
a. Write an equation for propan-1-ol formation, using [H] to represent the reducing agent.
b.
i What type of reaction is propanic acid formation?
ii. Suggest a suitable reagent and conditions for this reaction
Question 4
Two students try to prepare 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid in the laboratory as shown figure below
Both students oxidise butane‑1,2‑diol to form P in reaction 1. One student then reduces P using LiAlH4 . Q is formed. The other student reduces P using NaBH4. R is formed.

A. State the reagents and conditions required for reaction 1.
B. Identify which of Q or R is 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid and explain the difference between reactions 2 and 3
Question 5
A third student prepares 2‑hydroxybutanoic acid using propanal as the starting material as shown in the figure below. In step 1 the student reacts propanal with a mixture of NaCN and HCN.

A. Draw the mechanism for the reaction of propanal with the mixture of NaCN and HCN to form S.
B. Complete the equation for the reaction in step 2, when S is heated under reflux with HCl (aq).
Question 6
Two reaction sequences to produce glycolic acid are shown

A. Draw the structure of X
B. Name the reagent used for reaction 2
C. Name the mechanism for reaction 3
D. Suggest the essential condition for reaction 3
Question 7
Identify the types of reaction and the reagents for each step in the following synthesis of the ethyl ester X.
`CH_2=CH_2 → CH_3CH_2Br → CH_3CH_2OH → RCO_2CH_2CH_3 (X)`
Question 8
Which reaction does not produce propanoic acid?
A. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sodium hydroxide
B. Heating propanenitrile under reflux with dilute sulfuric acid
C. Heating propanal under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
D. Heating propanol under reflux with acidified sodium dichromate(VI)
Question 9
Propionitrile, CH3CH2C ≡ N, is used to produce propanoic acid.
What are the conditions for this reaction?
A. NaOH
B. H+ / Na2Cr2O7
C. NaBH4
D. H+ / H2O
Question 10
Apples contain a compound called malic acid

Which substance will react with only one hydroxyl groups in malic acid under suitable conditions?
A. Na (s)
B. PCl5
C. NaOH (aq)
D. `Cr_2O""_7^(2-)"/"H^+ (aq)`