Question 1
Name the following compounds:
a.
i. CH3COCH3
ii. CH3CH2CH2OH
iii. CH3CHO
iv. CH3CH(OH)CH3
v. CH3COCH2CH3
vi. CH3CH2CHO
b. Which of the compounds in part a are alcohols and which are carbonyl compounds?
c. Which of the carbonyl compounds in part a are aldehydes and which are ketones?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
From these compounds including CH3COCH3, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CHO, CH3CH(OH)CH3, CH3COCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CHO, two of the compounds could be made by oxidising two of the others.
A. Identify these four compounds, stating which could be made from which.
B. State the reagents and conditions you would use to carry out each oxidation and write a balanced chemical equation for each oxidation.
[O] can be used in oxidation equations.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
a. What reagent would you add to an unknown compound to see if it contains a carbonyl group?
b. What result would you get if the unknown compound did contain a carbonyl group?
c. Why would it be useful to find the melting point of the product of this test?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
a. Draw the skeletal formulae of:
i. pentan-2-one
ii. pentan-3-one
iii. pentanal
b. Describe the results you would expect to see if pentan-3-one and pentanal were separately treated with Tollens’ reagent. Where a reaction takes place, name the organic product and name the type of reaction that takes place
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Ethanol can be made from ethanal using sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) as a reducing agent
a. Give the formula of sodium tetrahydridoborate(III)
b. What other reagent is necessary for the reaction to take place?
c. The reaction mechanism proceeds in a similar way to the steps in the reaction of ethanal with HCN, but the initial attack is by the H– ion instead of the CN– ion. The intermediate then gains an H+ ion from a water molecule to form the product, ethanol. Name the mechanism and describe it as fully as you can, using curly arrows to show the movement of electron pairs
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A compound, X, has the following percentage composition: 66.7 % carbon, 11.1 % hydrogen and 22.2 % oxygen
a. Calculate the empirical formula of X
b. The relative molecular mass of X is 72. Calculate the molecular formula
c. Give the structural formulae and names of the three isomers of X that are carbonyl compounds
d. Explain how you could identify X using chemical means
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
An alcohol has the molecular formula C3H8O. When warmed with an alkaline solution of iodine it forms a yellow precipitate
a. Name the yellow precipitate
b. Draw the displayed formula of the alcohol
c. The first stage in the reaction of the alcohol with alkaline iodine solution is an oxidation reaction. Name the organic product of this first stage
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is formed when butanone is refluxed with a solution of NaBH4?
A. Butane
B. Butan-1-ol
C. Butan-2-ol
D. Butanal
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which carbonyl compound(s) react with both LiAlH4 and Tollens’ reagent?
A. Ketones only
B. Aldehydes only
C. Both aldehydes and ketones
D. Neither aldehydes nor ketones
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
In which reaction is the organic compound oxidised?
A. CH3CH2CN + dilute H2SO4
B. CH3CH2CHO + Tollens’ reagent
C. CH3COCH2CH3 + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
D. CH3CH2CH2OH + concentrated H3PO4
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Name the following compounds:
a.
i. CH3COCH3
ii. CH3CH2CH2OH
iii. CH3CHO
iv. CH3CH(OH)CH3
v. CH3COCH2CH3
vi. CH3CH2CHO
b. Which of the compounds in part a are alcohols and which are carbonyl compounds?
c. Which of the carbonyl compounds in part a are aldehydes and which are ketones?
a.
i. Propanone
ii. propan-1-ol
iii. Ethanal
iv. propan-2-ol
v. butanone
vi. propanal
b. The compounds alcohols are propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol. The carbonyl compounds are propanone, ethanal, butanone and propanal
c. Ethanal and propanal are aldehydes and propanone and butanone are ketones
Question 2
From these compounds including CH3COCH3, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CHO, CH3CH(OH)CH3, CH3COCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CHO, two of the compounds could be made by oxidising two of the others.
A. Identify these four compounds, stating which could be made from which.
B. State the reagents and conditions you would use to carry out each oxidation and write a balanced chemical equation for each oxidation.
[O] can be used in oxidation equations.
A.
Start with CH3CH2CH2OH to form CH3CH2CHO and start with CH3CH(OH)CH3 to form CH3COCH3.
B.
To obtain aldehyde conversion, the reagents and conditions you would use to carry out include potassium dichromate(VI) solution, acidified with dilute sulfuric acid, warm and distilled immediately.
`CH_3CH_2CH_2OH + [O] → CH_3CH_2CHO + H_2O`
Question 3
a. What reagent would you add to an unknown compound to see if it contains a carbonyl group?
b. What result would you get if the unknown compound did contain a carbonyl group?
c. Why would it be useful to find the melting point of the product of this test?
a. To see if it contains a carbonyl group, we can use 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH) solution which is so-called Brady’s reagent to test. In addition, this is an example of a condensation reaction.
b. The production we can obtain is deep-orange precipitate
c. It is possible to monitor the melting point of the precipitate and purify it through recrystallization. Melting point information can then be used to determine the identify of the compound that precipitated out. This makes it possible to identify the particular ketone or aldehyde that was utilized in the test.
Question 4
a. Draw the skeletal formulae of:
i. pentan-2-one
ii. pentan-3-one
iii. pentanal
b. Describe the results you would expect to see if pentan-3-one and pentanal were separately treated with Tollens’ reagent. Where a reaction takes place, name the organic product and name the type of reaction that takes place
a.
i. 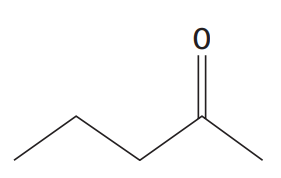
ii. 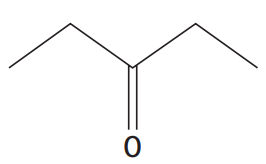
iii. 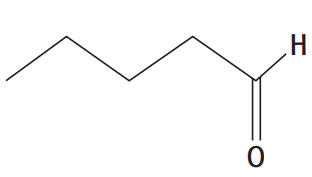
b.
Aqueous silver nitrate in excess ammonia solution, often known as ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, is Tollens' reagent. The solution's silver ions, Ag+, have a modest oxidizing effect. Ag+ ions will oxidize an aldehyde to produce a carboxylate ion when heated. Any carboxylic acid that forms in an alkaline environment is instantly neutralized to the carboxylate ion, COO–, as H+ is extracted from COOH, forming a salt. The Ag+ ions themselves undergo reduction to silver atoms in the redox reaction with an aldehyde. An aldehyde test is positive when the silver atoms create a "mirror" inside the tube.
When a ketone is heated with Tollens' reagent, no redox reaction occurs, hence no change will be seen. In the test tube, the mixture stays colorless, as such, pentan-3-one stay remain, whereas, pentanal will give pentanoic acid due to an oxidation.
Question 5
Ethanol can be made from ethanal using sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) as a reducing agent
a. Give the formula of sodium tetrahydridoborate(III)
b. What other reagent is necessary for the reaction to take place?
c. The reaction mechanism proceeds in a similar way to the steps in the reaction of ethanal with HCN, but the initial attack is by the H– ion instead of the CN– ion. The intermediate then gains an H+ ion from a water molecule to form the product, ethanol. Name the mechanism and describe it as fully as you can, using curly arrows to show the movement of electron pairs
a. The formula of sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) is NaBH4
b. Another reagent is essential for the reaction to occur is water
c. The name of this mechanism is the so-called nucleophilic addition
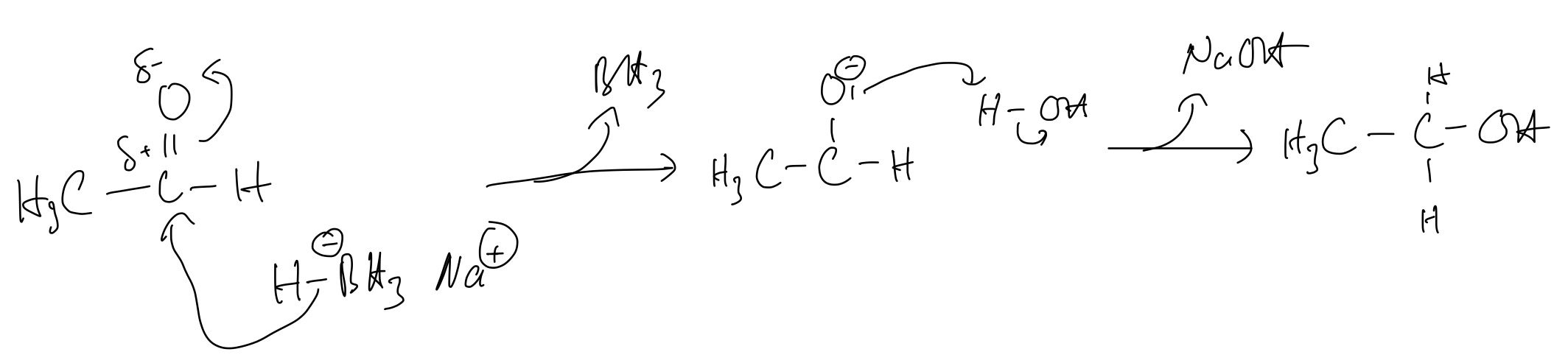
Question 6
A compound, X, has the following percentage composition: 66.7 % carbon, 11.1 % hydrogen and 22.2 % oxygen
a. Calculate the empirical formula of X
b. The relative molecular mass of X is 72. Calculate the molecular formula
c. Give the structural formulae and names of the three isomers of X that are carbonyl compounds
d. Explain how you could identify X using chemical means
a. We assume there is 100 g of compound X, in which the mass of Carbon is 66.7 g, and that of Hydrogen is 11.1 g and of Oxygen is 22.2 g.
Thus,
The number of moles of C = `66.7 / 12.0 = 5.56` moles
The number of moles of H = `11.1 / 1.0 = 11.1` moles
The number of moles of O = `22.2 / 16.0 = 1.39` moles
The ratio between 3 of them C:H:O
`C = 5.56 / 1.39 = 4`
`H = 11.1 / 1.39 = 8`
`O = 1.39 / 1.39 = 1`
The empirical formula of X is C4H8O
b. The relative molecular mass of `X = n xx (4xx12.0 + 1.0 xx 8 + 16.0 xx 1) = 72 => n = 1`
Thus, the molecular formula is C4H8O
c. The structural formulae and names of the three isomers of X that are carbonyl compounds
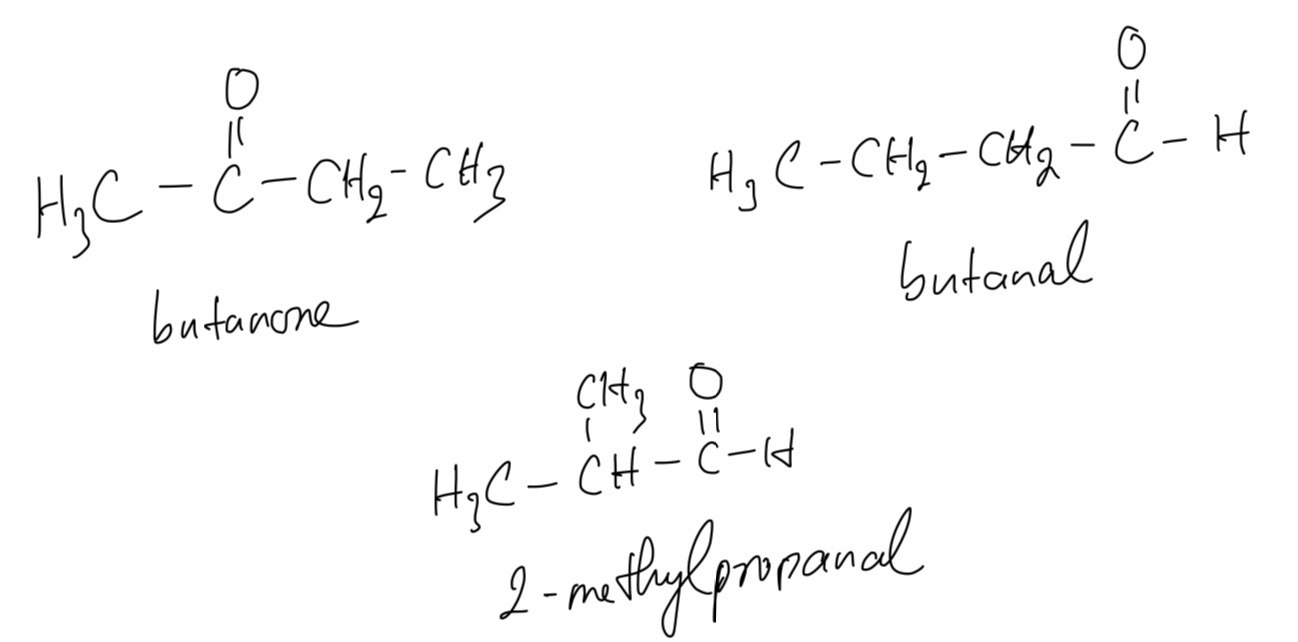
d. First we will test with Tollens’ reagent to identify which belongs to aldehydes or ketones. After that, we can add 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to filter precipitate and purify it through recrystallization. Melting point information can then be used to determine the identify of the compound that precipitated out.
Question 7
An alcohol has the molecular formula C3H8O. When warmed with an alkaline solution of iodine it forms a yellow precipitate
a. Name the yellow precipitate
b. Draw the displayed formula of the alcohol
c. The first stage in the reaction of the alcohol with alkaline iodine solution is an oxidation reaction. Name the organic product of this first stage
a. The name of the yellow precipitate is tri-iodomethane
b. The displayed formula of the alcohol
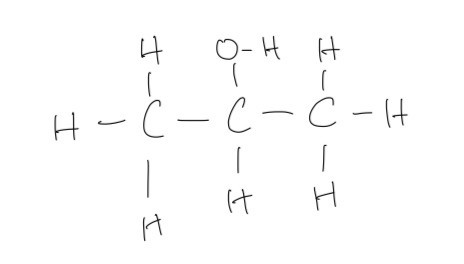
c. The organic product of this first stage is propanone
Question 8
What is formed when butanone is refluxed with a solution of NaBH4?
A. Butane
B. Butan-1-ol
C. Butan-2-ol
D. Butanal
The answer is C
A reduction reaction is the addition of hydrogen to an organic compound. Thus, butanone will generate a secondary alcohol.
A is incorrect because it does not have any carbonyl group
B is incorrect because it’s a primary alcohol
D is incorrect because it’s an aldehyde
Question 9
Which carbonyl compound(s) react with both LiAlH4 and Tollens’ reagent?
A. Ketones only
B. Aldehydes only
C. Both aldehydes and ketones
D. Neither aldehydes nor ketones
The answer is B
A and C are incorrect because ketones do not react with Tollens’ reagent
D is incorrect because both react with LiAlH4 to form alcohol
Question 10
In which reaction is the organic compound oxidised?
A. CH3CH2CN + dilute H2SO4
B. CH3CH2CHO + Tollens’ reagent
C. CH3COCH2CH3 + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
D. CH3CH2CH2OH + concentrated H3PO4
The answer is B
A is incorrect because this is a hydrolysis reaction, i.e., there is no change in oxidation state of any of the participating atoms. They just create an acid and a salt depending on reactants.
C is incorrect because this is a condensation reaction in which two molecule will react with each other to eliminate a small molecule without affecting oxidation state of any of the participating atoms
D is incorrect because this is the so-called dehydration in which an alcohol joining reaction will form an alkene and a water will be removed from that alcohol and it does not change any oxidation state of any atoms in compounds.
Question 1
Name the following compounds:
a.
i. CH3COCH3
ii. CH3CH2CH2OH
iii. CH3CHO
iv. CH3CH(OH)CH3
v. CH3COCH2CH3
vi. CH3CH2CHO
b. Which of the compounds in part a are alcohols and which are carbonyl compounds?
c. Which of the carbonyl compounds in part a are aldehydes and which are ketones?
Question 2
From these compounds including CH3COCH3, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CHO, CH3CH(OH)CH3, CH3COCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CHO, two of the compounds could be made by oxidising two of the others.
A. Identify these four compounds, stating which could be made from which.
B. State the reagents and conditions you would use to carry out each oxidation and write a balanced chemical equation for each oxidation.
[O] can be used in oxidation equations.
Question 3
a. What reagent would you add to an unknown compound to see if it contains a carbonyl group?
b. What result would you get if the unknown compound did contain a carbonyl group?
c. Why would it be useful to find the melting point of the product of this test?
Question 4
a. Draw the skeletal formulae of:
i. pentan-2-one
ii. pentan-3-one
iii. pentanal
b. Describe the results you would expect to see if pentan-3-one and pentanal were separately treated with Tollens’ reagent. Where a reaction takes place, name the organic product and name the type of reaction that takes place
Question 5
Ethanol can be made from ethanal using sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) as a reducing agent
a. Give the formula of sodium tetrahydridoborate(III)
b. What other reagent is necessary for the reaction to take place?
c. The reaction mechanism proceeds in a similar way to the steps in the reaction of ethanal with HCN, but the initial attack is by the H– ion instead of the CN– ion. The intermediate then gains an H+ ion from a water molecule to form the product, ethanol. Name the mechanism and describe it as fully as you can, using curly arrows to show the movement of electron pairs
Question 6
A compound, X, has the following percentage composition: 66.7 % carbon, 11.1 % hydrogen and 22.2 % oxygen
a. Calculate the empirical formula of X
b. The relative molecular mass of X is 72. Calculate the molecular formula
c. Give the structural formulae and names of the three isomers of X that are carbonyl compounds
d. Explain how you could identify X using chemical means
Question 7
An alcohol has the molecular formula C3H8O. When warmed with an alkaline solution of iodine it forms a yellow precipitate
a. Name the yellow precipitate
b. Draw the displayed formula of the alcohol
c. The first stage in the reaction of the alcohol with alkaline iodine solution is an oxidation reaction. Name the organic product of this first stage
Question 8
What is formed when butanone is refluxed with a solution of NaBH4?
A. Butane
B. Butan-1-ol
C. Butan-2-ol
D. Butanal
Question 9
Which carbonyl compound(s) react with both LiAlH4 and Tollens’ reagent?
A. Ketones only
B. Aldehydes only
C. Both aldehydes and ketones
D. Neither aldehydes nor ketones
Question 10
In which reaction is the organic compound oxidised?
A. CH3CH2CN + dilute H2SO4
B. CH3CH2CHO + Tollens’ reagent
C. CH3COCH2CH3 + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
D. CH3CH2CH2OH + concentrated H3PO4