Question 1
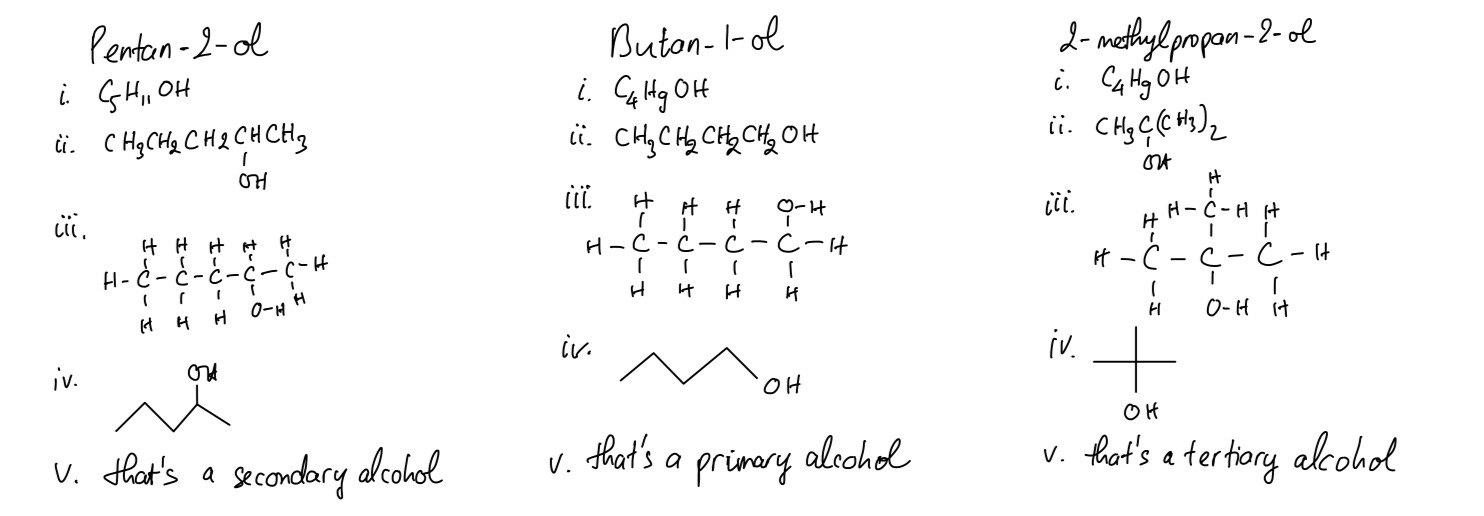
Pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol are alcohols.
For each one:
i. give its molecular formula
ii. give its structural formula
iii. give its displayed formula
iv. give its skeletal formula
v. state whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
a. Give the general formula that is used to represent alcohols
b. In pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two of the alcohols in this question are isomers of each other. Identify which two and identify the type of isomerism they show
c. Name the alcohol whose structural formula is `CH_3CH_2COH(CH_3)_2`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following processes. Structural or displayed formulae should be used for all organic substances
a. Making ethanol using ethene as feedstock. Include the formula of the catalyst used
b. The complete combustion of ethanol in oxygen.
c. The dehydration of butan-2-ol when passed over hot Al2O3. Give three equations, one for each of the three possible products
d. The reaction of ethanoic acid with ethanol. Name the catalyst used, the type of reaction and the products
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidised by heating with a mixture of potassium dichromate(VI) and dilute sulfuric(VI) acid
A primary alcohol can be oxidised to two different products, depending on the conditions used
A secondary alcohol forms one product when oxidised
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised
a. What is the formula of potassium dichromate(VI)?
b. Using a primary alcohol of your choice as an example:
i. give the displayed formulae of the two products it could be oxidised to
ii. state the conditions needed to give each product
iii. state which homologous series each product belongs to
iv. write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction (the convention [O] may be used for the oxidising agent)
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Why are tertiary alcohols resistant to oxidation?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Three different alcohols, A, B and C are shown in the figure below
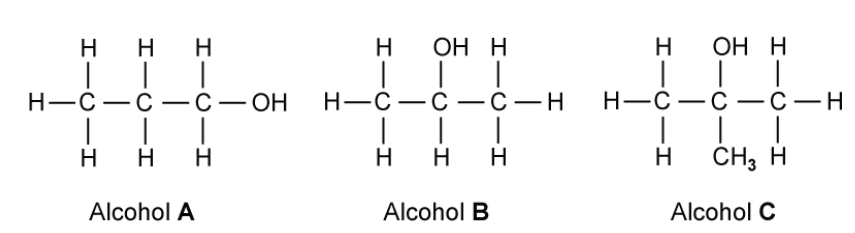
Alcohols A, B and C are heated separately with an alkaline solution of iodine. State which alcohol will give a yellow precipitate during this reaction.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which alcohol has a chiral centre and can be oxidised to a ketone?
A. Pentan-2-ol
B. Pentan-3-ol
C. 3-methylhexan-1-ol
D. 3-methylhexan-3-ol
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which reaction will distinguish between a primary and a secondary alcohol?
A. Warming with H+ / `MnO""_4^-`
B. Warming with H+ / `Cr_2O""_7^(2-`
C. Dehydration, followed by reaction with Br2(aq)
D. Oxidation, followed by reaction with Fehling’s (or Tollens’) reagent
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Buta-1,3-diene is currently obtained from fossil fuel sources. In future it may be obtained from ethanol, which can be produced from non-food agricultural crops. The sequence of reactions is as follows.
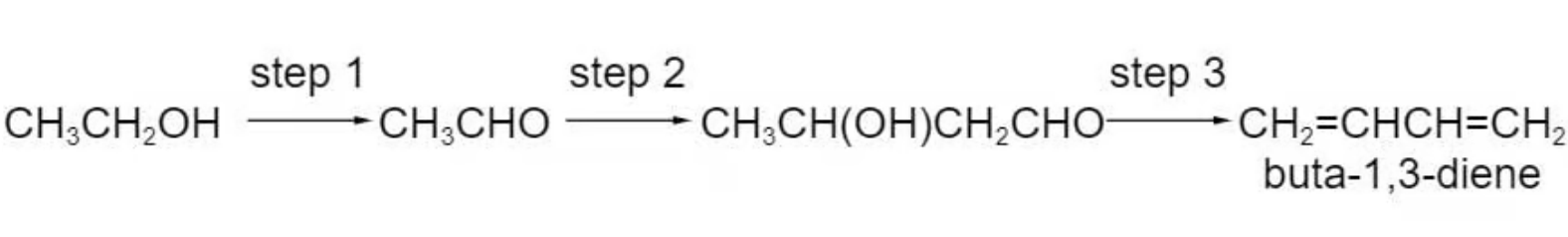
Which term could be used to describe step 1?
A. Condensation
B. Dehydration
C. Dehydrogenation
D. Hydrogenation
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
The diagram shows the structure of compound Z.
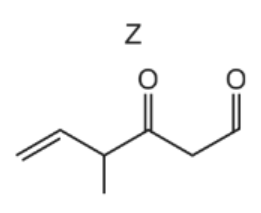
What is the product of the reaction between compound Z and an excess of NaBH4?
A. 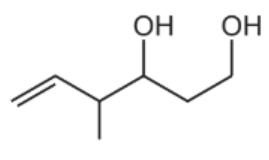
B. 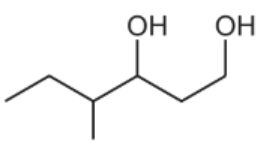
C. 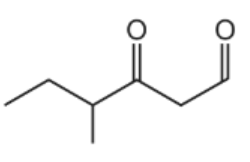
D. 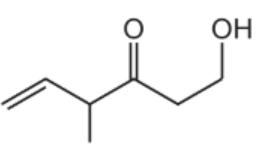
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol are alcohols.
For each one:
i. give its molecular formula
ii. give its structural formula
iii. give its displayed formula
iv. give its skeletal formula
v. state whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol
Question 2
a. Give the general formula that is used to represent alcohols
b. In pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two of the alcohols in this question are isomers of each other. Identify which two and identify the type of isomerism they show
c. Name the alcohol whose structural formula is `CH_3CH_2COH(CH_3)_2`
a. The general formula that is used to represent alcohols is CnH2n+1OH
b. butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol are isomers of each other and they belong to structural isomers
c. This is 2-methylbutan-2-ol
Question 3
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following processes. Structural or displayed formulae should be used for all organic substances
a. Making ethanol using ethene as feedstock. Include the formula of the catalyst used
b. The complete combustion of ethanol in oxygen.
c. The dehydration of butan-2-ol when passed over hot Al2O3. Give three equations, one for each of the three possible products
d. The reaction of ethanoic acid with ethanol. Name the catalyst used, the type of reaction and the products
a. The formula of the catalyst that we used is H3PO4 to convert ethene into ethanol via hydration reaction
`H_2C=CH_2 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH`
b. `CH_3CH_2OH + 3O_2 → 2CO_2 + 3H_2O`
c.
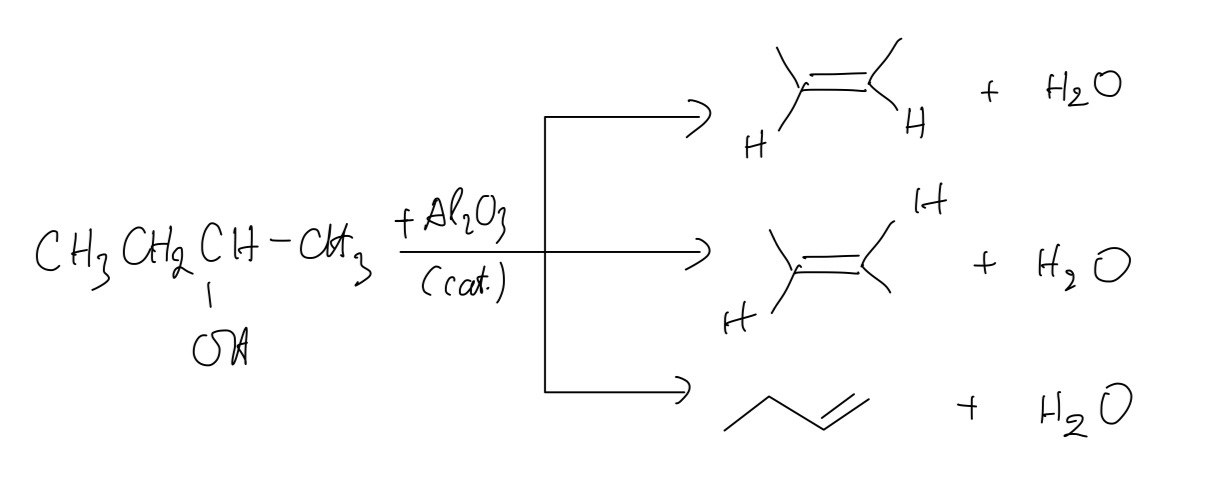
d. `CH_3COOH + CH_3CH_2OH → CH_3COOCH_2CH_3 + H_2O`
The type of this reaction is called esterification with the presence of concentrated sulfuric(VI) acid. From this reaction, we will create a ethyl ethanoate and water
Question 4
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidised by heating with a mixture of potassium dichromate(VI) and dilute sulfuric(VI) acid
A primary alcohol can be oxidised to two different products, depending on the conditions used
A secondary alcohol forms one product when oxidised
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised
a. What is the formula of potassium dichromate(VI)?
b. Using a primary alcohol of your choice as an example:
i. give the displayed formulae of the two products it could be oxidised to
ii. state the conditions needed to give each product
iii. state which homologous series each product belongs to
iv. write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction (the convention [O] may be used for the oxidising agent)
a. The formula of potassium dichromate(VI) is K2Cr2O7
b.
i. The displayed formulae of the two products it could be oxidised to include -CHO(aldehyde group) or -COOH(carboxylic acid group)
ii.
As for -CHO formation, we perform under mild heat and distilling immediately
As for -COOH formation, we perform under refluxing with excess oxidising agent
iii. They are aldehydes or carboxylic acids
iv. Take methanol as an example
`CH_3OH + [O] -> HCHO + H_2O`
`CH_3OH + 2[O] -> HCOOH + H_2O`
Question 5
Why are tertiary alcohols resistant to oxidation?
Because the carbon atom carrying the OH group is connected to other carbon atoms rather than having a hydrogen atom attached. A carbon-to-oxygen double bond is formed during the oxidation events we have discussed.
Question 6
Three different alcohols, A, B and C are shown in the figure below

Alcohols A, B and C are heated separately with an alkaline solution of iodine. State which alcohol will give a yellow precipitate during this reaction.
Alcohol will give a yellow precipitate during this reaction is B because this is a secondary alcohol. It will first create ketone then halogenated and hydrolysed to form an alkaline salt and the yello precipitate
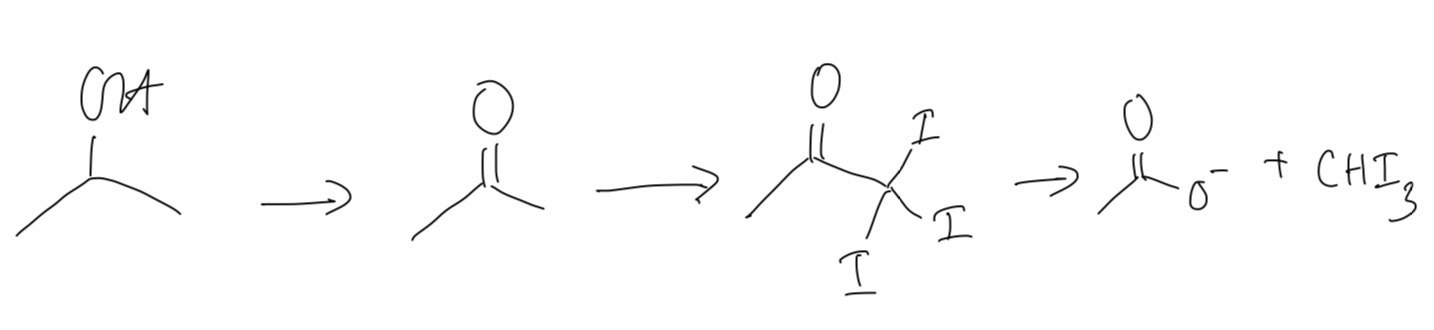
Question 7
Which alcohol has a chiral centre and can be oxidised to a ketone?
A. Pentan-2-ol
B. Pentan-3-ol
C. 3-methylhexan-1-ol
D. 3-methylhexan-3-ol
The answer is A
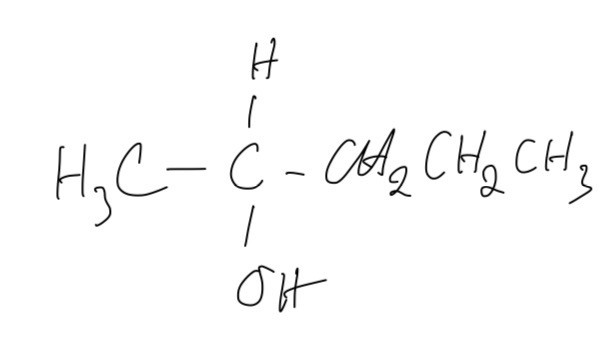
B is incorrect because this is a secondary alcohol and it does not have a chiral centre because it has the 2 same functional groups on C atom
C is incorrect because it is a primary alcohol
D is incorrect because it a tertiary alcohol
Question 8
Which reaction will distinguish between a primary and a secondary alcohol?
A. Warming with H+ / `MnO""_4^-`
B. Warming with H+ / `Cr_2O""_7^(2-`
C. Dehydration, followed by reaction with Br2(aq)
D. Oxidation, followed by reaction with Fehling’s (or Tollens’) reagent
The answer is D
As for unknown alcohol, when it is oxidiaed with a mild condition to form either the ketone or the aldehyde corresponding to secondary or primary alcohol, respectively.
Fehling’s solution is an alkaline solution containing copper(II) ions. When warmed with an aldehyde, the Cu2+ ions act as an oxidising agent. The aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylate ion while the Cu2+ ions are reduced to Cu+ ions. The clear blue Fehling’s solution turns an opaque red/orange colour as a precipitate of copper(I) oxide forms throughout the solution. Once again, ketones are not oxidised, so the Fehling’s solution remains blue when warmed.
A and B are incorrect because both oxidse a primary and a secondary alcohol
C is incorrect because both are dehydrated into alkenes
Question 9
Buta-1,3-diene is currently obtained from fossil fuel sources. In future it may be obtained from ethanol, which can be produced from non-food agricultural crops. The sequence of reactions is as follows.

Which term could be used to describe step 1?
A. Condensation
B. Dehydration
C. Dehydrogenation
D. Hydrogenation
The answer is C
A is incorrect because this will occur by breaking a bond to create 2 compounds with water
B is incorrect because this reaction will cause a water loss and generate double bonds in production
D is incorrect because this reaction will be the addition of hydrogen to a molecule
Question 10
The diagram shows the structure of compound Z.

What is the product of the reaction between compound Z and an excess of NaBH4?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
The answer is A
Aldehyde and ketone are reduced to primary and secondary alcohol, respectively, in the presence of reducing agents such as sodium borohydride. However, sodium borohydride is unable to reduce alkene.
As a result, compound Z has to have both of its carbonyls reduced to alcohol.
Question 1
Pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol are alcohols.
For each one:
i. give its molecular formula
ii. give its structural formula
iii. give its displayed formula
iv. give its skeletal formula
v. state whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol
Question 2
a. Give the general formula that is used to represent alcohols
b. In pentan-2-ol, butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two of the alcohols in this question are isomers of each other. Identify which two and identify the type of isomerism they show
c. Name the alcohol whose structural formula is `CH_3CH_2COH(CH_3)_2`
Question 3
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following processes. Structural or displayed formulae should be used for all organic substances
a. Making ethanol using ethene as feedstock. Include the formula of the catalyst used
b. The complete combustion of ethanol in oxygen.
c. The dehydration of butan-2-ol when passed over hot Al2O3. Give three equations, one for each of the three possible products
d. The reaction of ethanoic acid with ethanol. Name the catalyst used, the type of reaction and the products
Question 4
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidised by heating with a mixture of potassium dichromate(VI) and dilute sulfuric(VI) acid
A primary alcohol can be oxidised to two different products, depending on the conditions used
A secondary alcohol forms one product when oxidised
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised
a. What is the formula of potassium dichromate(VI)?
b. Using a primary alcohol of your choice as an example:
i. give the displayed formulae of the two products it could be oxidised to
ii. state the conditions needed to give each product
iii. state which homologous series each product belongs to
iv. write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction (the convention [O] may be used for the oxidising agent)
Question 5
Why are tertiary alcohols resistant to oxidation?
Question 6
Three different alcohols, A, B and C are shown in the figure below

Alcohols A, B and C are heated separately with an alkaline solution of iodine. State which alcohol will give a yellow precipitate during this reaction.
Question 7
Which alcohol has a chiral centre and can be oxidised to a ketone?
A. Pentan-2-ol
B. Pentan-3-ol
C. 3-methylhexan-1-ol
D. 3-methylhexan-3-ol
Question 8
Which reaction will distinguish between a primary and a secondary alcohol?
A. Warming with H+ / `MnO""_4^-`
B. Warming with H+ / `Cr_2O""_7^(2-`
C. Dehydration, followed by reaction with Br2(aq)
D. Oxidation, followed by reaction with Fehling’s (or Tollens’) reagent
Question 9
Buta-1,3-diene is currently obtained from fossil fuel sources. In future it may be obtained from ethanol, which can be produced from non-food agricultural crops. The sequence of reactions is as follows.

Which term could be used to describe step 1?
A. Condensation
B. Dehydration
C. Dehydrogenation
D. Hydrogenation
Question 10
The diagram shows the structure of compound Z.

What is the product of the reaction between compound Z and an excess of NaBH4?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 