Question 1
1-bromobutane will undergo reactions when heated, as shown by reactions A and B
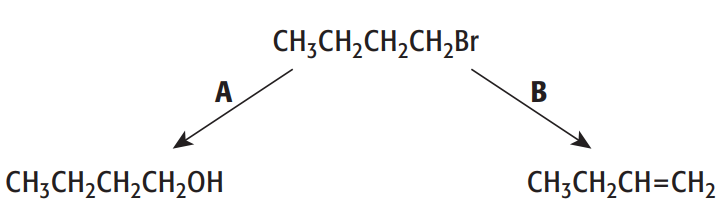
a. For reactions A and B give the reagents used in each case
b. Reaction A was repeated using 1-iodobutane instead of 1-bromobutane. Explain any difference in the rate of reaction observed
c. What type of organic reaction is A?
d. Show the mechanism for reaction A
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
2-bromo-2-methylpropane is reacted under aqueous sodium hydroxide (solution)
A. Name the organic compound formed
B. The mechanism of the reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane differs from the mechanism of reaction A in question 1. Describe how the mechanisms differ
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Bromochlorodifluoromethane has been used in fire extinguishers. However, its breakdown products were found to be toxic.
a. Draw the displayed formula of bromochlorodifluoromethane
b. CF3CH2F is being introduced as a replacement for various CFCs in refrigerants and aerosols. Name this compound
c. What is the main environmental problem caused by the use of CFCs?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The structure of a halogenoalkane containing bromine is shown in
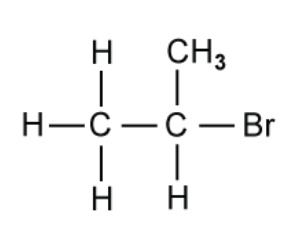
A. Name the compound shown above
B. State the class of halogenoalkane to which this compound belongs
C. State the colour of the precipitate formed in the reaction between the halogenoalkane in above in part (a) and acidified silver nitrate, AgNO3.
D. The compound drawn in the figure above in part (a) is reacted with alcoholic potassium cyanide, KCN. The reaction is heated under reflux.
Draw the product of this nucleophilic substitution reaction
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
a. The figure below shows the reaction profile for the production of propene

i. State the conditions required for step 1
ii. Name the mechanism for step 1
b.
The mechanism for step 1 in part (a) involves three different steps, initiation, propagation and termination.
Initiation:
`Cl_2 → 2Cl*`
Propagation:
Equation 1
Equation 2
Termination:
`Cl* + CH_3CH_2CH_2*`
The two propagation steps are missing. Write both of the equations that are required for this step
c.
i. Name the mechanism for step 2
ii. State the reagent and necessary conditions for step 2
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Many of the reactions of halogenoalkanes involve a nucleophile attacking the carbon attached to the halogen atom. The nucleophile replaces the halogen atom in a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The mechanism for the reaction is determined by the structure of the halogenoalkane. Primary and tertiary halogenoalkanes react via different reaction mechanisms.
A. State what is meant by the term tertiary halogenoalkane.
B. Tertiary halogenoalkanes react via an SN1 mechanism, whereas primary halogenoalkanes react via an SN2 mechanism.
Explain what the numbers 1 and 2 refer to in SN1 and SN2
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
An ethanolic solution of excess ammonia (NH3 in ethanol) is heated under pressure with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
A. Draw the structure of the resulting organic product.
B. State the name of the functional group of the organic product.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
X and Y are the reagents required to convert 1-bromopropane into butanoic acid.
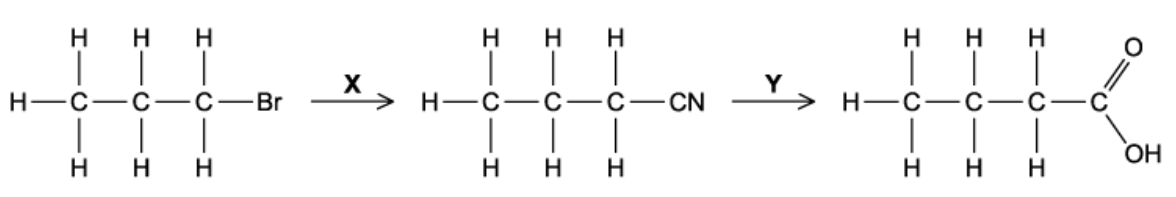
What are the correct identities of X and Y?
A. NH3 - HCl (aq)
B. KCN in C2H5OH - NaOH (aq)
C. KCN in C2H5OH - HCl (aq)
D. HCN - NaOH (aq)
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution?
A. `CH_3CH_2Br → CH_2=CH_2 + HBr`
B. `CH_2=CH_2 + HBr → CH_3CH_2Br`
C. `C_3H_7Br + H_2O → C_3H_7OH + HBr`
D. `C_2H_6 + Br_2 → C_2H_5Br + HBr`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Bromomethane, CH3Br, is used as a fumigant to destroy insect pests in grain that is to be stored. It can be made by reacting methanol with hydrogen bromide.
`CH_3OH + HBr → CH_3Br + H_2O`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Condensation
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic substitution
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
1-bromobutane will undergo reactions when heated, as shown by reactions A and B
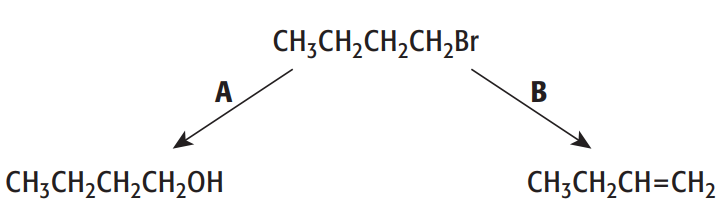
a. For reactions A and B give the reagents used in each case
b. Reaction A was repeated using 1-iodobutane instead of 1-bromobutane. Explain any difference in the rate of reaction observed
c. What type of organic reaction is A?
d. Show the mechanism for reaction A
a. As for reaction A, the reagent that we use is the NaOH solution for nucleophilic substitution reaction. As for reaction B, the reagent that we use is NaOH(ethanol) - ethanolic sodium hydroxide for elimination reaction.
b. The nucleophilic substitution reactions take place with the 1-iodobutane faster than 1-bromobutane because this reaction depends on the breaking of the carbon-halogen bond. Thus, when we move down the group, the bond energies will decrease, leading to the C-I bond being the weakest, as such, it will be broken most easily.
c. The type of organic reaction in A is nucleophilic substitution in which the aqueous hydroxide ion behaves as a nucleophile here, because it is donating a pair of electrons to the carbon atom bonded to the halogen in the halogenoalkane.
d.
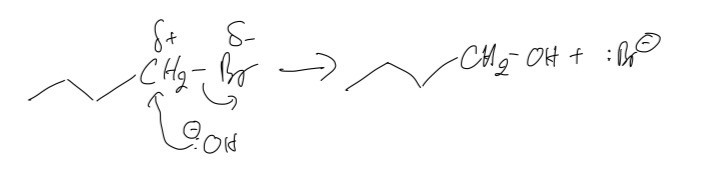
Question 2
2-bromo-2-methylpropane is reacted under aqueous sodium hydroxide (solution)
A. Name the organic compound formed
B. The mechanism of the reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane differs from the mechanism of reaction A in question 1. Describe how the mechanisms differ
A. The organic compound formed from the reaction between 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and aqueous sodium hydroxide (solution) is 2-methylpropan-2-ol
B. As for the mechanism of the reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane, it will occur according to SN1, i.e., the mechanism for tertiary halogenoalkanes. That means that it will create a carbocation, which is then attacked by the hydroxide ion instead of breaking the C-Br bond as the new C-OH bond is being generated.
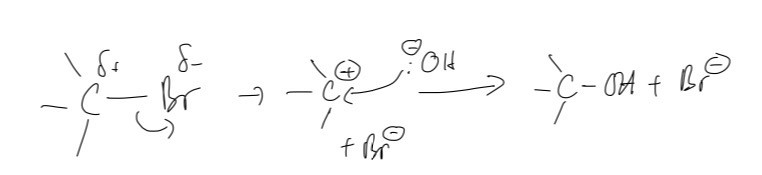
Question 3
Bromochlorodifluoromethane has been used in fire extinguishers. However, its breakdown products were found to be toxic.
a. Draw the displayed formula of bromochlorodifluoromethane
b. CF3CH2F is being introduced as a replacement for various CFCs in refrigerants and aerosols. Name this compound
c. What is the main environmental problem caused by the use of CFCs?
a. The displayed formula of bromochlorodifluoromethane is
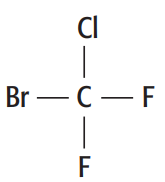
b. This compound is 1-fluoro-2-trifluoroethane
c. It destroys the ozone layers.
Question 4
The structure of a halogenoalkane containing bromine is shown in

A. Name the compound shown above
B. State the class of halogenoalkane to which this compound belongs
C. State the colour of the precipitate formed in the reaction between the halogenoalkane in above in part (a) and acidified silver nitrate, AgNO3.
D. The compound drawn in the figure above in part (a) is reacted with alcoholic potassium cyanide, KCN. The reaction is heated under reflux.
Draw the product of this nucleophilic substitution reaction
A. The compound shown above is 2-bromopropane
B. The class of halogenoalkane is secondary which the brom atom is bonded to the C atom bonded to two other alkyl groups.
C. The precipitate formed is AgBr which will be cream colour.
D. This reaction will involve nucleophilic substitution, as such, the product will be as follows:
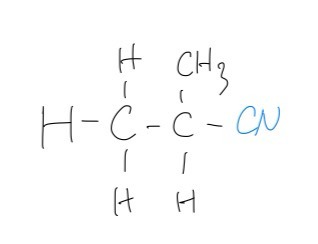
Question 5
a. The figure below shows the reaction profile for the production of propene

i. State the conditions required for step 1
ii. Name the mechanism for step 1
b.
The mechanism for step 1 in part (a) involves three different steps, initiation, propagation and termination.
Initiation:
`Cl_2 → 2Cl*`
Propagation:
Equation 1
Equation 2
Termination:
`Cl* + CH_3CH_2CH_2*`
The two propagation steps are missing. Write both of the equations that are required for this step
c.
i. Name the mechanism for step 2
ii. State the reagent and necessary conditions for step 2
a.
i. The conditions required for step 1 are UV/light and Chlorine included
ii. The mechanism for step to occur is free-radical substitution
b.
As for equation 1
`Cl * + CH_3CH_2CH_3 -> CH_3CH_2CH_2* + HCl`
As for equation 2
`CH_3CH_2CH_2* + Cl_2 -> CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + Cl*`
c.
i. The mechanism for step 2 is the elimination
ii. The reagent and necessary conditions for step 2 include EtOH, concentrated NaOH and heat
Question 6
Many of the reactions of halogenoalkanes involve a nucleophile attacking the carbon attached to the halogen atom. The nucleophile replaces the halogen atom in a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The mechanism for the reaction is determined by the structure of the halogenoalkane. Primary and tertiary halogenoalkanes react via different reaction mechanisms.
A. State what is meant by the term tertiary halogenoalkane.
B. Tertiary halogenoalkanes react via an SN1 mechanism, whereas primary halogenoalkanes react via an SN2 mechanism.
Explain what the numbers 1 and 2 refer to in SN1 and SN2
A.
The term tertiary halogenoalkane means that the carbon atom bonded to the halogen atom is also bonded to three other carbon atoms (alkyl groups).
B.
1 shows that the rate of the reaction only depends on one reagent, in this case the concentration of the halogenoalkane, as shown in the first (slow) step of the mechanism, whereas, 2 shows that the rate of the reaction, which is determined by the slow step in the mechanism involves two reacting species.
Question 7
An ethanolic solution of excess ammonia (NH3 in ethanol) is heated under pressure with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
A. Draw the structure of the resulting organic product.
B. State the name of the functional group of the organic product.
A.
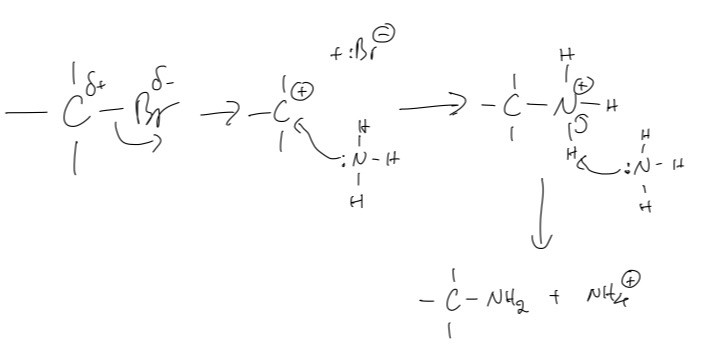
B.
The name of the functional group of the organic product is the amine group
Question 8
X and Y are the reagents required to convert 1-bromopropane into butanoic acid.

What are the correct identities of X and Y?
A. NH3 - HCl (aq)
B. KCN in C2H5OH - NaOH (aq)
C. KCN in C2H5OH - HCl (aq)
D. HCN - NaOH (aq)
The answer is C
A is incorrect because the reaction of a halogenoalkane and ammonia will form a primary amine
B and D are incorrect because reagent Y could not be NaOH due to sodium butanoate generation instead
Question 9
Which reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution?
A. `CH_3CH_2Br → CH_2=CH_2 + HBr`
B. `CH_2=CH_2 + HBr → CH_3CH_2Br`
C. `C_3H_7Br + H_2O → C_3H_7OH + HBr`
D. `C_2H_6 + Br_2 → C_2H_5Br + HBr`
The answer is C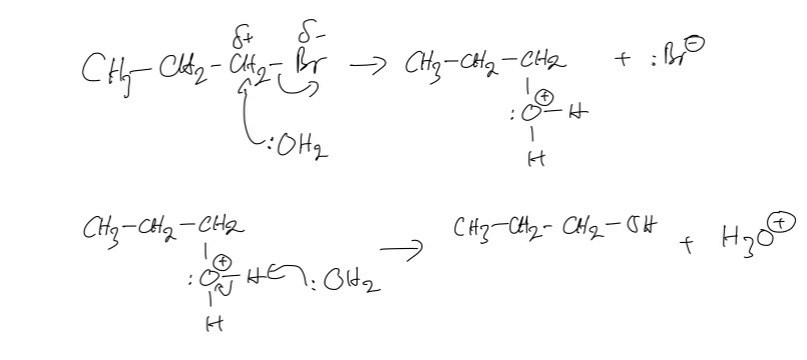
A is incorrect because this is an elimination reaction
B is incorrect because this is an electrophilic addition reaction
D is incorrect because this is a free-radical substitution
Question 10
Bromomethane, CH3Br, is used as a fumigant to destroy insect pests in grain that is to be stored. It can be made by reacting methanol with hydrogen bromide.
`CH_3OH + HBr → CH_3Br + H_2O`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Condensation
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic substitution
The answer is D
When a group or atom is replaced by a nucleophile, the result is a nucleophilic, which can be defined as either a functional group with a lone pair of electrons or a negative charge.
Question 1
1-bromobutane will undergo reactions when heated, as shown by reactions A and B
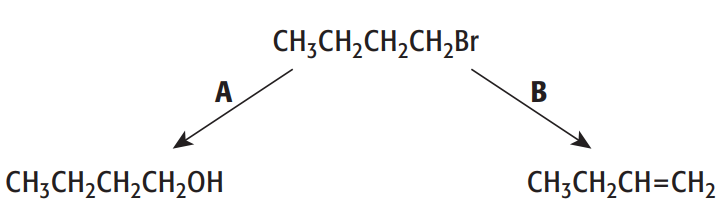
a. For reactions A and B give the reagents used in each case
b. Reaction A was repeated using 1-iodobutane instead of 1-bromobutane. Explain any difference in the rate of reaction observed
c. What type of organic reaction is A?
d. Show the mechanism for reaction A
Question 2
2-bromo-2-methylpropane is reacted under aqueous sodium hydroxide (solution)
A. Name the organic compound formed
B. The mechanism of the reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane differs from the mechanism of reaction A in question 1. Describe how the mechanisms differ
Question 3
Bromochlorodifluoromethane has been used in fire extinguishers. However, its breakdown products were found to be toxic.
a. Draw the displayed formula of bromochlorodifluoromethane
b. CF3CH2F is being introduced as a replacement for various CFCs in refrigerants and aerosols. Name this compound
c. What is the main environmental problem caused by the use of CFCs?
Question 4
The structure of a halogenoalkane containing bromine is shown in

A. Name the compound shown above
B. State the class of halogenoalkane to which this compound belongs
C. State the colour of the precipitate formed in the reaction between the halogenoalkane in above in part (a) and acidified silver nitrate, AgNO3.
D. The compound drawn in the figure above in part (a) is reacted with alcoholic potassium cyanide, KCN. The reaction is heated under reflux.
Draw the product of this nucleophilic substitution reaction
Question 5
a. The figure below shows the reaction profile for the production of propene

i. State the conditions required for step 1
ii. Name the mechanism for step 1
b.
The mechanism for step 1 in part (a) involves three different steps, initiation, propagation and termination.
Initiation:
`Cl_2 → 2Cl*`
Propagation:
Equation 1
Equation 2
Termination:
`Cl* + CH_3CH_2CH_2*`
The two propagation steps are missing. Write both of the equations that are required for this step
c.
i. Name the mechanism for step 2
ii. State the reagent and necessary conditions for step 2
Question 6
Many of the reactions of halogenoalkanes involve a nucleophile attacking the carbon attached to the halogen atom. The nucleophile replaces the halogen atom in a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The mechanism for the reaction is determined by the structure of the halogenoalkane. Primary and tertiary halogenoalkanes react via different reaction mechanisms.
A. State what is meant by the term tertiary halogenoalkane.
B. Tertiary halogenoalkanes react via an SN1 mechanism, whereas primary halogenoalkanes react via an SN2 mechanism.
Explain what the numbers 1 and 2 refer to in SN1 and SN2
Question 7
An ethanolic solution of excess ammonia (NH3 in ethanol) is heated under pressure with 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
A. Draw the structure of the resulting organic product.
B. State the name of the functional group of the organic product.
Question 8
X and Y are the reagents required to convert 1-bromopropane into butanoic acid.

What are the correct identities of X and Y?
A. NH3 - HCl (aq)
B. KCN in C2H5OH - NaOH (aq)
C. KCN in C2H5OH - HCl (aq)
D. HCN - NaOH (aq)
Question 9
Which reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution?
A. `CH_3CH_2Br → CH_2=CH_2 + HBr`
B. `CH_2=CH_2 + HBr → CH_3CH_2Br`
C. `C_3H_7Br + H_2O → C_3H_7OH + HBr`
D. `C_2H_6 + Br_2 → C_2H_5Br + HBr`
Question 10
Bromomethane, CH3Br, is used as a fumigant to destroy insect pests in grain that is to be stored. It can be made by reacting methanol with hydrogen bromide.
`CH_3OH + HBr → CH_3Br + H_2O`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Condensation
B. Electrophilic substitution
C. Free radical substitution
D. Nucleophilic substitution