Question 1
Propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes.
For each one give:
i. its molecular formula
ii. its structural formula
iii. its displayed formula
iv. its skeletal formula
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A. Give the general formula that is used to represent alkenes.
B. In propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes, two of these alkenes are isomers of each other. Identify which two.
C. Why is it not possible to change one of these two isomers into the other at room temperature?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
3-Methylpent-2-ene has two cis–trans isomers. Draw and name the two isomers.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Using structural formulae throughout, give balanced symbol equations for the following reactions.
A. Propene with bromine
B. Propene with hydrogen. Name the catalyst used. Which industrial process uses a similar reaction?
C. Propene with hydrogen bromide. Give structural formulae for both possible products.
D. Propene with steam. Give structural formulae for both possible products. Give the formula of the catalyst used
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
i. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Explain the word unsaturated.
ii. Describe and draw the shape of an ethene molecule, labelling all bond angles.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A. Explain the meaning of the term functional group. Which functional group is present in all alkenes?
B. Describe a simple chemical test to determine whether an unknown hydrocarbon is unsaturated. Describe the result if the test is positive.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Use the passage below and your own knowledge to answer the questions that follow. Ethene reacts with bromine to give 1,2-dibromoethane as the only product. The mechanism for the reaction is electrophilic addition and involves heterolytic fission of chemical bonds. The bromine molecules behave as electrophiles in this reaction.
A. By what mechanism does bromine react with ethene?
B. Write a balanced symbol equation for this reaction.
C. Bonds break in this reaction. What type of bond breaking is involved?
D. Show the mechanism of the reaction as fully as you can, using curly arrows.
E. Which substance behaves here as an electrophile? Explain what is meant by the term electrophile.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Alkenes are important industrial chemicals, particularly as raw materials for the manufacture of polymers. Ethene can be used to make poly(ethene). Ethene is used to make chloroethene, which is then used to make poly(chloroethene), and ethene is also used to make tetrafluoroethene, which is used to make poly(tetrafluoroethene).
a. Use displayed formulae to write an equation for the formation of poly(chloroethene) from chloroethene.
b. Why do waste (used) poly(alkene)s cause problems in a landfill site?
c. Burning halogenated polymers such as PVC can release toxic waste products, such as HCl, into the environment. Explain how this can be minimised.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which compound would produce two different carboxylic acids when treated with hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions?
A. 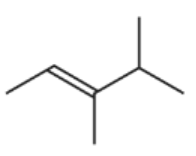
B. 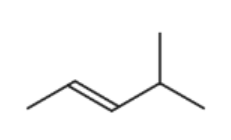
C. 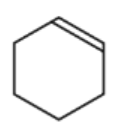
D. 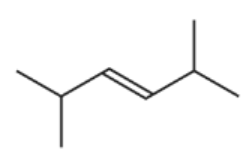
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Ethene reacts with steam in the presence of sulfuric acid.
`C_2H_4 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Acid/Base
B. Addition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Substitution
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
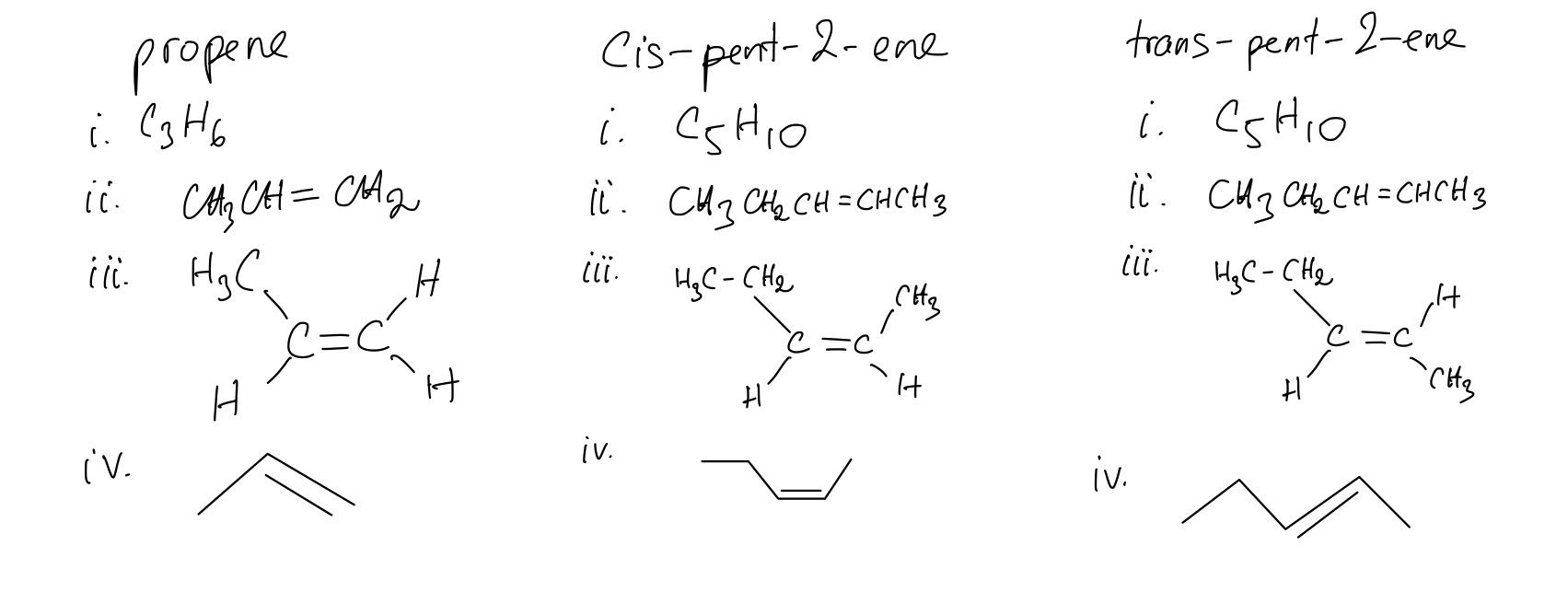
Propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes.
For each one give:
i. its molecular formula
ii. its structural formula
iii. its displayed formula
iv. its skeletal formula
Question 2
A. Give the general formula that is used to represent alkenes.
B. In propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes, two of these alkenes are isomers of each other. Identify which two.
C. Why is it not possible to change one of these two isomers into the other at room temperature?
A. The general formula that is used to represent alkenes is CnH2n
B. Two of these alkenes are isomers of each other are cis- and trans-pent-2-ene
C. It is not possible to change one of these two isomers into the other at room temperature because cis–trans isomers arise from the restricted rotation around a C=C double bond and there are two distinct groups bonded to each carbon in the C=C double bond.
Question 3
3-Methylpent-2-ene has two cis–trans isomers. Draw and name the two isomers.
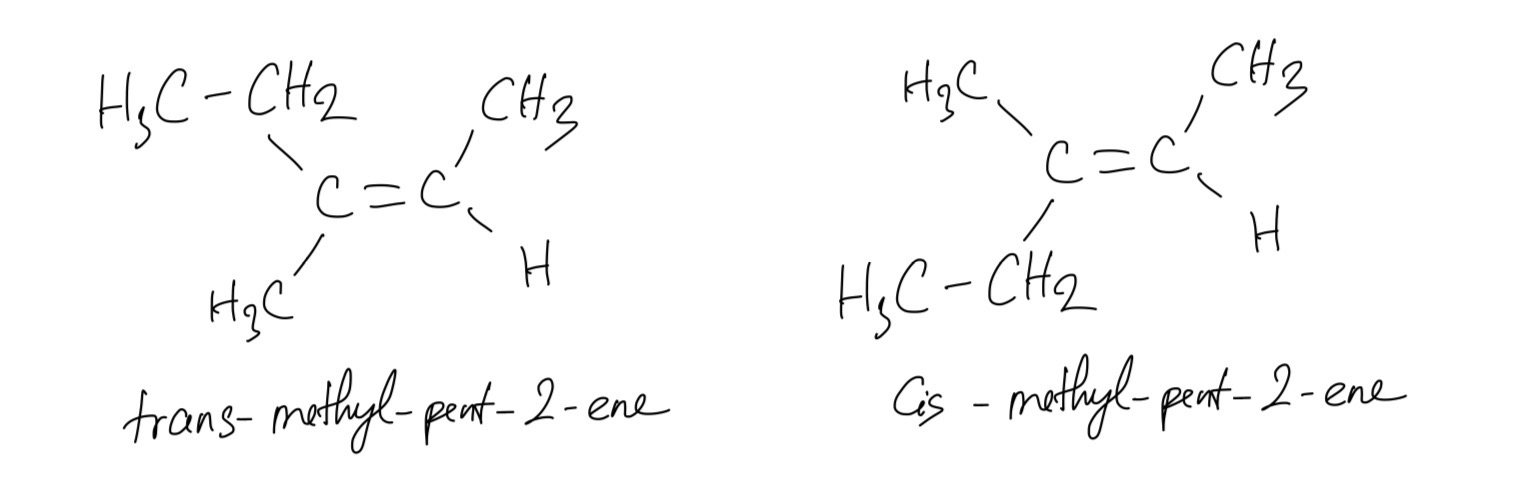
Question 4
Using structural formulae throughout, give balanced symbol equations for the following reactions.
A. Propene with bromine
B. Propene with hydrogen. Name the catalyst used. Which industrial process uses a similar reaction?
C. Propene with hydrogen bromide. Give structural formulae for both possible products.
D. Propene with steam. Give structural formulae for both possible products. Give the formula of the catalyst used
A. `CH_3CH=CH_2 + Br_2 → CH_3CHBrCH_2Br`
B. The common catalyst is used for the reaction `CH_3CH=CH_2 + H_2 → CH_3CH_2CH_3` is nickel and it is applied to produce margarine
C. The possibile products can be formed
`CH_3CH=CH_2 + HBr → CH_3CH_2CH_2Br` or `CH_3CHBrCH_3`
D. We normally use H3PO4 catalyst for reaction of propene with steam
`CH_3CH=CH_2 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2CH_2OH` or `CH_3CHOHCH_3`
Question 5
i. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Explain the word unsaturated.
ii. Describe and draw the shape of an ethene molecule, labelling all bond angles.
i.The word unsaturated means that there are one or more double bonds in the compound
ii.
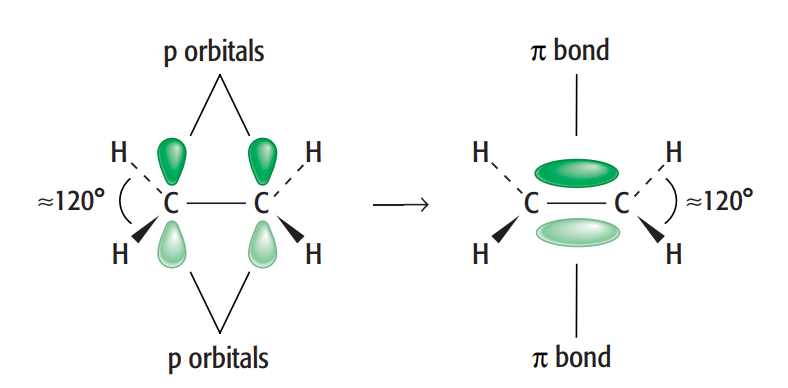
In ethene compound, carbon can create both single and double bonds between its atoms. A σ bond and a π bond combine to form a C=C double bond, which is present in ethene. This is an specific example of sp2 hybridisation.
In an ethene molecule, the two lobes that comprise the π bond are located above and below the plane of the atoms. This maximizes the p orbitals' overlap. In the σ bonds, three pairs of electrons encircle each of the carbon atoms that form part of the double bond. All of these are in the molecule's plane and work against one another to create bond angles of roughly 120 °.
Therefore, ethene is described as a planar molecule.
Question 6
A. Explain the meaning of the term functional group. Which functional group is present in all alkenes?
B. Describe a simple chemical test to determine whether an unknown hydrocarbon is unsaturated. Describe the result if the test is positive.
A. The term functional group represents the specific chemical properties of that compound. in all alkenes, there is always at least a C=C double bond.
B. We can perform tests by bubbling an alkene through a solution of chlorine or bromine at room temperature. The colour of the halogen molecules in solution will be removed and if it is unsaturated, the bromine water or chlorine water will be decolorised.
Question 7
Use the passage below and your own knowledge to answer the questions that follow. Ethene reacts with bromine to give 1,2-dibromoethane as the only product. The mechanism for the reaction is electrophilic addition and involves heterolytic fission of chemical bonds. The bromine molecules behave as electrophiles in this reaction.
A. By what mechanism does bromine react with ethene?
B. Write a balanced symbol equation for this reaction.
C. Bonds break in this reaction. What type of bond breaking is involved?
D. Show the mechanism of the reaction as fully as you can, using curly arrows.
E. Which substance behaves here as an electrophile? Explain what is meant by the term electrophile.
A. Bromine reacts with ethene through electrophilic addition
B. A balanced symbol equation for this reaction
`C_2H_4 + Br_2 -> C_2H_4Br_2`
C. Type of bond breaking involved is heterolytic fission in which one atom takes both original bonding electrons from the other atom
D.
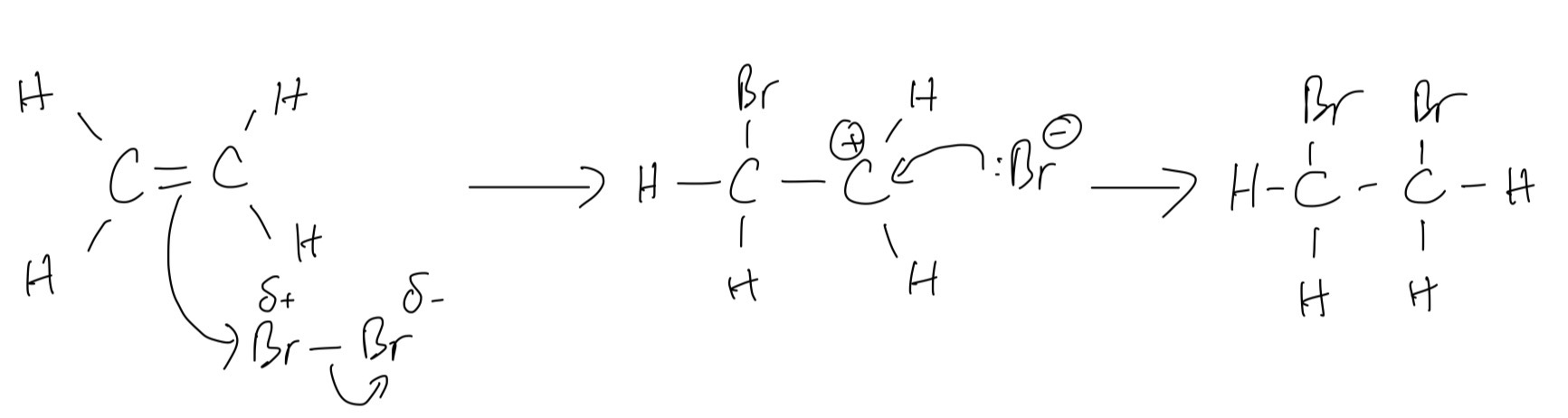
E. As we learned, the term electrophile means that is an electron-pair acceptor and here we have Br2 serving as an electrophil
Question 8
Alkenes are important industrial chemicals, particularly as raw materials for the manufacture of polymers. Ethene can be used to make poly(ethene). Ethene is used to make chloroethene, which is then used to make poly(chloroethene), and ethene is also used to make tetrafluoroethene, which is used to make poly(tetrafluoroethene).
a. Use displayed formulae to write an equation for the formation of poly(chloroethene) from chloroethene.
b. Why do waste (used) poly(alkene)s cause problems in a landfill site?
c. Burning halogenated polymers such as PVC can release toxic waste products, such as HCl, into the environment. Explain how this can be minimised.
a.
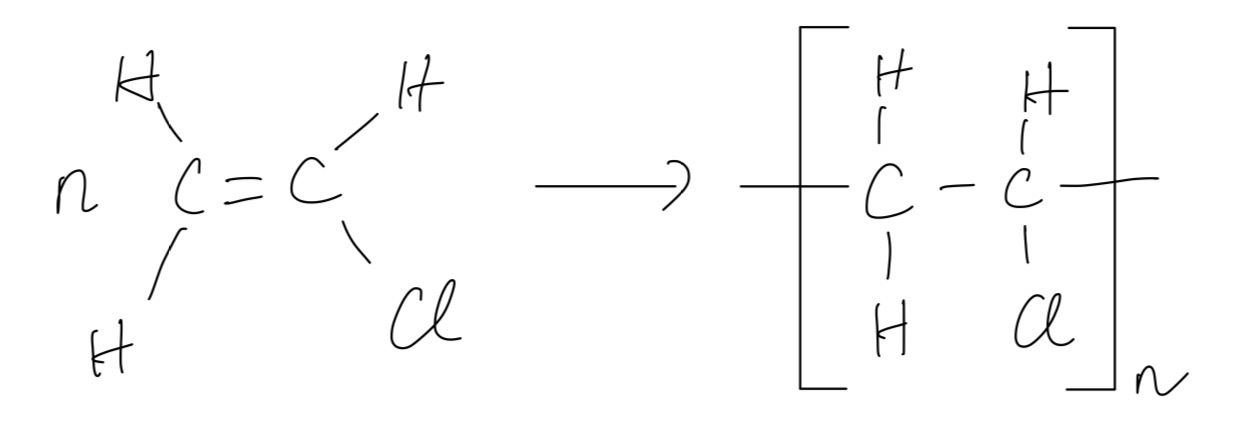
b. Because they are not easily biodegradable and they occupy various spaces. Thus, waste (used) poly(alkene)s cause problems in a landfill site
c. HCl is acidic, as such, we can minimize them by neutralizing with a basic solution. From that, we could reduce the affection for environment
Question 9
Which compound would produce two different carboxylic acids when treated with hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
The answer is B
Hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions leads to cleavage of C=C double bond. The product formed depends on the carbon atom on either side of carbon atom
A is incorrect because the carbon atom is attached to one H and one R group, it will form aldehyde and then carboxylic acid.
C is incorrect because it will open the ring and then generate 2 carboxylic acids on a compound.
D is incorrect because it will form 2 identical structures of carboxylic acid
Question 10
Ethene reacts with steam in the presence of sulfuric acid.
`C_2H_4 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Acid/Base
B. Addition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Substitution
The answer is B
The addition reaction is two compounds that will be combined together to generate one larger compound.
A is incorrect because this reaction will involve an acid and a base reactant
C is incorrect because a hydrolysis reaction is to break down chemical bonds by water addition
D is incorrect because this reaction is an atom or functional group which is replaced by another similar piece
Question 1
Propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes.
For each one give:
i. its molecular formula
ii. its structural formula
iii. its displayed formula
iv. its skeletal formula
Question 2
A. Give the general formula that is used to represent alkenes.
B. In propene, cis-pent-2-ene and trans-pent-2-ene are alkenes, two of these alkenes are isomers of each other. Identify which two.
C. Why is it not possible to change one of these two isomers into the other at room temperature?
Question 3
3-Methylpent-2-ene has two cis–trans isomers. Draw and name the two isomers.
Question 4
Using structural formulae throughout, give balanced symbol equations for the following reactions.
A. Propene with bromine
B. Propene with hydrogen. Name the catalyst used. Which industrial process uses a similar reaction?
C. Propene with hydrogen bromide. Give structural formulae for both possible products.
D. Propene with steam. Give structural formulae for both possible products. Give the formula of the catalyst used
Question 5
i. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Explain the word unsaturated.
ii. Describe and draw the shape of an ethene molecule, labelling all bond angles.
Question 6
A. Explain the meaning of the term functional group. Which functional group is present in all alkenes?
B. Describe a simple chemical test to determine whether an unknown hydrocarbon is unsaturated. Describe the result if the test is positive.
Question 7
Use the passage below and your own knowledge to answer the questions that follow. Ethene reacts with bromine to give 1,2-dibromoethane as the only product. The mechanism for the reaction is electrophilic addition and involves heterolytic fission of chemical bonds. The bromine molecules behave as electrophiles in this reaction.
A. By what mechanism does bromine react with ethene?
B. Write a balanced symbol equation for this reaction.
C. Bonds break in this reaction. What type of bond breaking is involved?
D. Show the mechanism of the reaction as fully as you can, using curly arrows.
E. Which substance behaves here as an electrophile? Explain what is meant by the term electrophile.
Question 8
Alkenes are important industrial chemicals, particularly as raw materials for the manufacture of polymers. Ethene can be used to make poly(ethene). Ethene is used to make chloroethene, which is then used to make poly(chloroethene), and ethene is also used to make tetrafluoroethene, which is used to make poly(tetrafluoroethene).
a. Use displayed formulae to write an equation for the formation of poly(chloroethene) from chloroethene.
b. Why do waste (used) poly(alkene)s cause problems in a landfill site?
c. Burning halogenated polymers such as PVC can release toxic waste products, such as HCl, into the environment. Explain how this can be minimised.
Question 9
Which compound would produce two different carboxylic acids when treated with hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
Question 10
Ethene reacts with steam in the presence of sulfuric acid.
`C_2H_4 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH`
What type of reaction is this?
A. Acid/Base
B. Addition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Substitution