Question 1
State the three different types of structural isomerism
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
State the type of isomerism that occurs between the following pairs of compounds.
A. 2-methylpentane and 2,3-dimethylbutane
B. Butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A. Name the two types of stereoisomers
B. Describe what a chiral centre is
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The structure of one optical isomer of a chlorofluorocarbon is shown in the figure below
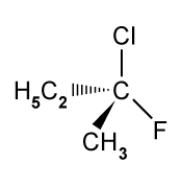
Draw the structure of the other enantiomer.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
C4H8 exists as several isomers.
A. Name the homologous series that C4H8 belongs to.
B. Draw the skeletal formulae of two cyclic C4H8 isomers and two C4H8 isomers that show cis / trans isomerism.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Explain why compound Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol exists as two stereoisomers, but compound 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid does not.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Draw the two isomers of compound 2-chloropropanal to explain how this type of isomerism occurs.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
A molecule can have optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism. Which of the compounds below show both?
A. CH3CH2CHBrCH=CHBr
B. CH3CBr=CBrCH3
C. CH3CH=CHCH2CH3
D. CH3CHBrCH=CH2
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which carbon atom is the chiral centre in the following molecule?
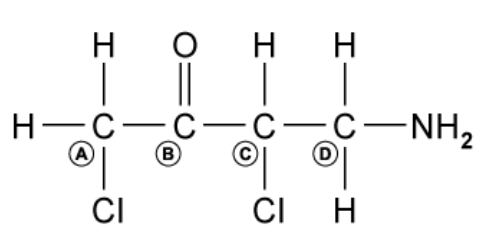
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
2,2-dimethylpropane is an isomer of pentane.
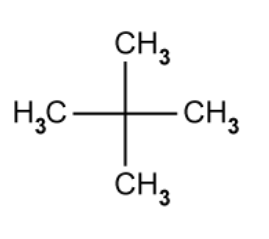
What type of isomerism is shown by 2,2-dimethylpropane?
A. Stereoisomerism
B. Functional group
C. Cyclic
D. Chain
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
State the three different types of structural isomerism
Structural isomerims are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae.
There are three different types of structural isomerism including chain, positional and functional group isomerisms.
Question 2
State the type of isomerism that occurs between the following pairs of compounds.
A. 2-methylpentane and 2,3-dimethylbutane
B. Butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol
A. The type of isomerism that occurs between these compounds is chain isomerism which has the same molecular formula but not same length of hydrocarbon chain
B. The type of isomerism that occurs between these compounds is positional isomerism which has differences in the position of a functional group in each isomer
Question 3
A. Name the two types of stereoisomers
B. Describe what a chiral centre is
A. The two types of stereoisomers which are described as the same structural formula but having differences in arrangement of atoms in 30 space are geometric and optical
B. A chiral centre is a carbon atom with the four different groups attached.
Question 4
The structure of one optical isomer of a chlorofluorocarbon is shown in the figure below

Draw the structure of the other enantiomer.
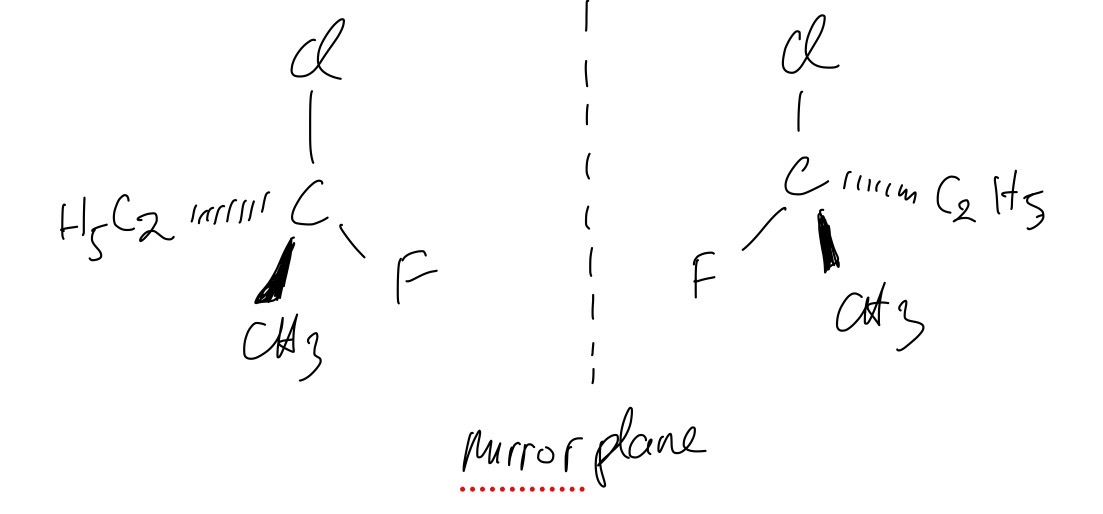
Question 5
C4H8 exists as several isomers.
A. Name the homologous series that C4H8 belongs to.
B. Draw the skeletal formulae of two cyclic C4H8 isomers and two C4H8 isomers that show cis / trans isomerism.
A. The homologous series that C4H8 belongs to alkenes
B.
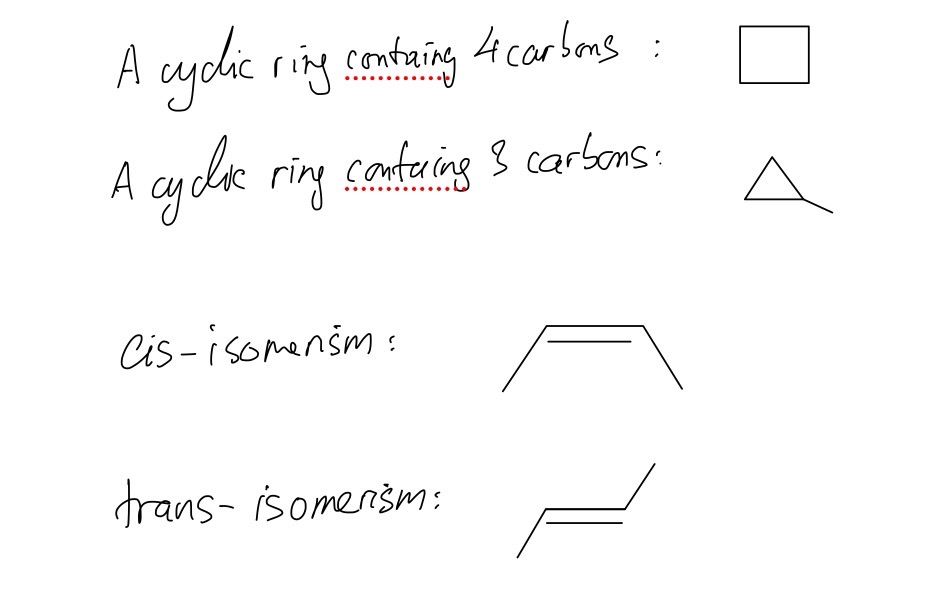
Question 6
Explain why compound Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol exists as two stereoisomers, but compound 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid does not.
Skeletal formula of Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol
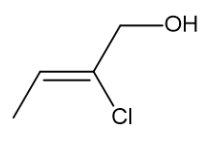
Skeletal formula of 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid
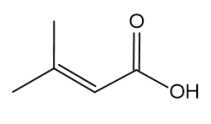
Because there is restricted rotation by the presence of π bonds in the C=C double bond. It’s easily noticed that there are 4 different substituted groups on C=C bond of Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol whereas, there are same functional group of methyl on one side on C=C bond of 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid. Therefore, compound Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol exists as two stereoisomers, but compound 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid does not.
Question 7
Draw the two isomers of compound 2-chloropropanal to explain how this type of isomerism occurs.
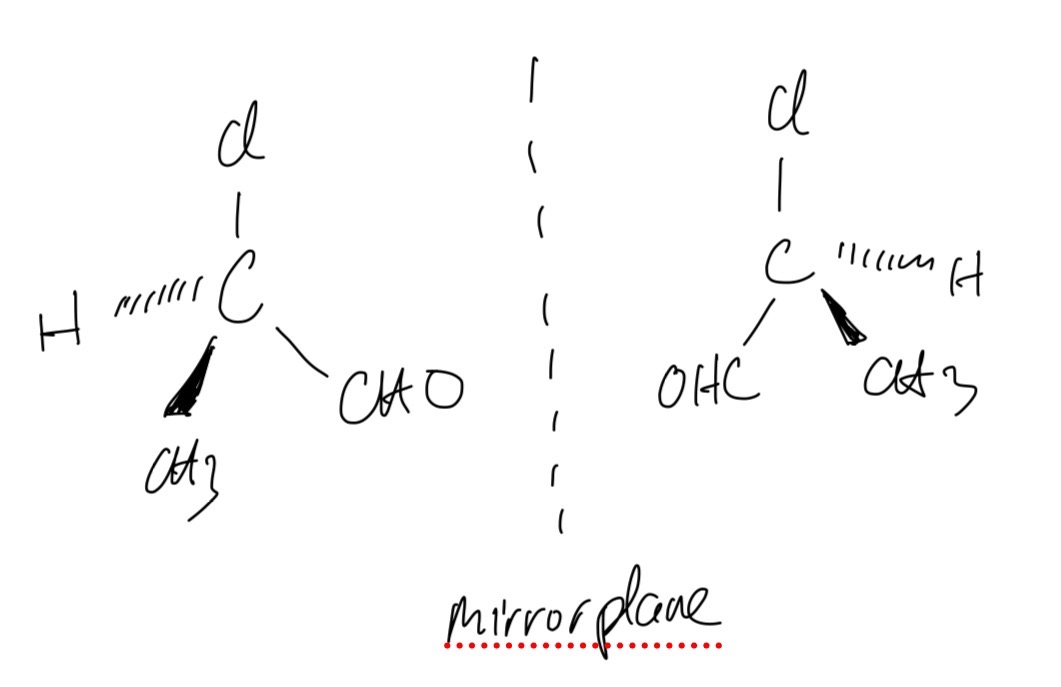
This type of isomerism occurs because of the chiral centre which is a carbon atom having 4 different atoms or groups attached. Therefore, there are two molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Question 8
A molecule can have optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism. Which of the compounds below show both?
A. CH3CH2CHBrCH=CHBr
B. CH3CBr=CBrCH3
C. CH3CH=CHCH2CH3
D. CH3CHBrCH=CH2
The answer is A
If a molecule contains a carbon atom that is bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms which refers to as the chiral centre of the molecule, it can form two optical isomers.
The term geometric isomerism refers to complexes with the same molecular formula but different geometrical arrangements of their atoms, more specific is due to the restriction surrounding the C=C double bond
B is incorrect because this has no chiral carbons
C is incorrect because this has no chiral carbons
D is incorrect because this has no cis-trans isomerism due to the presence of 3 H groups surrounding C=C double bond.
Question 9
Which carbon atom is the chiral centre in the following molecule?

A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
The answer is C
A chiral centre is a carbon atom with the four different groups attached.
A is incorrect because this carbon has two hydrogen atoms attached
B is incorrect because this carbon has C=O carbonyl group attached
D is incorrect because this carbon has two hydrogen atoms attached
Question 10
2,2-dimethylpropane is an isomer of pentane.

What type of isomerism is shown by 2,2-dimethylpropane?
A. Stereoisomerism
B. Functional group
C. Cyclic
D. Chain
The answer is D
A is incorrect because 2,2-dimethylpropane is not a stereoisomer
B is incorrect because there is not a different functional group in 2,2-dimethylpropane compared to pentane
C is incorrect because cyclic is not a type of isomerism.
Question 1
State the three different types of structural isomerism
Question 2
State the type of isomerism that occurs between the following pairs of compounds.
A. 2-methylpentane and 2,3-dimethylbutane
B. Butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol
Question 3
A. Name the two types of stereoisomers
B. Describe what a chiral centre is
Question 4
The structure of one optical isomer of a chlorofluorocarbon is shown in the figure below

Draw the structure of the other enantiomer.
Question 5
C4H8 exists as several isomers.
A. Name the homologous series that C4H8 belongs to.
B. Draw the skeletal formulae of two cyclic C4H8 isomers and two C4H8 isomers that show cis / trans isomerism.
Question 6
Explain why compound Z-2-chloro-but-2-en-1-ol exists as two stereoisomers, but compound 3-methyl-but-2-enoic acid does not.
Question 7
Draw the two isomers of compound 2-chloropropanal to explain how this type of isomerism occurs.
Question 8
A molecule can have optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism. Which of the compounds below show both?
A. CH3CH2CHBrCH=CHBr
B. CH3CBr=CBrCH3
C. CH3CH=CHCH2CH3
D. CH3CHBrCH=CH2
Question 9
Which carbon atom is the chiral centre in the following molecule?

A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Question 10
2,2-dimethylpropane is an isomer of pentane.

What type of isomerism is shown by 2,2-dimethylpropane?
A. Stereoisomerism
B. Functional group
C. Cyclic
D. Chain