Question 1
Aliphatic compounds can be organised into three different categories depending on their structure.
One of the categories is straight-chain. Name the other two categories of aliphatic compounds.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Complete table below to show the type and number of bonds in hybridised bonds
| Hybridisation | Number of σ bonds | Number of π bonds |
| sp3 | ||
| sp2 | ||
| sp |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Four compounds are shown in the figure below
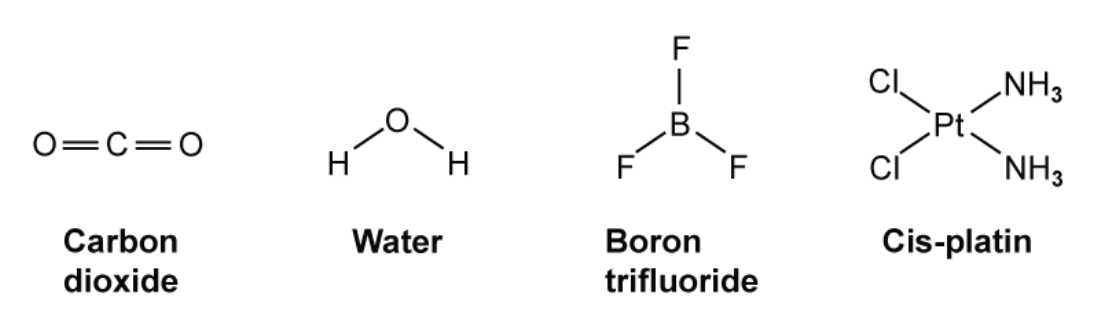
| Molecule | Shape | Bond angle /o |
| Carbon dioxide | ||
| Water | ||
| Boron trifluoride | ||
| Cis-platin |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Explain how the concept of hybridisation can be used to explain the triple bond present in propyne.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Use the term planar to describe the arrangement of atoms in ethene
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which type of bond results from the side-to-side overlap of p orbitals?
A. Sigma (σ) bond
B. Pi (π) bond
C. Covalent bond
D. Ionic bond
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in a double bond?
A. 2 - 0
B. 1 - 1
C. 0 - 2
D. 1 - 2
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is the hybridisation of the carbon atom in methane, CH4?
A. sp
B. sp2
C. sp3
D. sp3d
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which of the following molecules is a straight-chain hydrocarbon?
A. Benzene
B. Cycloentane
C. 2-methylpropane
D. Propane
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Methyl isocyanate, CH3NCO, is a toxic liquid which is used in the production of adhesives.
The sequence of atoms in a methyl isocyanate molecule is H3C—N=C=O.
What is the approximate angle between the bonds formed by the N atom?
A. 180 o
B. 120 o
C. 109 o
D. 104 o
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Aliphatic compounds can be organised into three different categories depending on their structure.
One of the categories is straight-chain. Name the other two categories of aliphatic compounds.
The other two categories of aliphatic compound are branched and cyclic.
Question 2
Complete table below to show the type and number of bonds in hybridised bonds
| Hybridisation | Number of σ bonds | Number of π bonds |
| sp3 | ||
| sp2 | ||
| sp |
| Hybridisation | Number of σ bonds | Number of π bonds |
| sp3 | 4 | 0 |
| sp2 | 3 | 1 |
| sp | 2 | 2 |
Sp3 indicates all four orbitals are hybridised
Sp2 is used in double bonds
Sp is used in triple bonds
Question 3
Four compounds are shown in the figure below

| Molecule | Shape | Bond angle /o |
| Carbon dioxide | ||
| Water | ||
| Boron trifluoride | ||
| Cis-platin |
| Molecule | Shape | Bond angle /o |
| Carbon dioxide | Linear | 180 |
| Water | Bent | 104.5 |
| Boron trifluoride | Trigonol planar | 120 |
| Cis-platin | Square planar | 90 |
Question 4
Explain how the concept of hybridisation can be used to explain the triple bond present in propyne.
The concept of hybridisation can be used to explain the triple bond present in propyne as follows:
There is sp hybridization between the two carbon atoms. Sigma bond produced by overlap of sp orbitals of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom's unhybridized p orbitals overlapped to make two pi bonds at the same time. Therefore, one σ bond and two π bonds make up a triple bond.
Question 5
Use the term planar to describe the arrangement of atoms in ethene
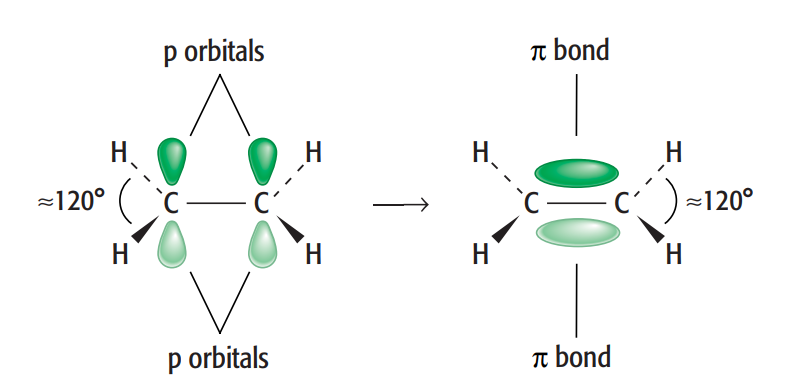
In ethene compound, carbon can create both single and double bonds between its atoms. A σ bond and a π bond combine to form a C=C double bond, which is present in ethene. This is an specific example of sp2 hybridisation.
In an ethene molecule, the two lobes that comprise the π bond are located above and below the plane of the atoms. This maximizes the p orbitals' overlap. In the σ bonds, three pairs of electrons encircle each of the carbon atoms that form part of the double bond. All of these are in the molecule's plane and work against one another to create bond angles of roughly 120 °.
Therefore, ethene is described as a planar molecule.
Question 6
Which type of bond results from the side-to-side overlap of p orbitals?
A. Sigma (σ) bond
B. Pi (π) bond
C. Covalent bond
D. Ionic bond
The answer is B
A is incorrect because it is formed from the end-on overlap of atomic orbitals.
C is incorrect because it is a description of a shared pair of electrons not how orbitals are involved in bonding
D is incorrect because it is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged particles
Question 7
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in a double bond?
A. 2 - 0
B. 1 - 1
C. 0 - 2
D. 1 - 2
The answer is B
A, C and D are incorrect because they have wrong number of sigma and pi bonds in a double bond.
Question 8
What is the hybridisation of the carbon atom in methane, CH4?
A. sp
B. sp2
C. sp3
D. sp3d
The answer is C
Sp3 indicates all four orbitals are hybridised and methane comprises 4 sigma bonds
A is incorrect because it’s responsible for triple bonds
B is incorrect because it’s responsible for double bonds
D is incorrect because it’s responsible for involving d orbital
Question 9
Which of the following molecules is a straight-chain hydrocarbon?
A. Benzene
B. Cycloentane
C. 2-methylpropane
D. Propane
The answer is D
A is incorrect because it’s a cyclic molecule
B is incorrect because is’s a cyclic molecule
C is incorrect because it’s a branched molecule
Question 10
Methyl isocyanate, CH3NCO, is a toxic liquid which is used in the production of adhesives.
The sequence of atoms in a methyl isocyanate molecule is H3C—N=C=O.
What is the approximate angle between the bonds formed by the N atom?
A. 180 o
B. 120 o
C. 109 o
D. 104 o
The answer is B
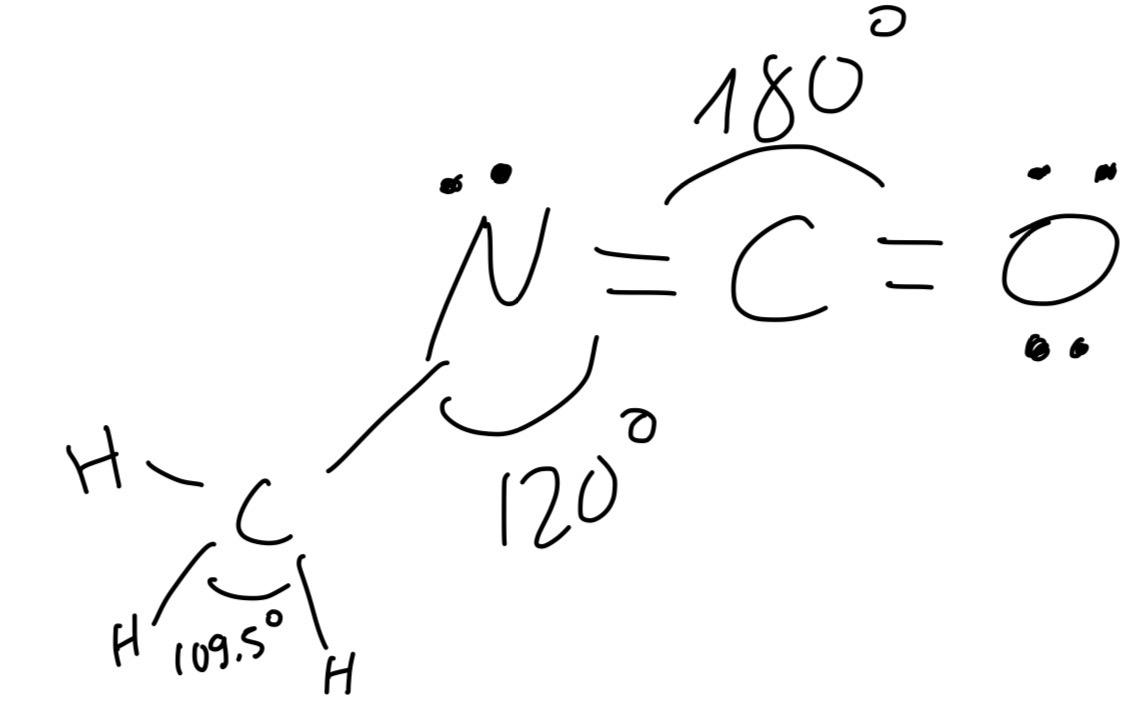
The VESPR theory states that electron pairs repel each other whether or not they are in bond pairs or lone pairs. Therefore, the electrons will spead as much as possible to reduce repulsion. Thus, in nitrogen position, there is only 1 lone pair of electrons, however, it is noticed that there are 2 different bonding electrons groups which are the areas of electron density around the central atom, causing the bond angle of N atom position. That makes this angle less than 120 o, around 117.5 o.
Question 1
Aliphatic compounds can be organised into three different categories depending on their structure.
One of the categories is straight-chain. Name the other two categories of aliphatic compounds.
Question 2
Complete table below to show the type and number of bonds in hybridised bonds
| Hybridisation | Number of σ bonds | Number of π bonds |
| sp3 | ||
| sp2 | ||
| sp |
Question 3
Four compounds are shown in the figure below

| Molecule | Shape | Bond angle /o |
| Carbon dioxide | ||
| Water | ||
| Boron trifluoride | ||
| Cis-platin |
Question 4
Explain how the concept of hybridisation can be used to explain the triple bond present in propyne.
Question 5
Use the term planar to describe the arrangement of atoms in ethene
Question 6
Which type of bond results from the side-to-side overlap of p orbitals?
A. Sigma (σ) bond
B. Pi (π) bond
C. Covalent bond
D. Ionic bond
Question 7
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in a double bond?
A. 2 - 0
B. 1 - 1
C. 0 - 2
D. 1 - 2
Question 8
What is the hybridisation of the carbon atom in methane, CH4?
A. sp
B. sp2
C. sp3
D. sp3d
Question 9
Which of the following molecules is a straight-chain hydrocarbon?
A. Benzene
B. Cycloentane
C. 2-methylpropane
D. Propane
Question 10
Methyl isocyanate, CH3NCO, is a toxic liquid which is used in the production of adhesives.
The sequence of atoms in a methyl isocyanate molecule is H3C—N=C=O.
What is the approximate angle between the bonds formed by the N atom?
A. 180 o
B. 120 o
C. 109 o
D. 104 o