Question 1
Propane and hexane are part of the alkane homologous series.
A. Define the term hydrocarbon.
B. Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkanes.
C. State the formula of an alkane containing five carbon atoms.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
State three characteristics of a homologous series
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
a. Free radical substitution reactions involve hydrogen atoms in alkanes being replaced by halogen atoms.
Name the three steps involved in a free radical substitution reaction.
b. When a molecule of chlorine, Cl, is exposed to UV light two chlorine radicals are formed.
i. Write an equation for this reaction.
ii. State the type of bond fission involved.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The figure below shows the breaking of a covalent bond, where the more electronegative atom B has taken both electrons from the bond to form a negative ion.
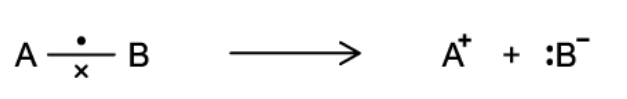
State the name of this type of bond fission
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Name three other types of reaction mechanism
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What is the term oxidation in organic reactions? Give an example for that.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The following mechanism shows hydrogen cyanide reacting with propanone.
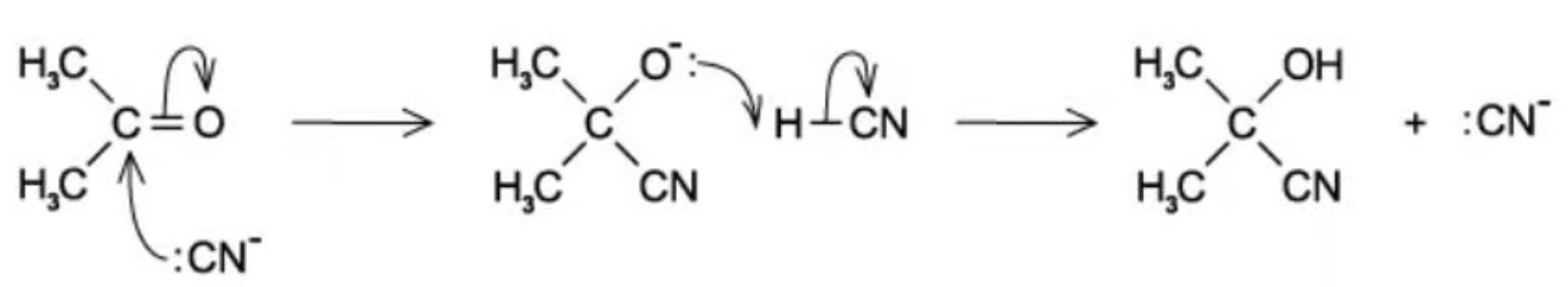
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Heterolytic bond breaking is involved.
B. CN- is an electrophile.
C. This is an addition reaction.
D. Propanone is a ketone.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which of these compounds would act as a nucleophile?
A. `C_2H_6`
B. `H^+`
C. `OH^-`
D. `Cl*`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
1-chloroethane, CH3CH2Cl and NaOH (aq) are reagents in a reaction.
Which row correctly describes what type of reaction this would be?
A. Nucleophilic addition
B. Nucleophilic substitution
C. Electrophilic addition
D. Electrophilic substitution
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Which pairs of homologous series do not have the same C:H ratio in their general formulae?
A. Aldehydes and ketones
B. Alkanes and alkenes
C. Carboxylic acids and esters
D. Alkenes and aldehydes
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Propane and hexane are part of the alkane homologous series.
A. Define the term hydrocarbon.
B. Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkanes.
C. State the formula of an alkane containing five carbon atoms.
A. Hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen
B. The general formula for the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2
C. The formula of an alkane containing five carbon atoms is C5H12
Question 2
State three characteristics of a homologous series
Characteristics of a homologous series are
Question 3
a. Free radical substitution reactions involve hydrogen atoms in alkanes being replaced by halogen atoms.
Name the three steps involved in a free radical substitution reaction.
b. When a molecule of chlorine, Cl, is exposed to UV light two chlorine radicals are formed.
i. Write an equation for this reaction.
ii. State the type of bond fission involved.
a. The three steps involved in a free radical substitution reaction are initiation, propagation and termination
b.
i. The equation for this reaction
`Cl_2 -> 2Cl*`
ii. The type of bond fission involved is homolytic bond fission which a single-headed arrow is required.
Question 4
The figure below shows the breaking of a covalent bond, where the more electronegative atom B has taken both electrons from the bond to form a negative ion.

State the name of this type of bond fission
The type of bond fission involved is heterolytic bond fission in which one atom takes both original bonding electrons from the other atom. In heterolytic fission the more electronegative atom takes both the electrons in the covalent bond.
Question 5
Name three other types of reaction mechanism
Types of reaction mechanism include
Question 6
What is the term oxidation in organic reactions? Give an example for that.
Oxidation is the addition of oxygen atoms to a molecule and/or removing hydrogen atoms from a molecule.
Example: The partial oxidation of ethanol to ethanal using acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution
`C _2H_5OH + [O] → CH_3CHO + H_2O`
Notice the use of [O] to simplify the chemical equation used to describe oxidation reactions.
Question 7
The following mechanism shows hydrogen cyanide reacting with propanone.

Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Heterolytic bond breaking is involved.
B. CN- is an electrophile.
C. This is an addition reaction.
D. Propanone is a ketone.
The answer is B
A nucleophile is a donator of a pair of electrons, whereas an electrophile is an acceptor of a pair of electrons. Thus, CN- is donating a pair of electrons
Question 8
Which of these compounds would act as a nucleophile?
A. `C_2H_6`
B. `H^+`
C. `OH^-`
D. `Cl*`
The answer is C
A nucleophile is a donator of a pair of electrons. They are either negative ions or have a lone pair of electrons capable of being donated.
A is incorrect because C2H6 has no lone pairs
B is incorrect because H+ is an electrophile because of accepting a pair of electrons instead
D is incorrect because it is a neutral free radical
Question 9
1-chloroethane, CH3CH2Cl and NaOH (aq) are reagents in a reaction.
Which row correctly describes what type of reaction this would be?
A. Nucleophilic addition
B. Nucleophilic substitution
C. Electrophilic addition
D. Electrophilic substitution
The answer is B

Because OH- is taking the place of the halogen in the compound, making this reaction substitution. In addition, the hydroxide ion is a nucleophile because of electron-pair donor.
Question 10
Which pairs of homologous series do not have the same C:H ratio in their general formulae?
A. Aldehydes and ketones
B. Alkanes and alkenes
C. Carboxylic acids and esters
D. Alkenes and aldehydes
The answer is B
A homologous series is a group with the same functional group and similar chemical properties.
Alkanes have single bonds and the general formula CnH2n+2
Alkenes have a double bond and the general formula CnH2n
A is incorrect because both have the general formula of CnH2nO
C is incorrect because the general formula of carboxylic acid is CnH2n+1COOH and that of ester is RCOOR’
D is incorrect because both have same carbon-hydrogen ration in their general formula.
Question 1
Propane and hexane are part of the alkane homologous series.
A. Define the term hydrocarbon.
B. Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkanes.
C. State the formula of an alkane containing five carbon atoms.
Question 2
State three characteristics of a homologous series
Question 3
a. Free radical substitution reactions involve hydrogen atoms in alkanes being replaced by halogen atoms.
Name the three steps involved in a free radical substitution reaction.
b. When a molecule of chlorine, Cl, is exposed to UV light two chlorine radicals are formed.
i. Write an equation for this reaction.
ii. State the type of bond fission involved.
Question 4
The figure below shows the breaking of a covalent bond, where the more electronegative atom B has taken both electrons from the bond to form a negative ion.

State the name of this type of bond fission
Question 5
Name three other types of reaction mechanism
Question 6
What is the term oxidation in organic reactions? Give an example for that.
Question 7
The following mechanism shows hydrogen cyanide reacting with propanone.

Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Heterolytic bond breaking is involved.
B. CN- is an electrophile.
C. This is an addition reaction.
D. Propanone is a ketone.
Question 8
Which of these compounds would act as a nucleophile?
A. `C_2H_6`
B. `H^+`
C. `OH^-`
D. `Cl*`
Question 9
1-chloroethane, CH3CH2Cl and NaOH (aq) are reagents in a reaction.
Which row correctly describes what type of reaction this would be?
A. Nucleophilic addition
B. Nucleophilic substitution
C. Electrophilic addition
D. Electrophilic substitution
Question 10
Which pairs of homologous series do not have the same C:H ratio in their general formulae?
A. Aldehydes and ketones
B. Alkanes and alkenes
C. Carboxylic acids and esters
D. Alkenes and aldehydes